Meter Bridge is the simplest practical application of Wheatstone Bridge.
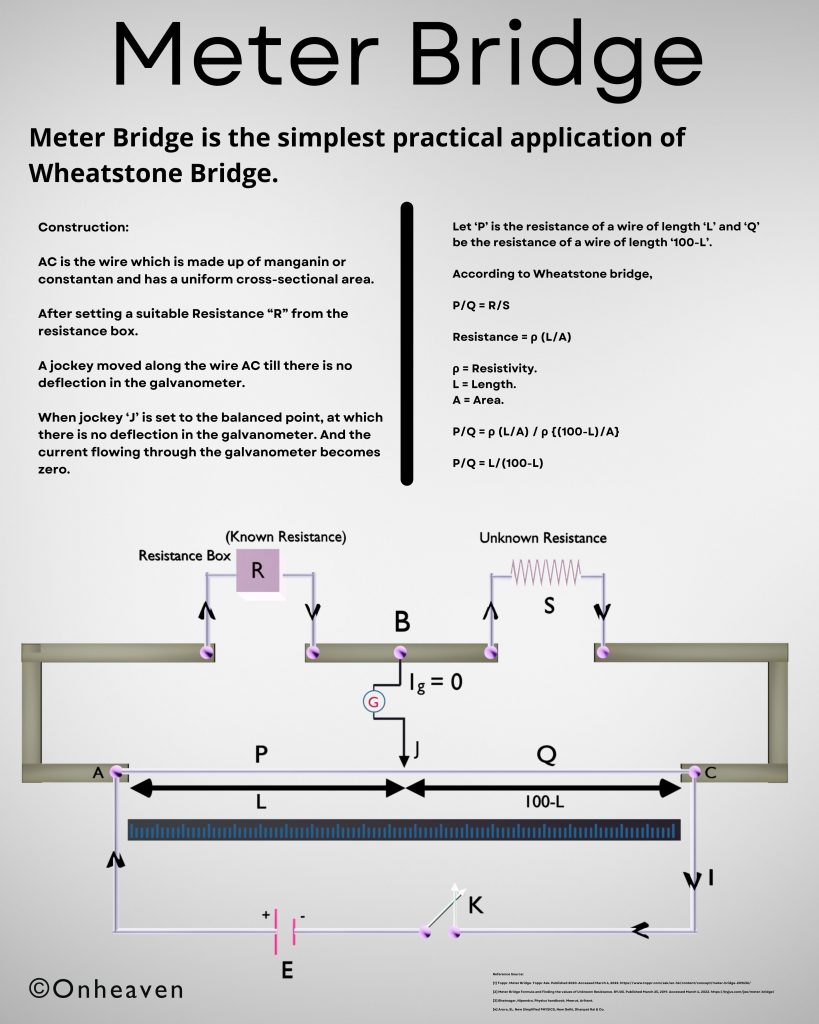
Construction:
AC is the wire which is made up of manganin or constantan and has a uniform cross-sectional area.
After setting a suitable Resistance “R” from the resistance box.
A jockey moved along the wire AC till there is no deflection in the galvanometer.
When jockey ‘J’ is set to the balanced point, at which there is no deflection in the galvanometer. And the current flowing through the galvanometer becomes zero.
Let ‘P’ is the resistance of a wire of length ‘L’ and ‘Q’ be the resistance of a wire of length ‘100-L’.
According to Wheatstone bridge,
P/Q = R/S
Resistance = ρ (L/A)
ρ = Resistivity.
L = Length.
A = Area.
P/Q = ρ (L/A) / ρ {(100-L)/A}
P/Q = L/(100-L)
Reference Source:
[1] Toppr. Meter Bridge. Toppr Ask. Published 2020. Accessed March 4, 2022. https://www.toppr.com/ask/en-hk/content/concept/meter-bridge-209636/
[2] Meter Bridge Formula and Finding the values of Unknown Resistance. BYJUS. Published March 25, 2019. Accessed March 4, 2022. https://byjus.com/jee/meter-bridge/
[3] Bhatnagar, Nipendra. Physics handbook. Meerut, Arihant.
[4] Arora, SL. New Simplified PHYSICS, New Delhi, Dhanpat Rai & Co.