Faraday's Law of Induction: Video Illustration
Advertisement:
Description:
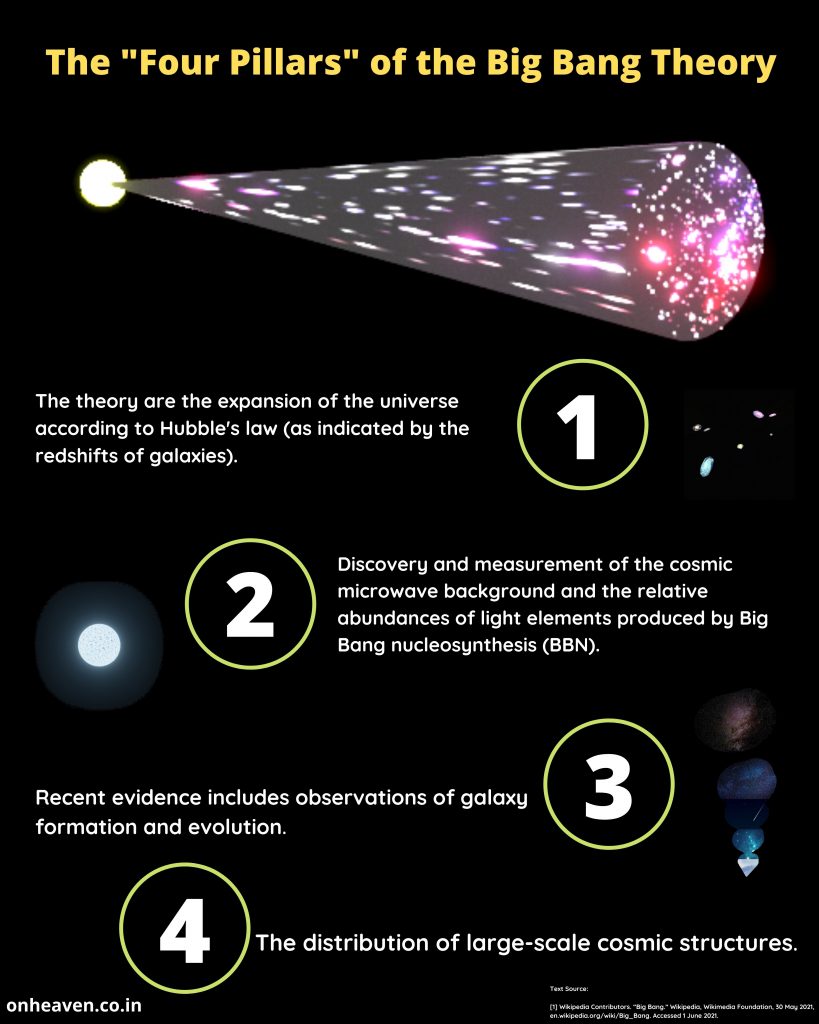
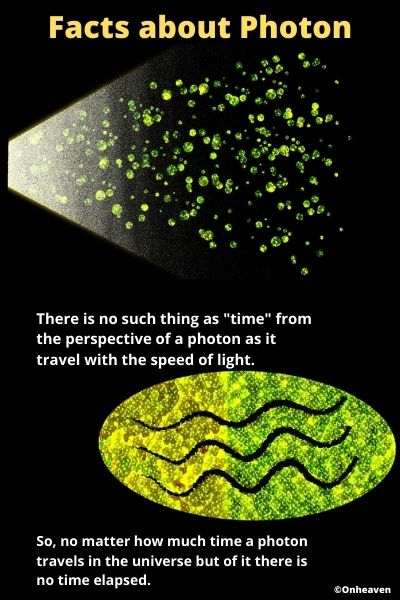
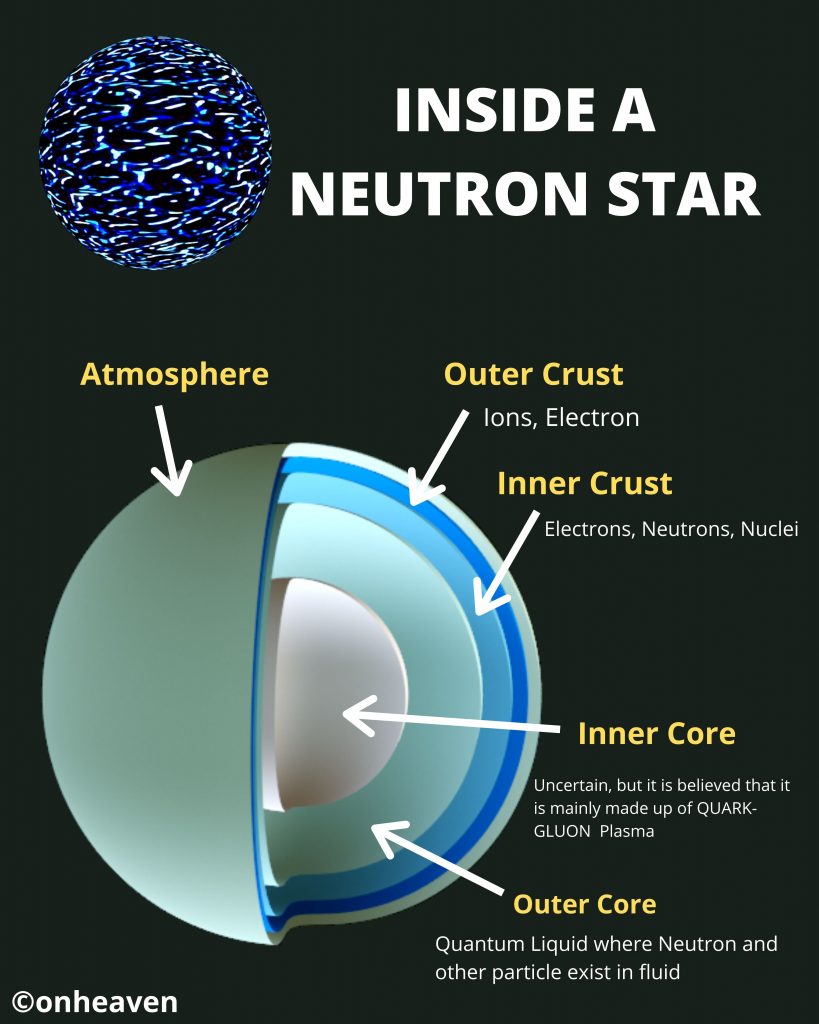
