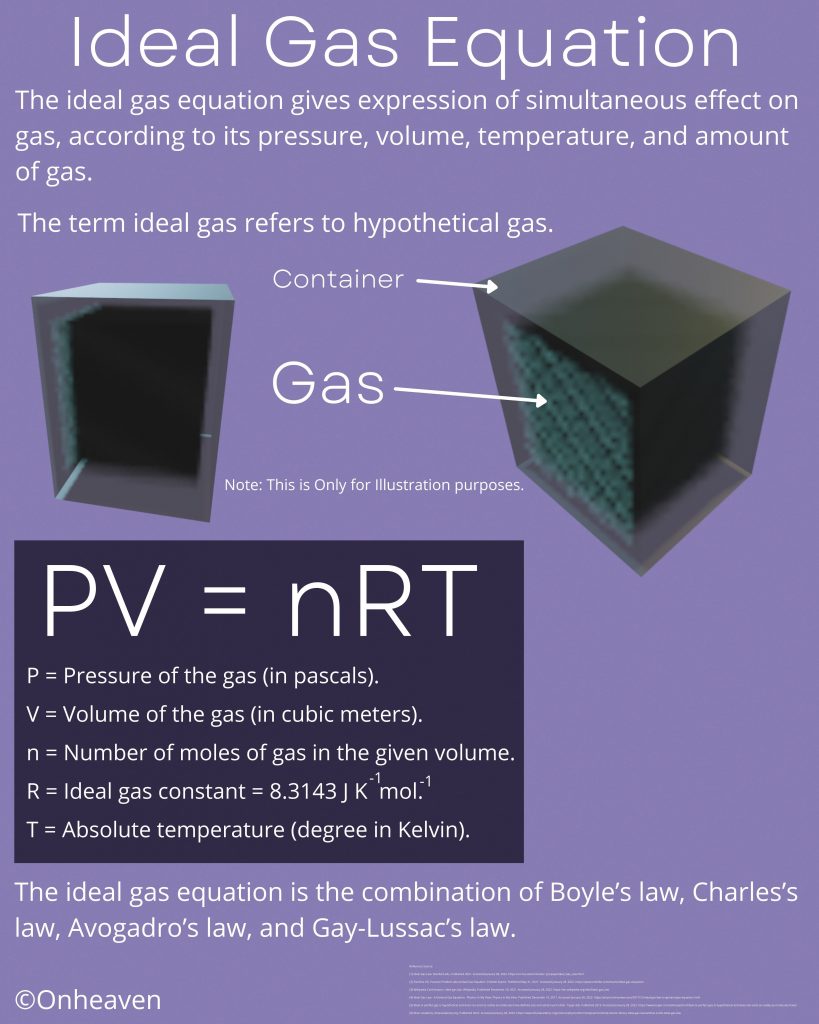
Ideal gas equation gives expression of simultaneous effect on gas, according to its pressure, volume, temperature, and the amount of gas.
The term ideal gas refers to hypothetical gas.
PV = nRT
P = Pressure of the gas (in pascals).
V = Volume of the gas (in cubic meters).
n = Number of moles of gas in the given volume.
R = Ideal gas constant = 8.3143 J K^-1 mol^-1.
T = Absolute temperature (degree in Kelvin).
The ideal gas equation is the combination of Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, Avogadro’s law, and Gay-Lussac’s law.
Reference Source:
[1] Ideal Gas Law. Stanford.edu. Published 2021. Accessed January 28, 2022. https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~jos/pasp/Ideal_Gas_Law.html
[2] Pavithra VG. Practice Problem about Ideal Gas Equation. Embibe Exams. Published May 31, 2021. Accessed January 28, 2022. https://www.embibe.com/exams/ideal-gas-equation/
[3] Wikipedia Contributors. Ideal gas law. Wikipedia. Published November 20, 2021. Accessed January 28, 2022. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ideal_gas_law
[4] Ideal Gas Law – A General Gas Equation – Physics In My View. Physics In My View. Published December 16, 2017. Accessed January 28, 2022. https://physicsinmyview.com/2017/12/ideal-gas-law-or-general-gas-equation.html
[5] Ideal or perfect gas is hypothetical and does not exist as reality as molecules have definite size and attract each other. Toppr Ask. Published 2019. Accessed January 28, 2022. https://www.toppr.com/ask/question/ideal-or-perfect-gas-is-hypothetical-and-does-not-exist-as-reality-as-molecules-have/
[6] Khan Academy. Khanacademy.org. Published 2022. Accessed January 28, 2022. https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/thermodynamics/temp-kinetic-theory-ideal-gas-law/a/what-is-the-ideal-gas-law