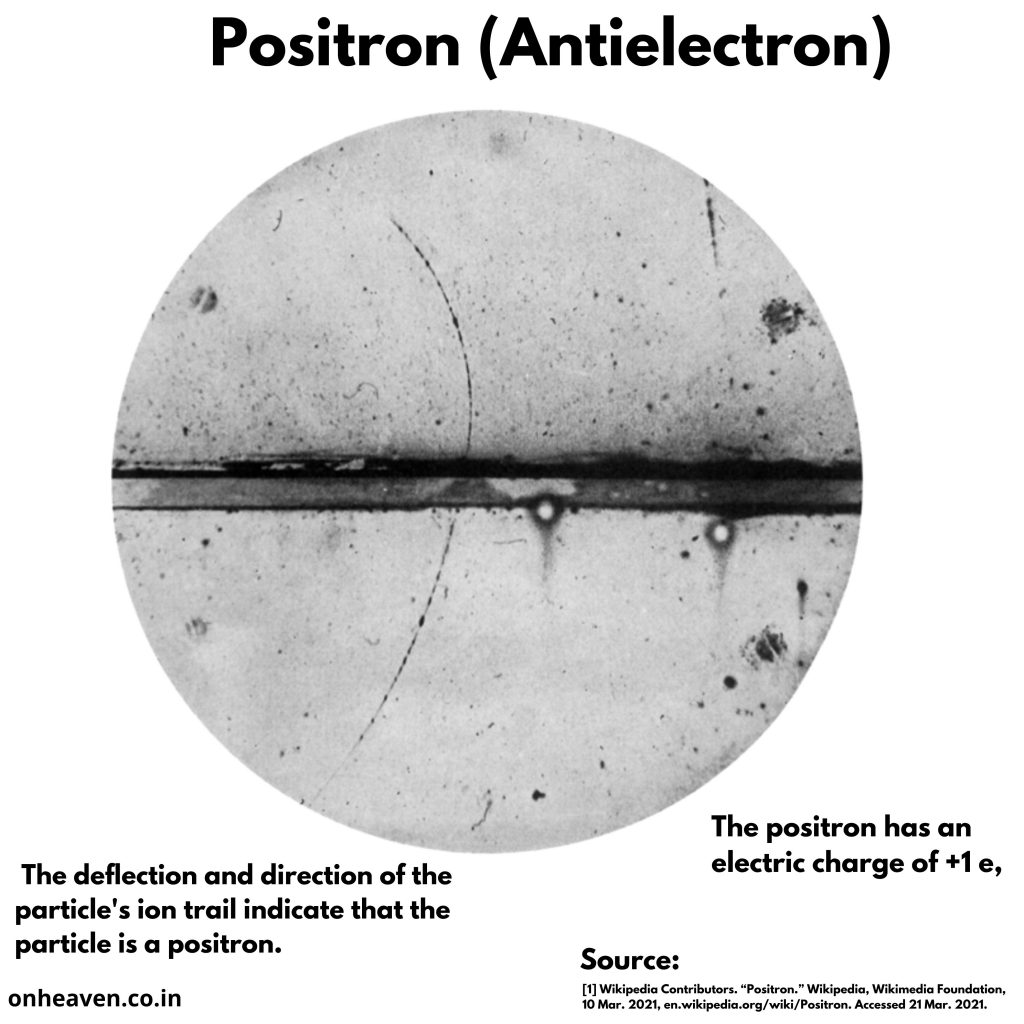
The positron has an electric charge of +1 e, a spin of 1/2 , and has the same mass as an electron.

😊 The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron.
😊When a positron collides with an electron, annihilation occurs. If this collision occurs at low energies, it results in the production of two or additional photons.
Positrons are produced naturally in β+ decays of naturally occurring radioactive isotopes and in interactions of gamma quanta with matter.
😊Positron production from radioactive β+ decay can be considered both artificial and natural production, as the generation of the radioisotope can be natural or artificial.
😊Perhaps the best familiar naturally-occurring radioisotope which produces positrons is potassium-40, a long-lived isotope of potassium that occurs as a primordial isotope of potassium.
😊 Recent observations indicate black holes and neutron stars produce vast amounts of positron-electron plasma in astrophysical jets.
😊Large clouds of positron-electron plasma own also been associated with neutron stars.
Source:
[1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Positron.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 2 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Positron. Accessed 8 Nov. 2020.
[2] rolandoemail. “Space Star Astronomy – Free Photo on Pixabay.” Pixabay.com, 15 June 2017, pixabay.com/photos/space-star-astronomy-cosmos-cosmic-2406426/. Accessed 8 Nov. 2020.