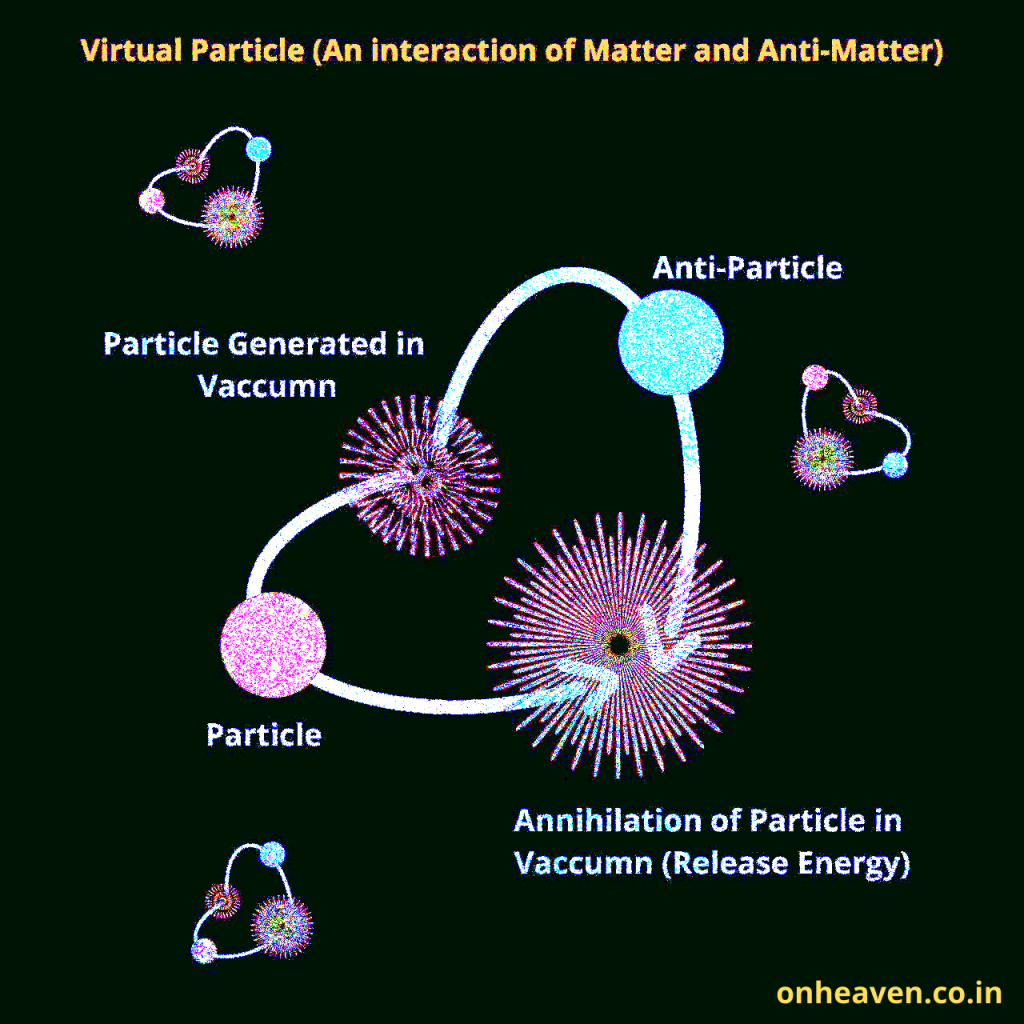
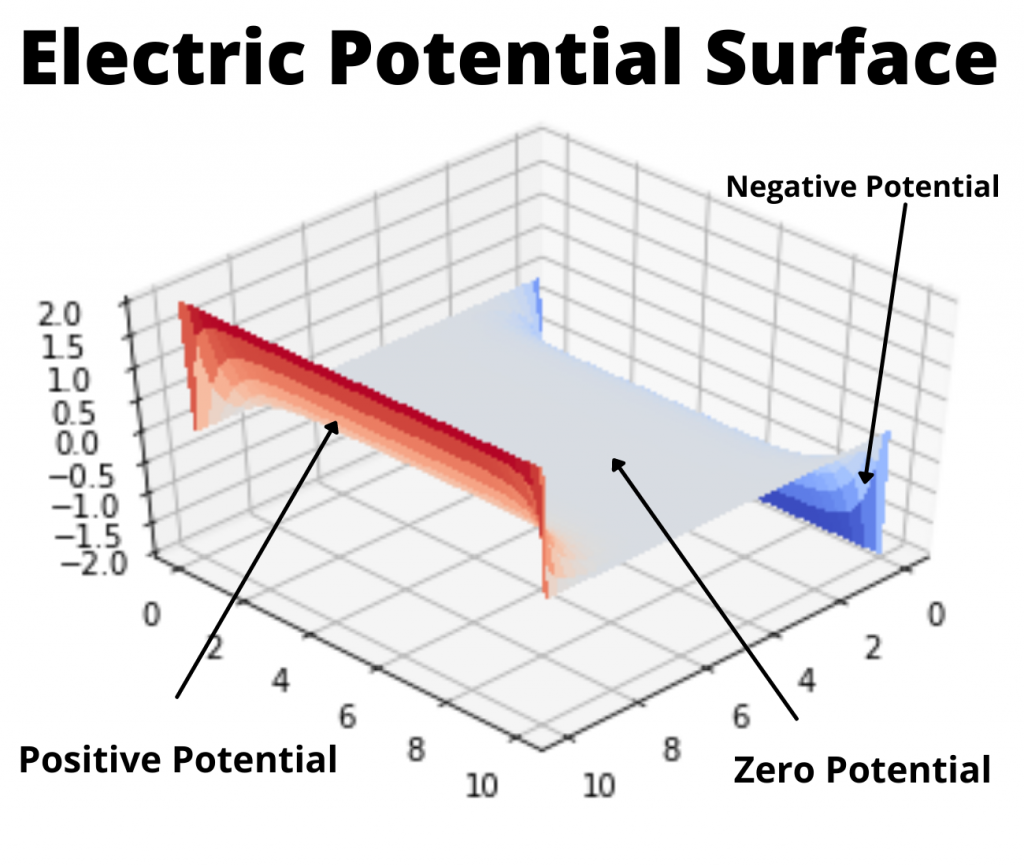
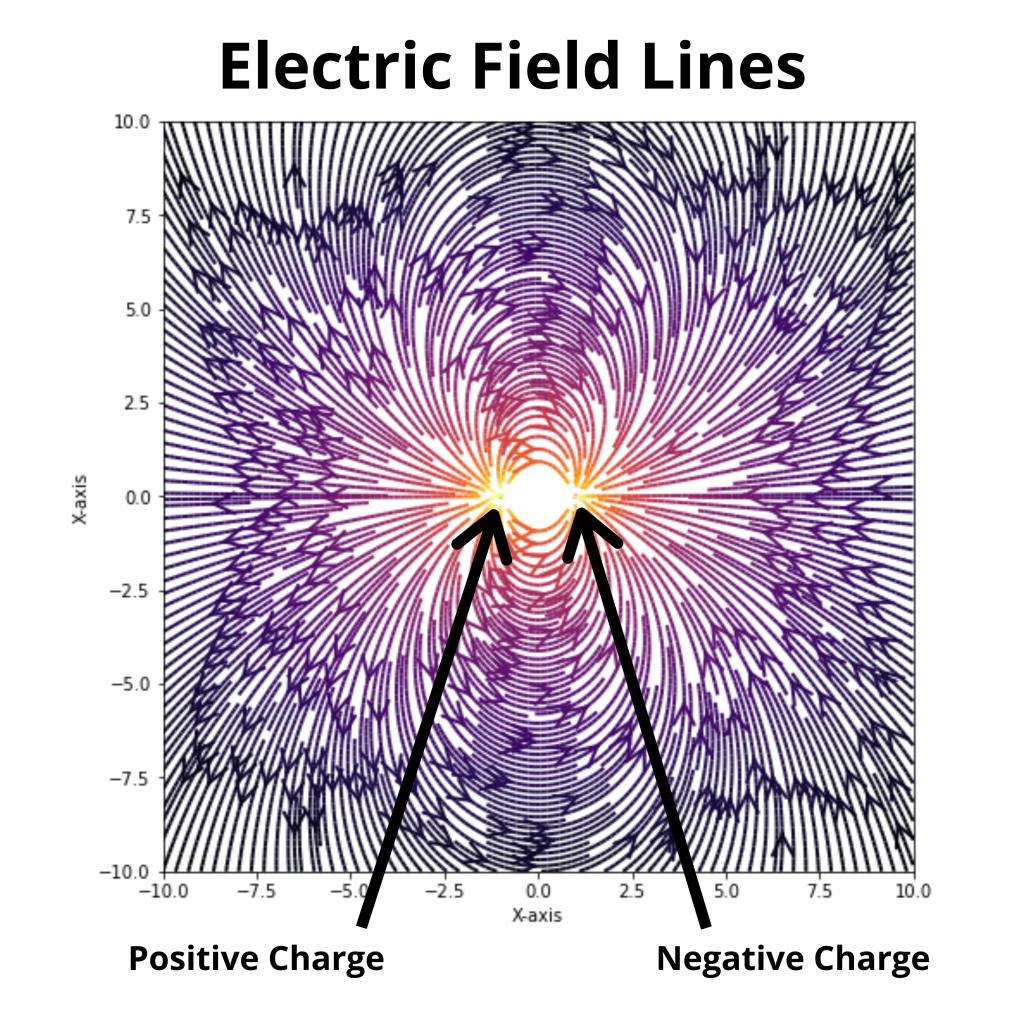
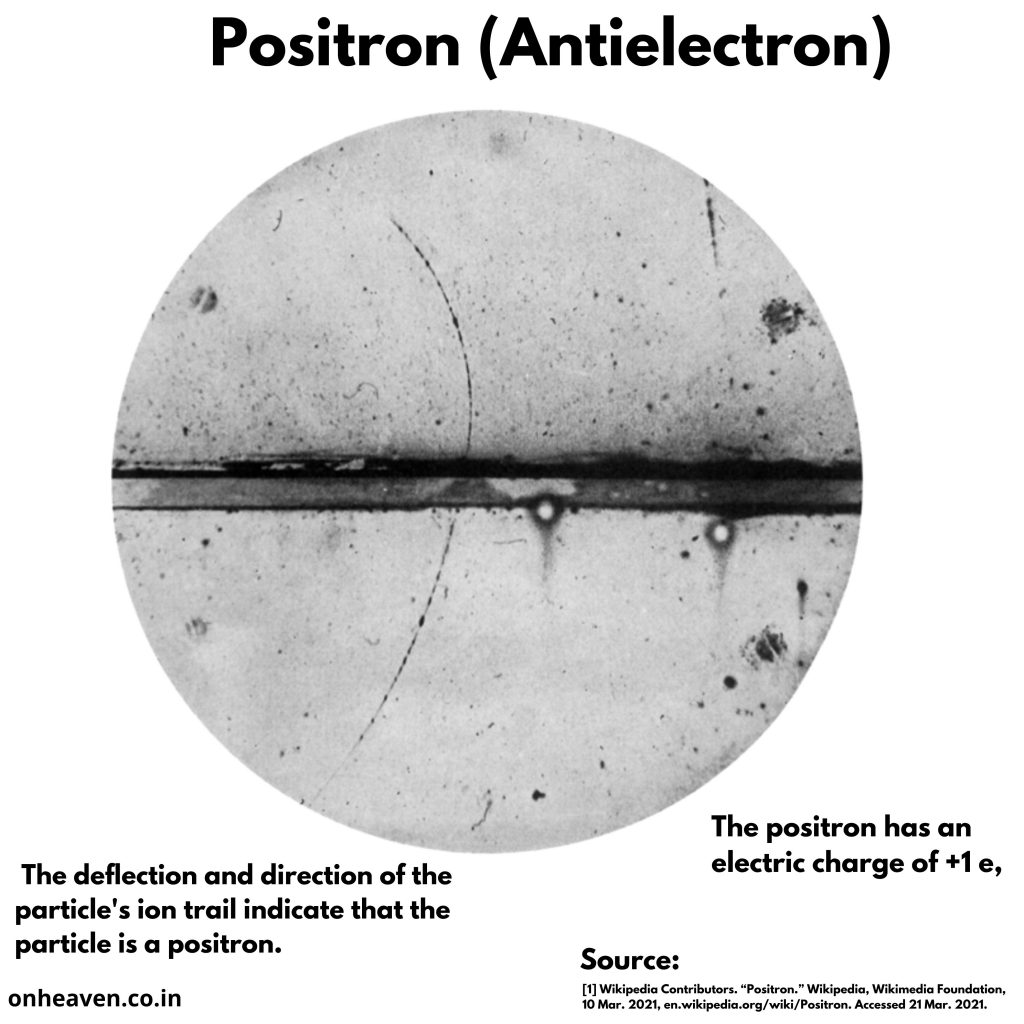
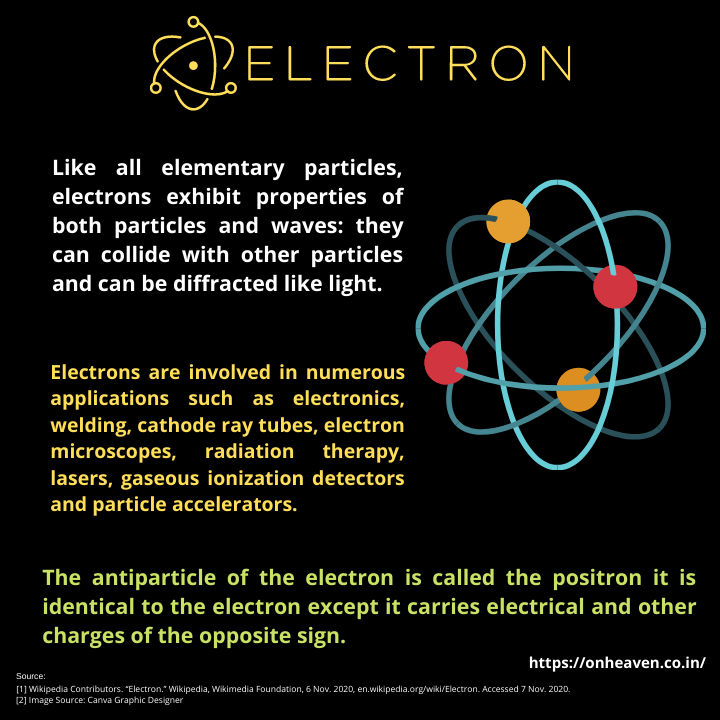
