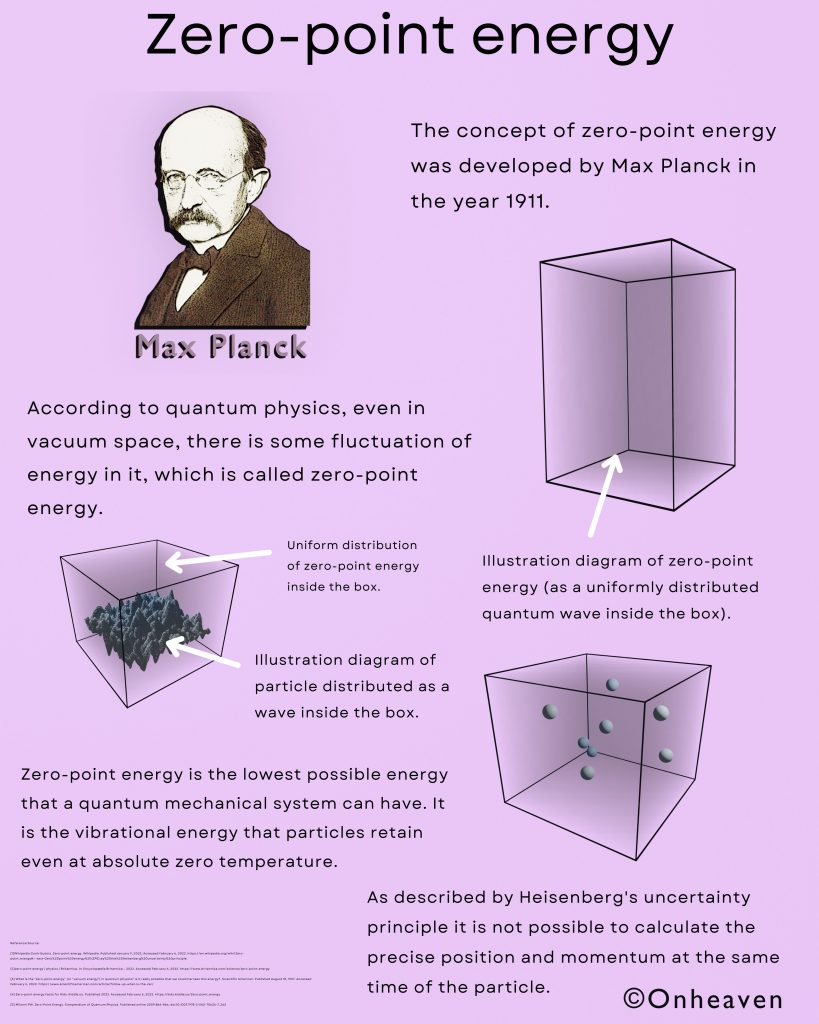
The concept of zero-point energy was developed by Max Planck in the year 1911.
According to quantum physics, even in vacuum space, there is some fluctuation of energy in it, which is called zero-point energy.
Zero-point energy is the lowest possible energy that a quantum mechanical system can have. It is the vibrational energy that particles retain even at absolute zero temperature.
Reference Source:
[1]Wikipedia Contributors. Zero-point energy. Wikipedia. Published January 9, 2022. Accessed February 6, 2022. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zero-point_energy#:~:text=Zero%2Dpoint%20energy%20(ZPE),by%20the%20Heisenberg%20uncertainty%20principle.
[2]zero-point energy | physics | Britannica. In: Encyclopædia Britannica. ; 2022. Accessed February 6, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/science/zero-point-energy
[3] What is the “zero-point energy” (or “vacuum energy”) in quantum physics? Is it really possible that we could harness this energy?. Scientific American. Published August 18, 1997. Accessed February 6, 2022. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/follow-up-what-is-the-zer/
[4] Zero-point energy Facts for Kids. Kiddle.co. Published 2022. Accessed February 6, 2022. https://kids.kiddle.co/Zero-point_energy
[5] Milonni PW. Zero-Point Energy. Compendium of Quantum Physics. Published online 2009:864-866. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-70626-7_242