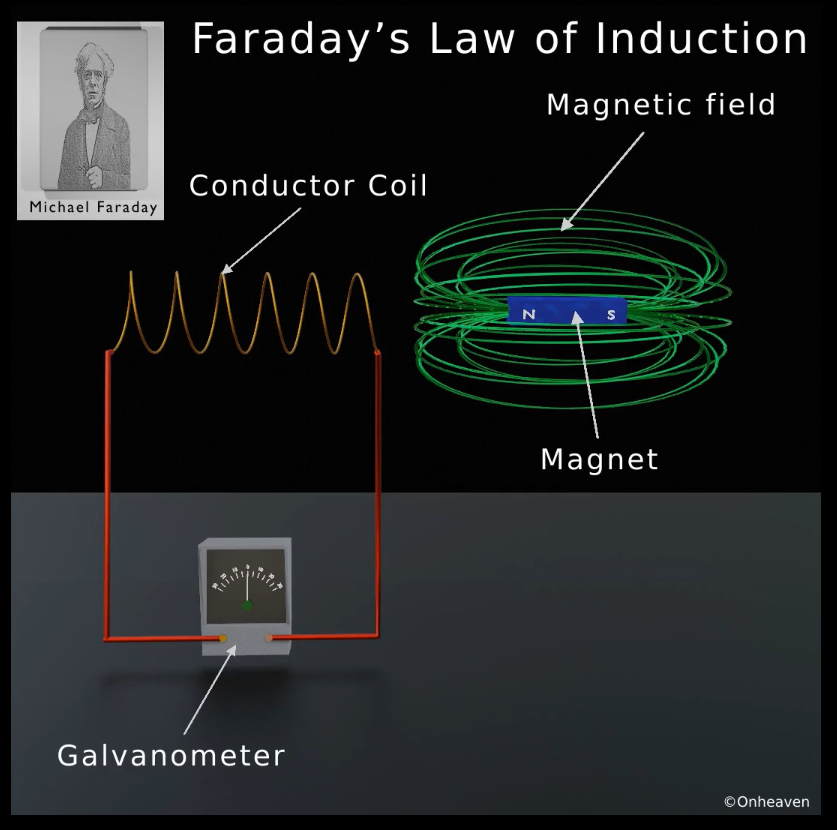
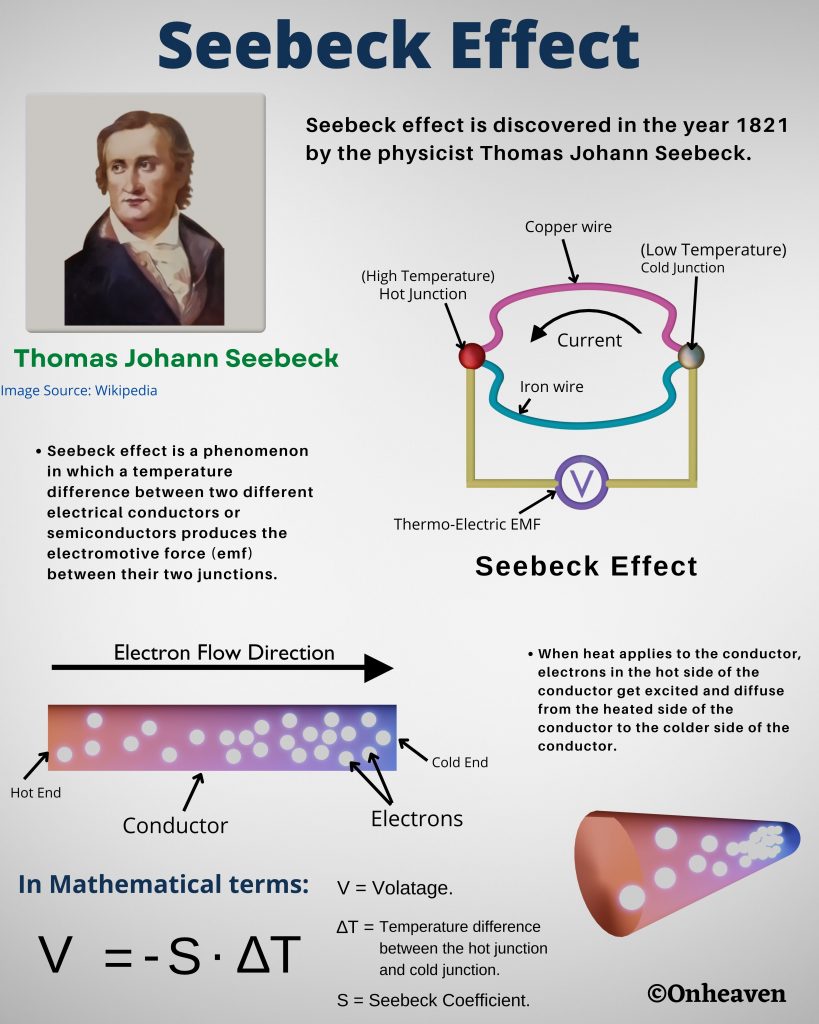
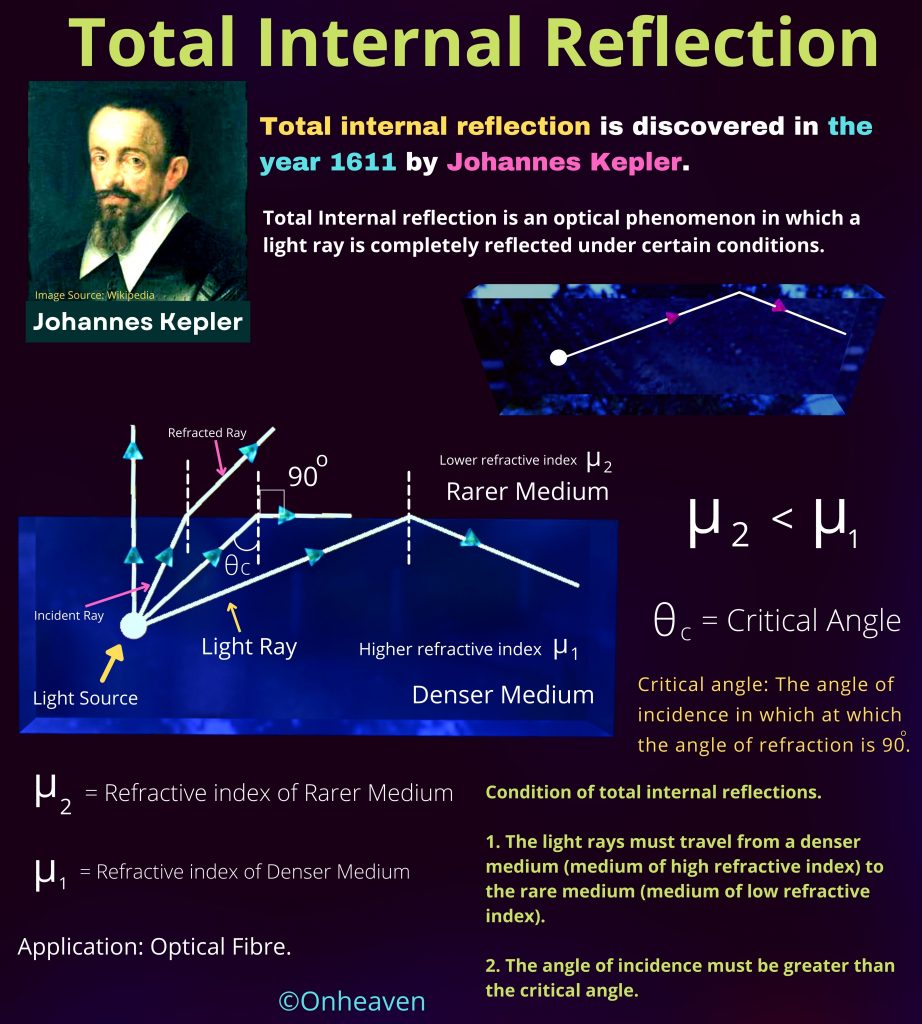
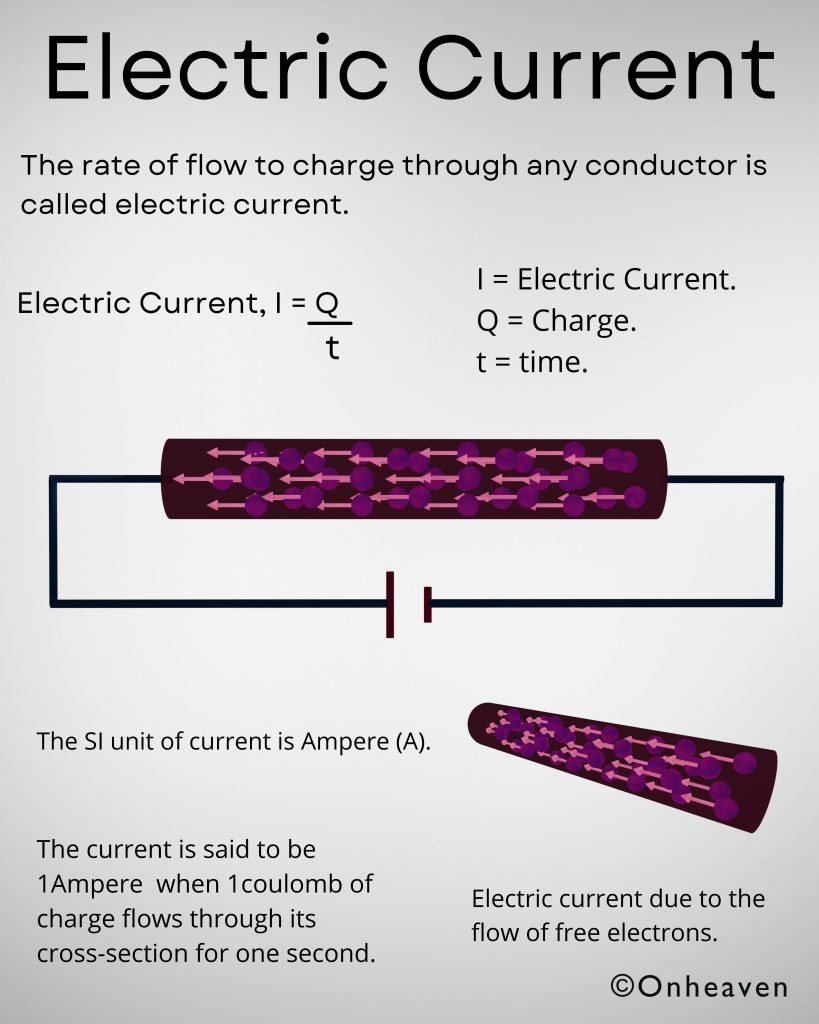
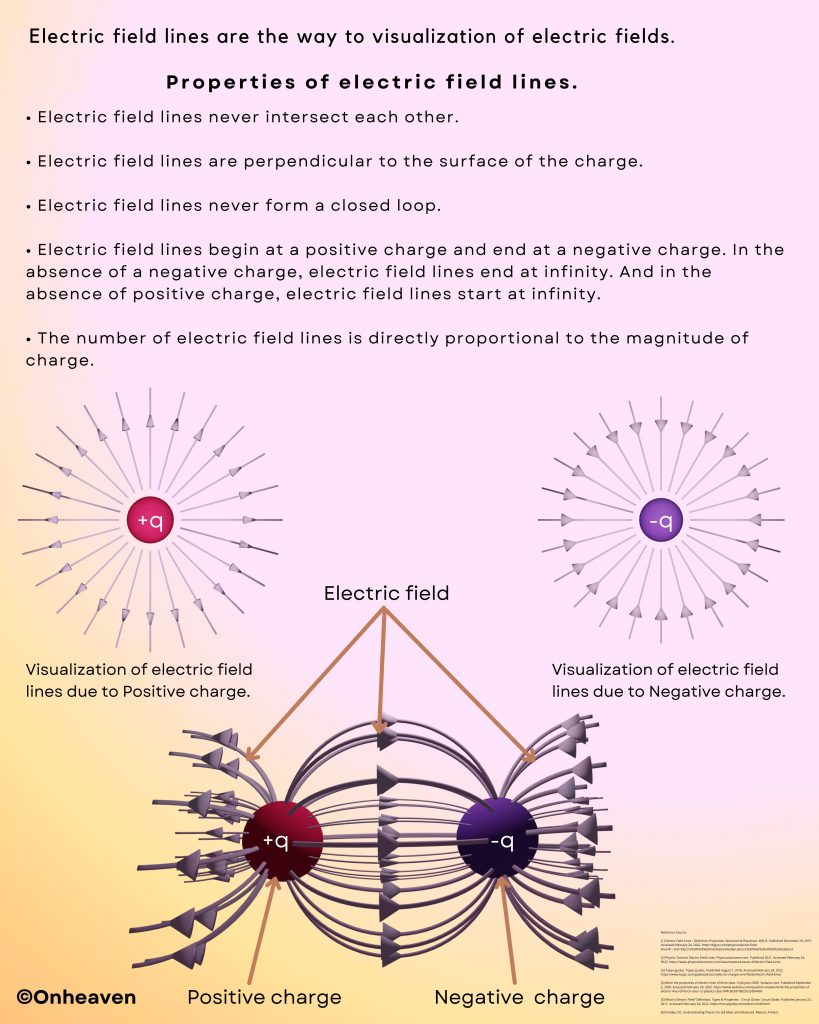
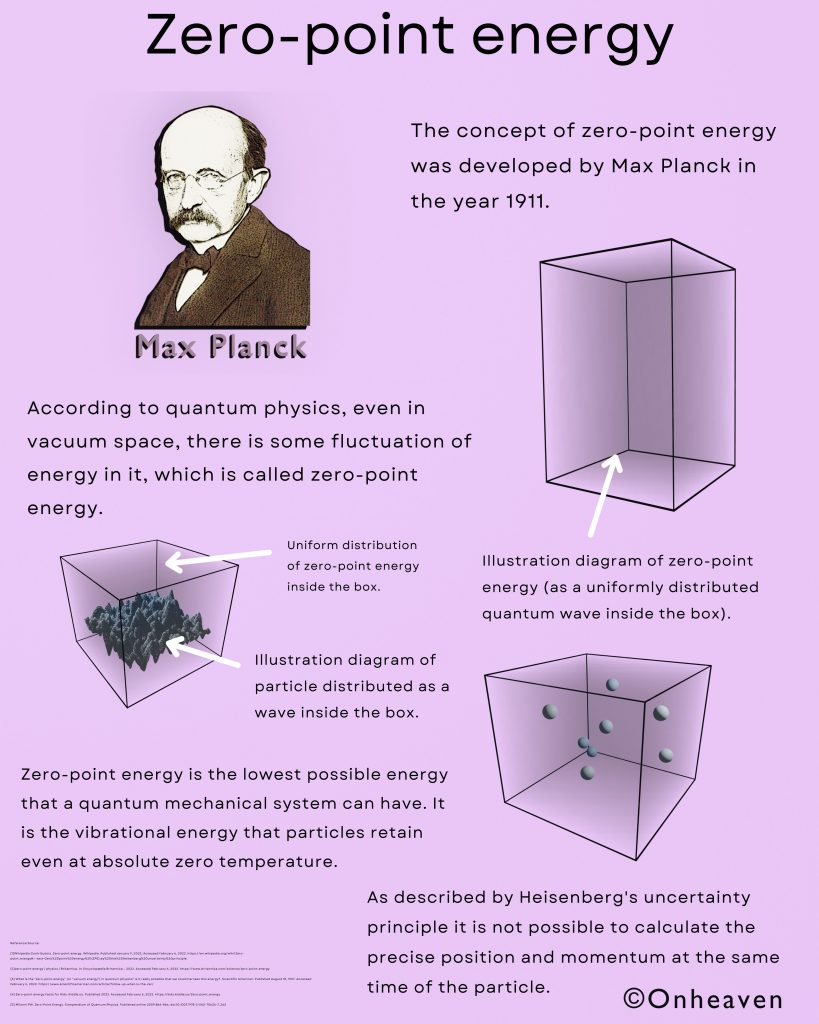
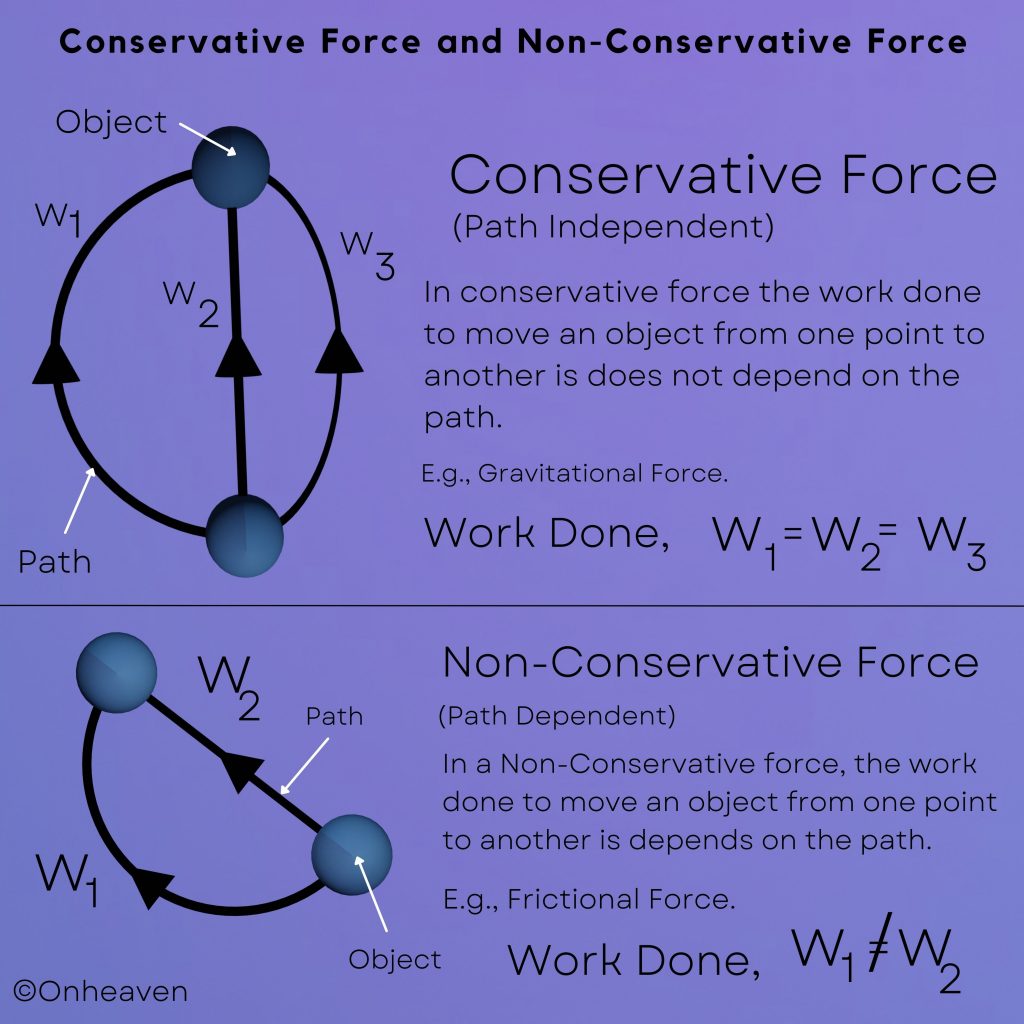
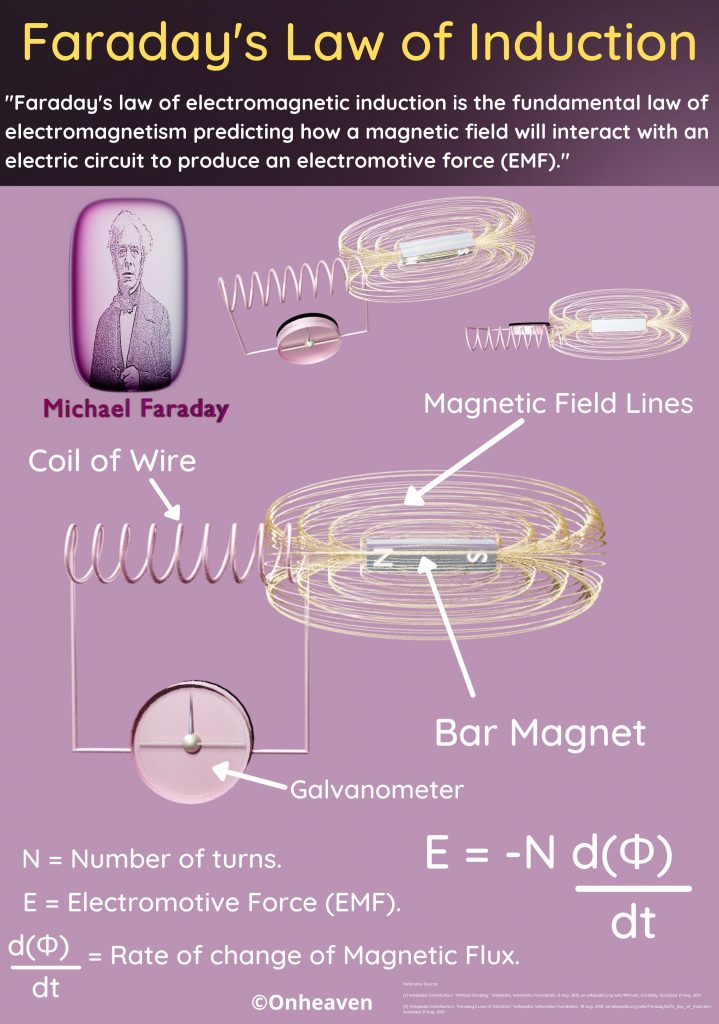
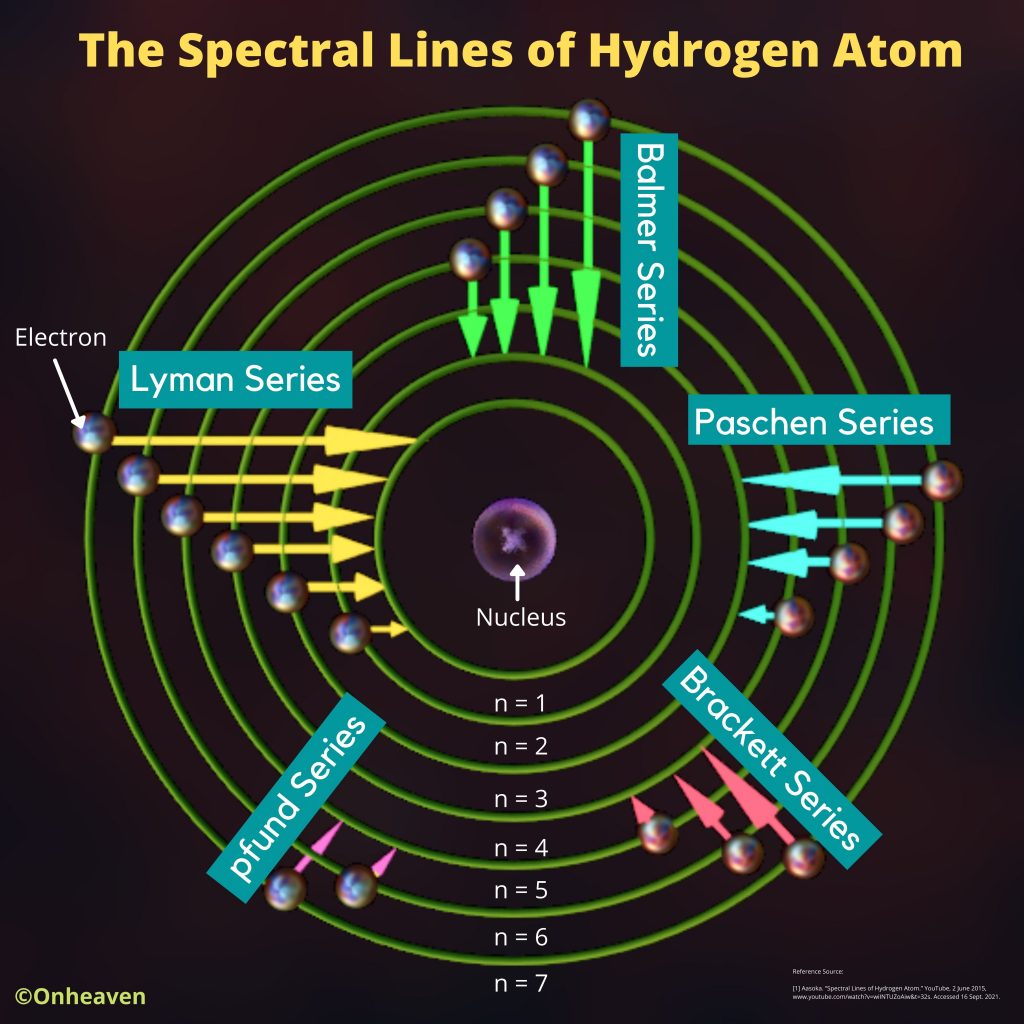
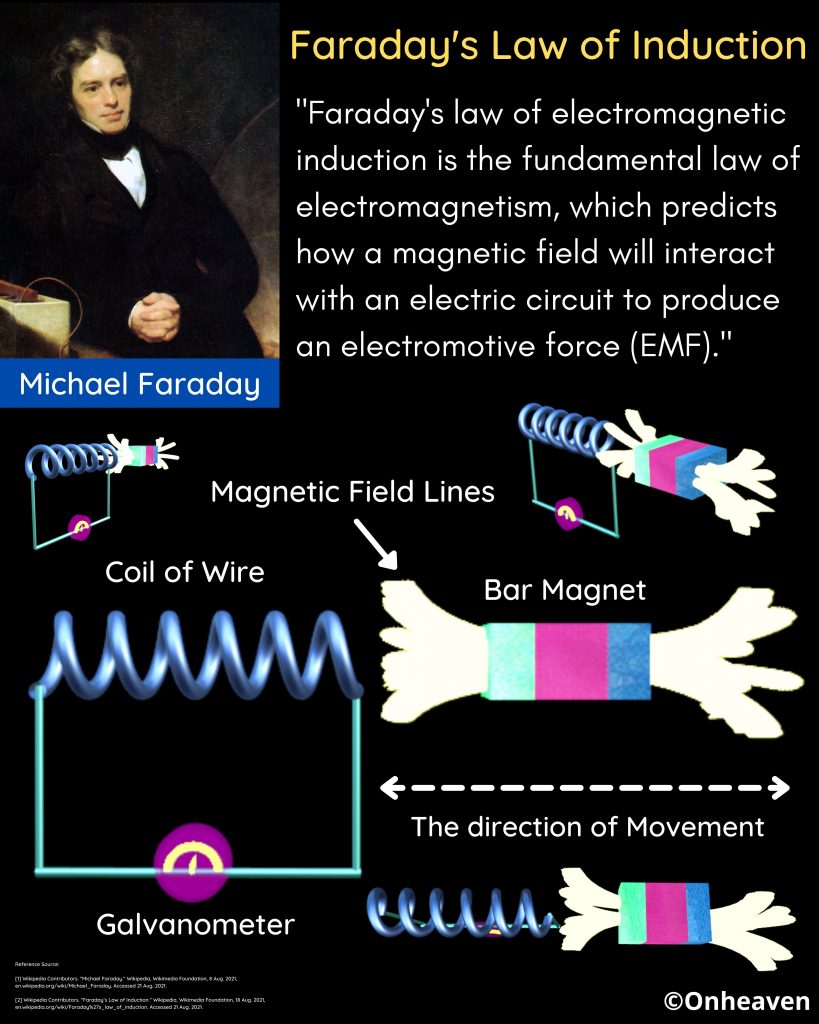
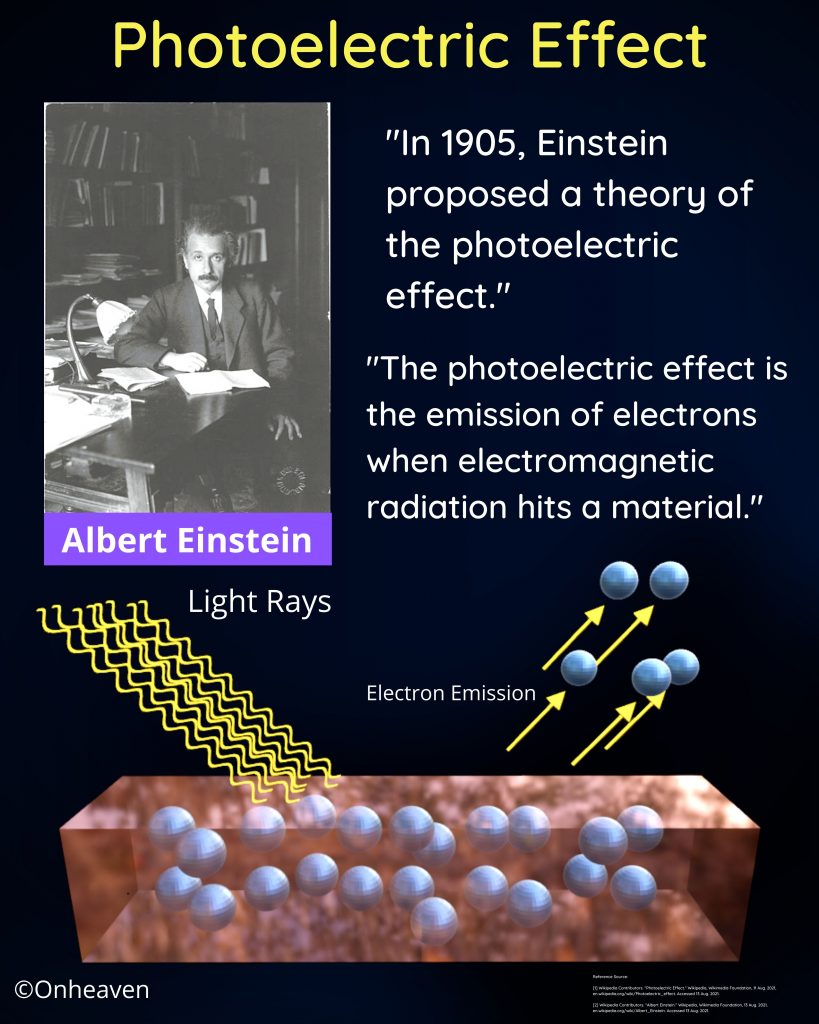
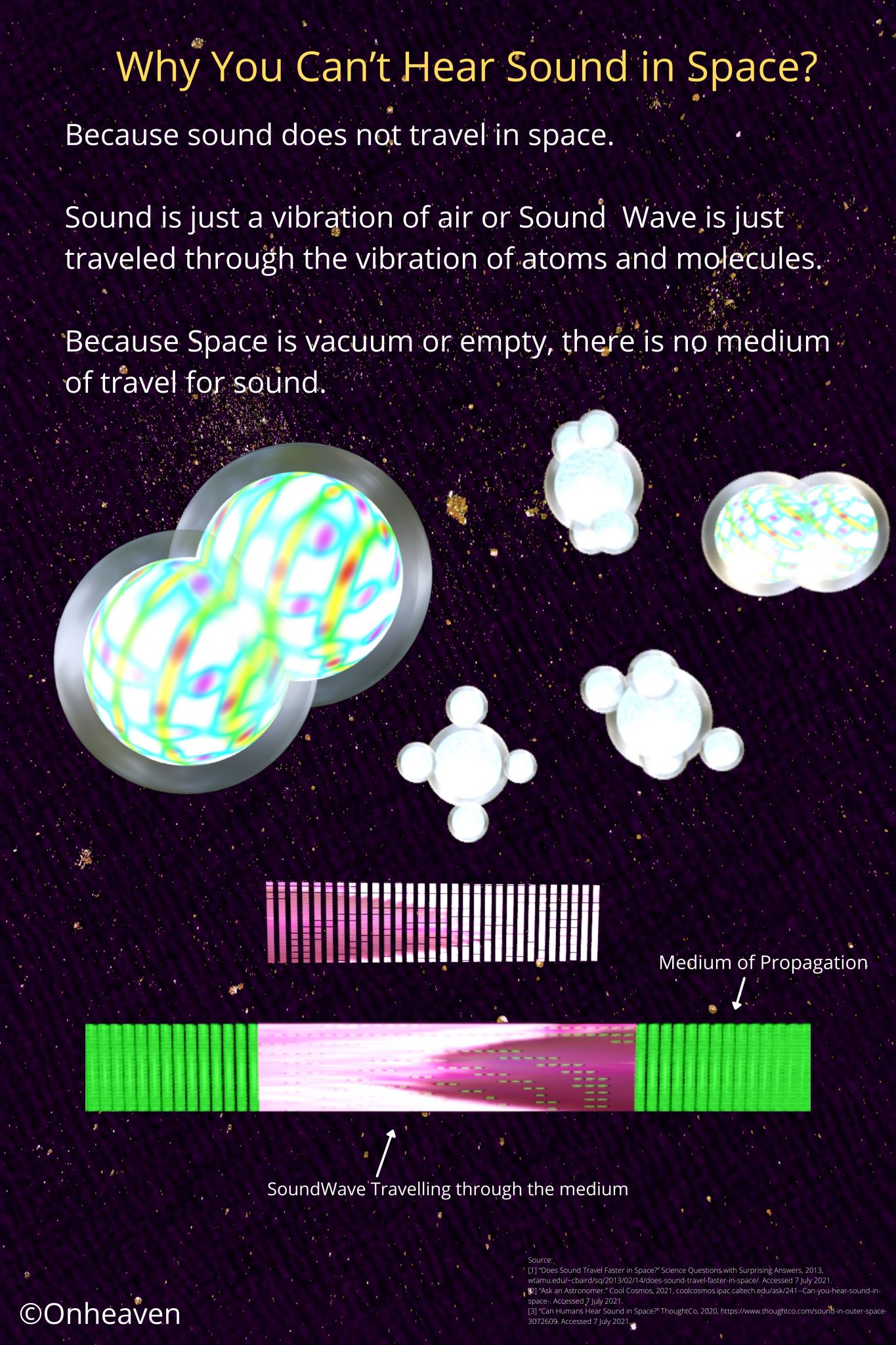
Faraday’s law of induction was proposed by the Michael Faraday in the year 1831.
This law states that how the change in the magnetic field linked with the conductor induces the electromotive force in the conductor.
The conductor coil is connected to the galvanometer.
A bar magnet is going near the conductor coil.
As the magnetic field of the bar magnet starts interacting with the coil. The galvanometer starts showing deflection.
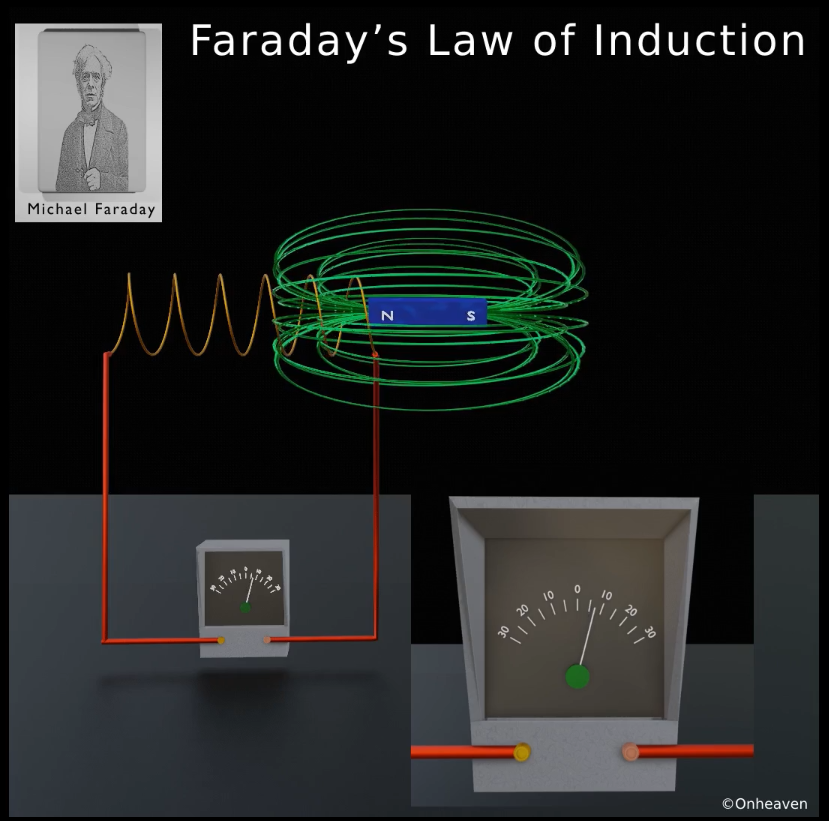
As the higher amount of magnetic field of the bar magnet is linked with the coil, the galvanometer which is connected to the conductor coil shows more and more deflection.
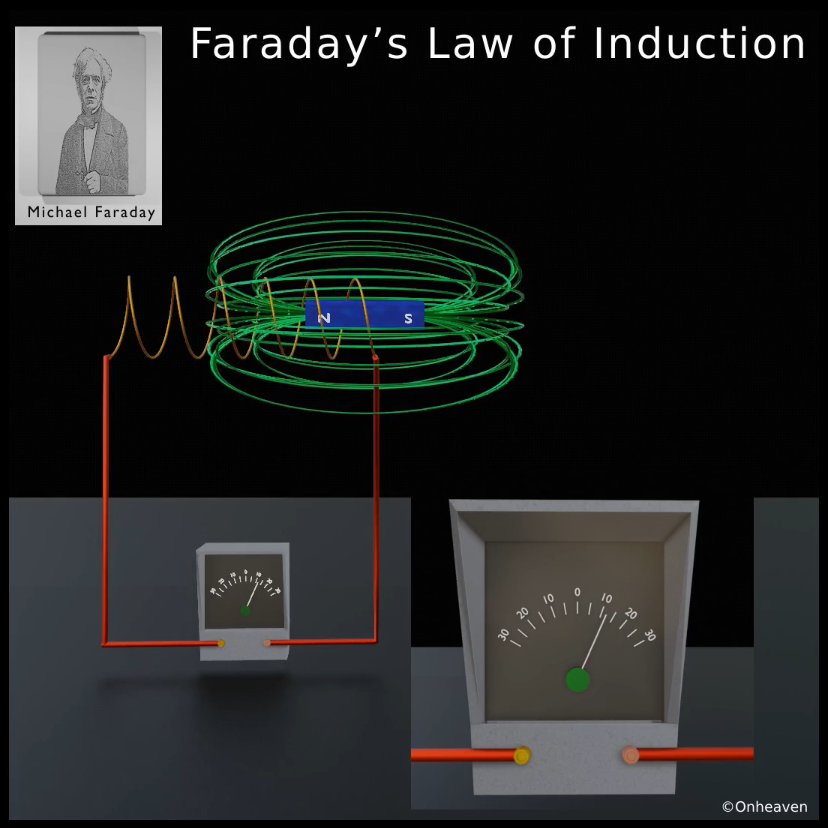
When the bar magnet stops movement the galvanometer switches back to no deflection which shows no current in the conductor coil.
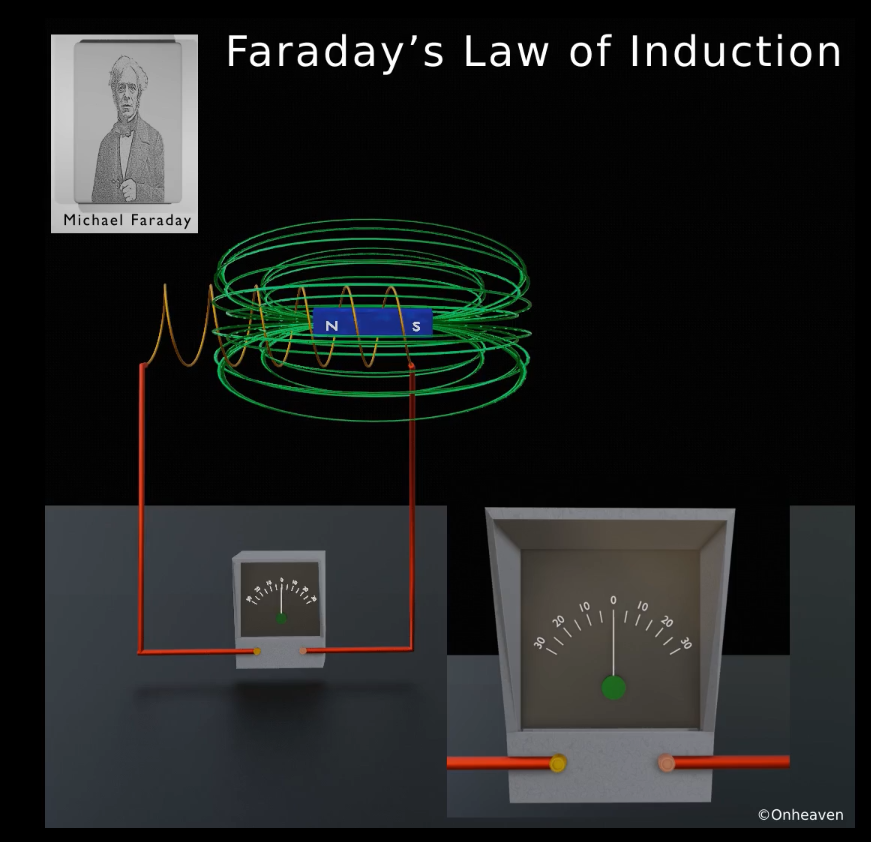
Again after moving the magnet in the backward direction the galvanometer starts showing deflection in opposite direction.
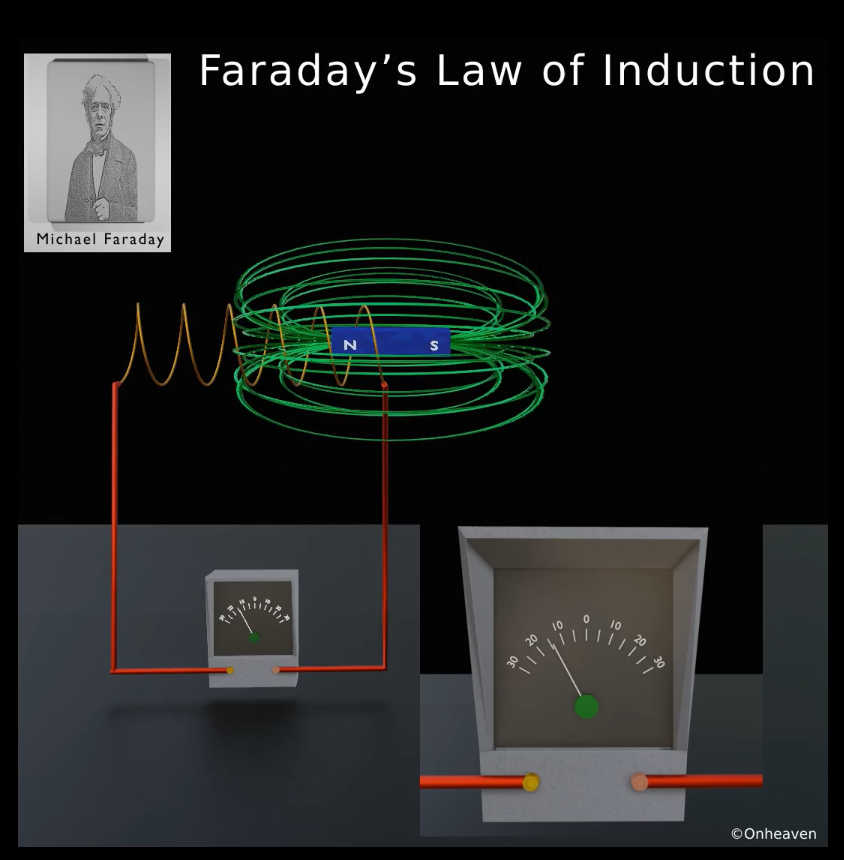
As the bar magnet moves back from the galvanometer the magnetic field linked with the conductor coil starts decreasing, then the deflection magnitude in the galvanometer is also starts decreasing.
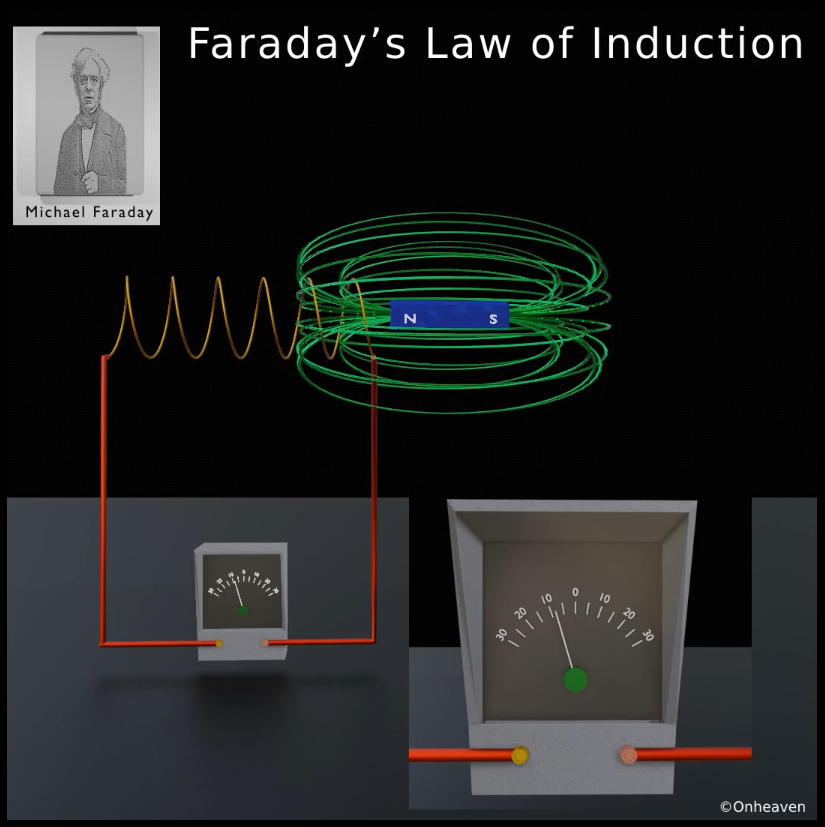
When the bar magnet moves far away from the conductor coil so that no magnetic field of the bar magnet is linked with the coil. The deflection needle in the galvanometer switches back to the no deflection, which shows no current in the coil.
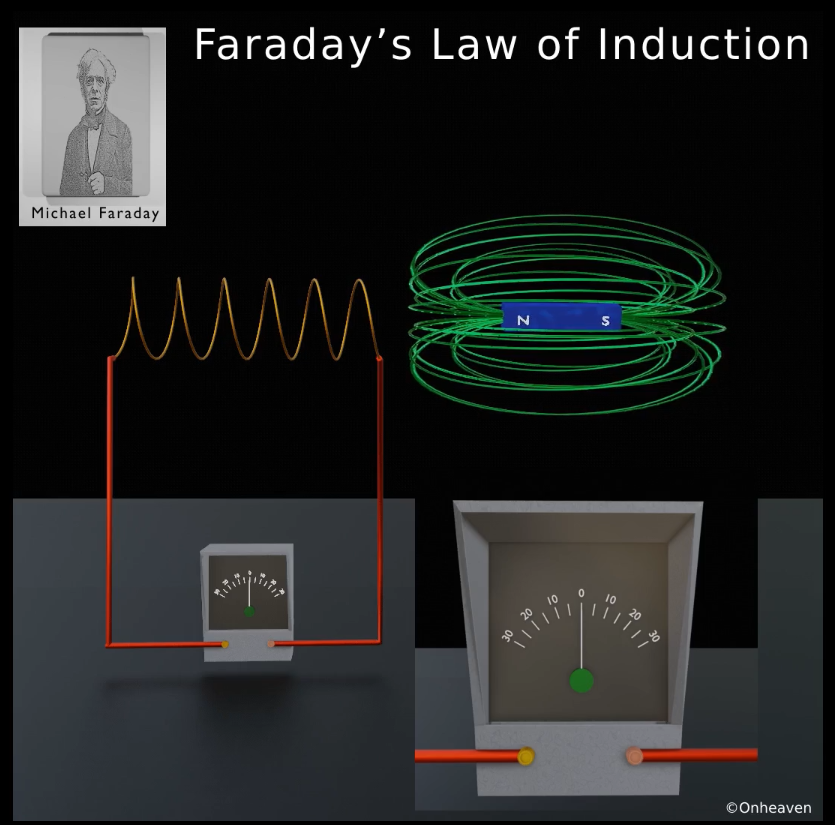
Again repeat this process,
As the change in the magnetic field of the bar magnet link with the conductor coil, the emf induces in the coil.
And when the change in the magnetic field stops, the induced emf in the conductor coil became zero.
And when the bar magnet moves backward, then the change in the magnetic field link with the conductor coil produces emf in the conductor coil, but this time the direction of the induced emf in the coil in opposite direction.
When the bar magnet moves far away from the conductor coil so that, no magnetic field of the bar magnet is linked with the coil, the deflection needle in the galvanometer switches back to the no deflection, because of no induced emf in the conductor coil.
After this experiment Micheal Faraday come to the conclusion that,
The emf induced in the coil is directly proportional to the change in the magnetic field link with the conductor coil.
Advertisement:
Reference Source:
[1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Michael Faraday.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 8 Aug. 2021, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Michael_Faraday. Accessed 21 Aug. 2021.
[2] Wikipedia Contributors. “Faraday’s Law of Induction.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 18 Aug. 2021, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Faraday%27s_law_of_induction. Accessed 21 Aug. 2021.
[3] File:Faraday-Millikan-Gale-1913.jpg. (2021, November 24). Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Retrieved 14:33, April 2, 2023 from https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Faraday-Millikan-Gale-1913.jpg&oldid=609705446.
[4] Physics and animation. faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction | faraday’s law of induction | faraday’s experiment | #2. YouTube. Published online June 21, 2021. Accessed April 2, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t-EhLjdAY0M
[5] Khan Academy India. Electromagnetic induction (& Faraday’s experiments) (Hindi) | Physics | Khan Academy. YouTube. Published online April 10, 2019. Accessed April 2, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rxrOibylNAg
[6] LabInApp. Electromagnetic Induction: by Magnet. YouTube. Published online September 12, 2018. Accessed April 2, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uESCEU5Thqs
[7] BYJU’S. Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction Explained. YouTube. Published online October 30, 2018. Accessed April 2, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ARk3C29B0D4
Background Music:
[1] Pixabay. Cosmic Glow | Royalty Free Music. Pixabay.com. Published 2021. Accessed April 3, 2023. https://pixabay.com/music/ambient-cosmic-glow-6703/
Recent Posts (Science Gallery)
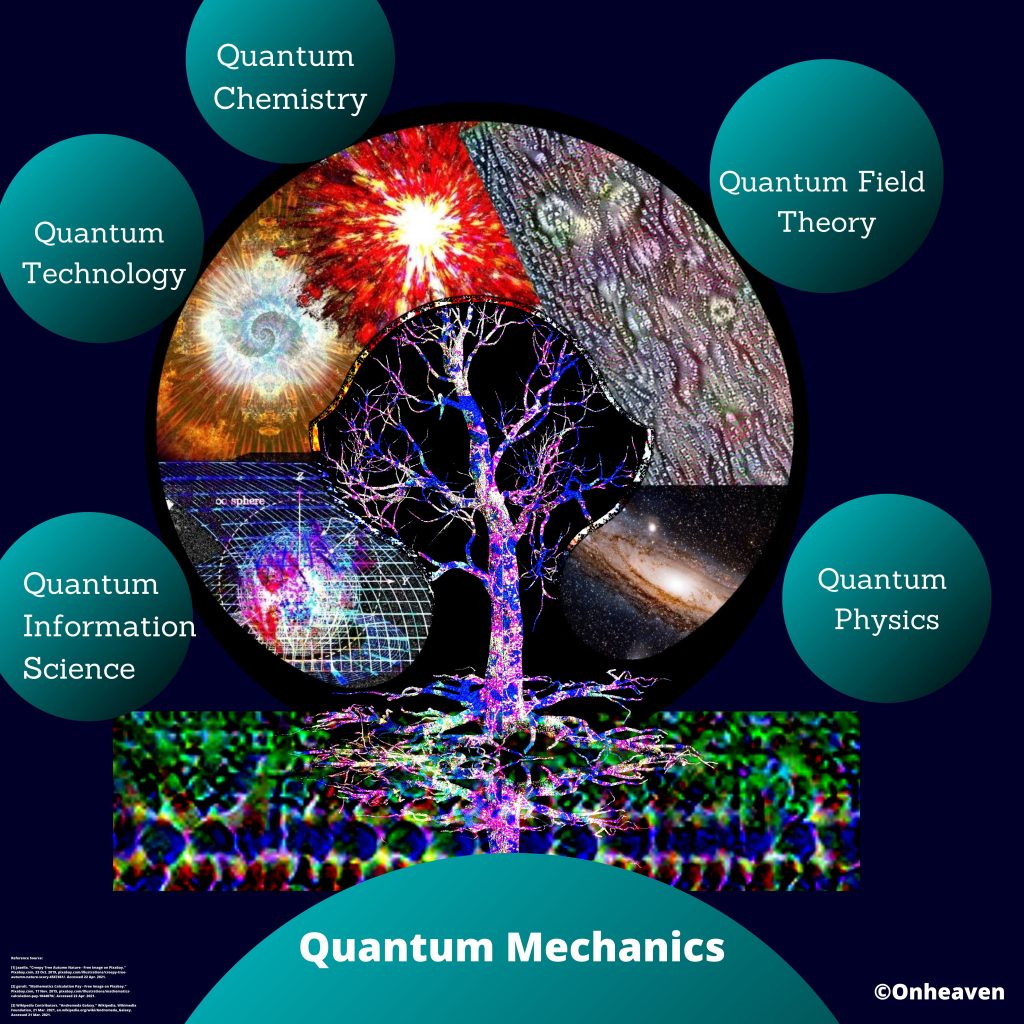
Nanotechnology
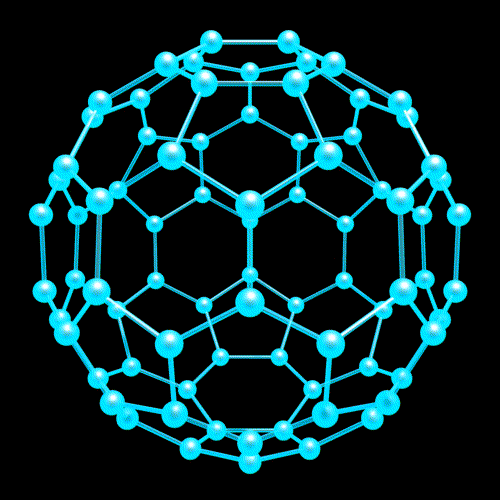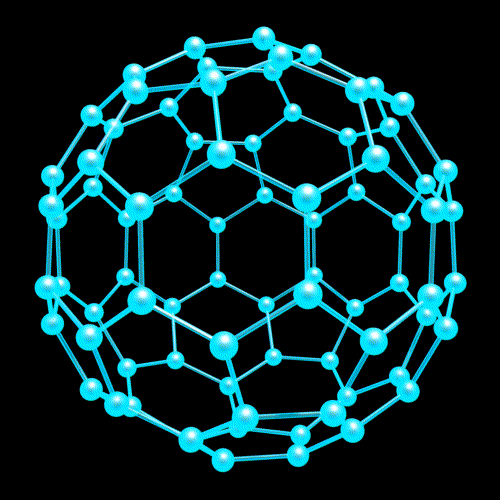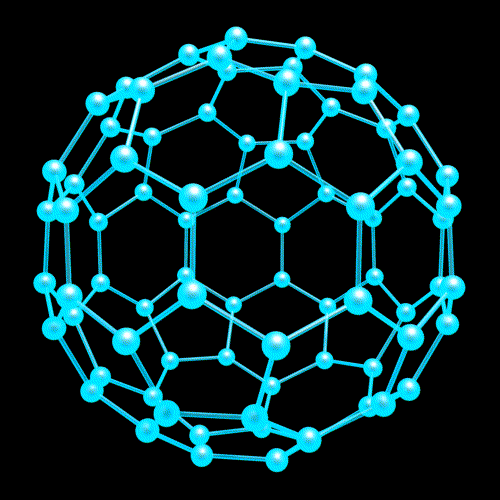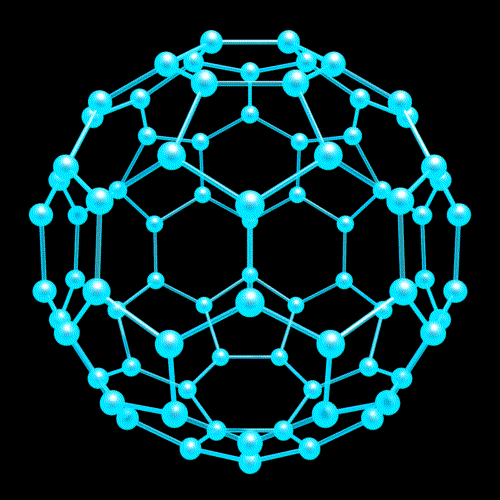
Nanostructure

Nanostructure (3D Viewer)
Leyden Jar

Leyden Jar
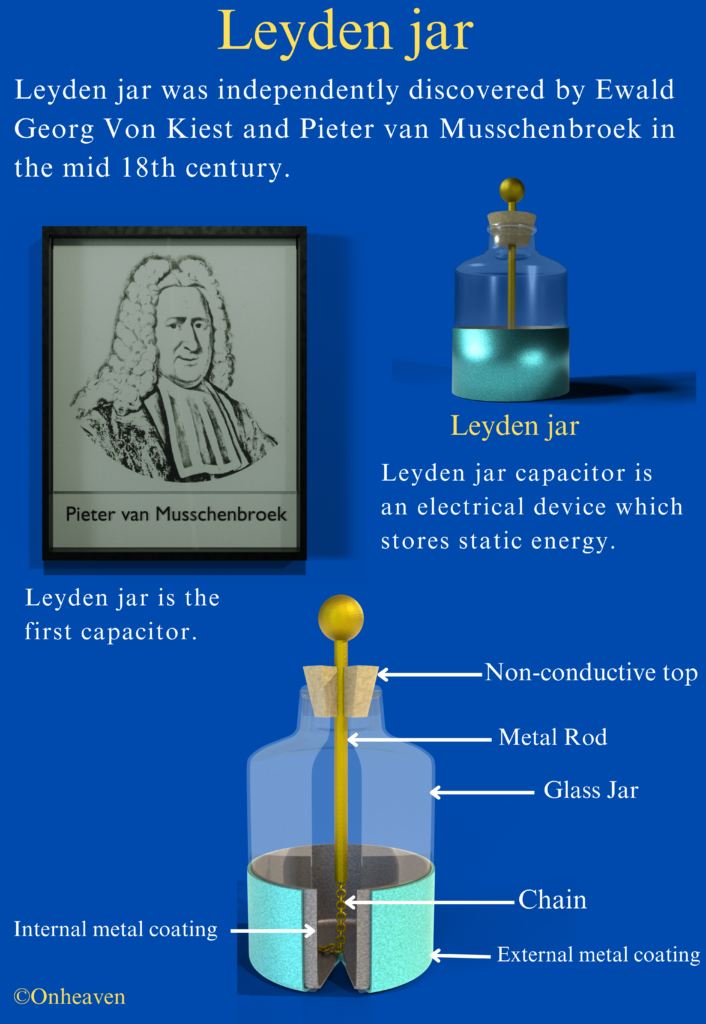
Leyden Jar (3D Viewer)
Ceramic Capacitor
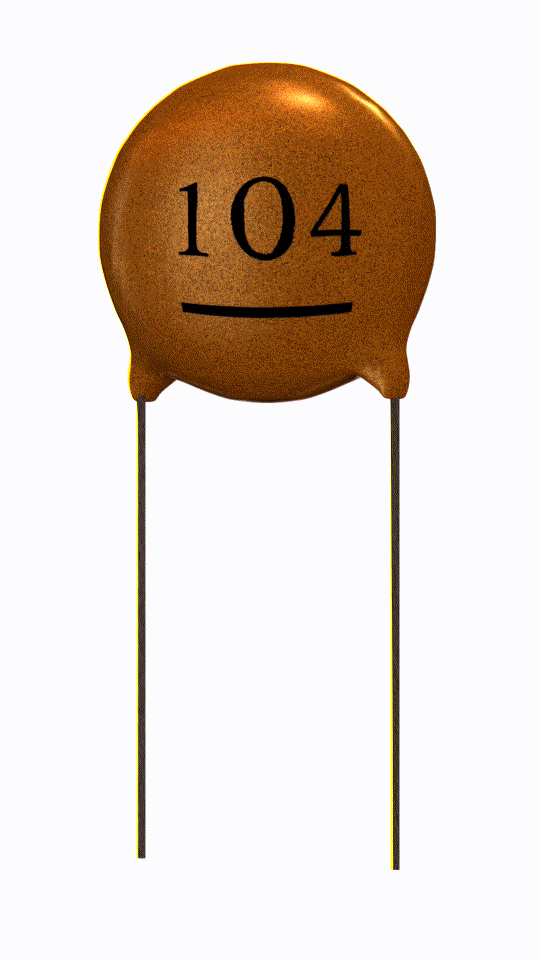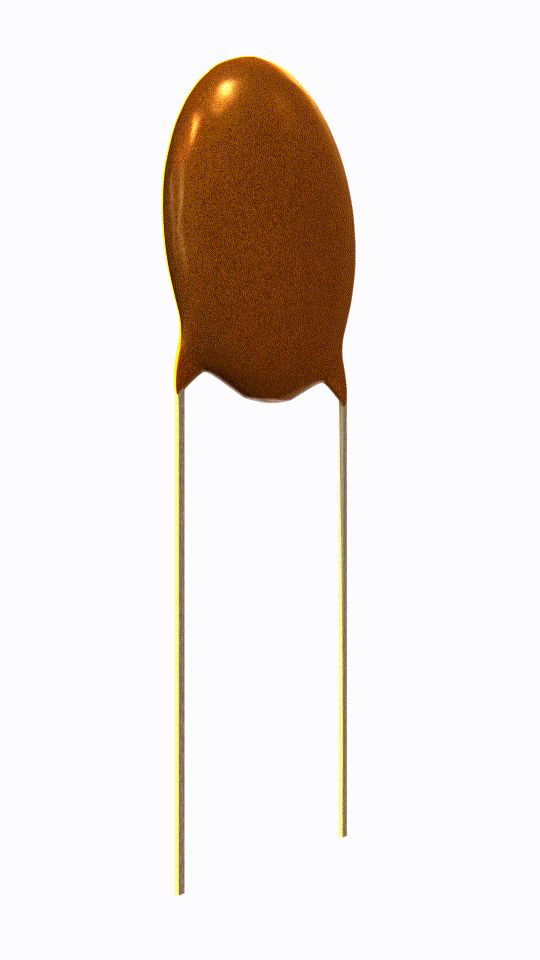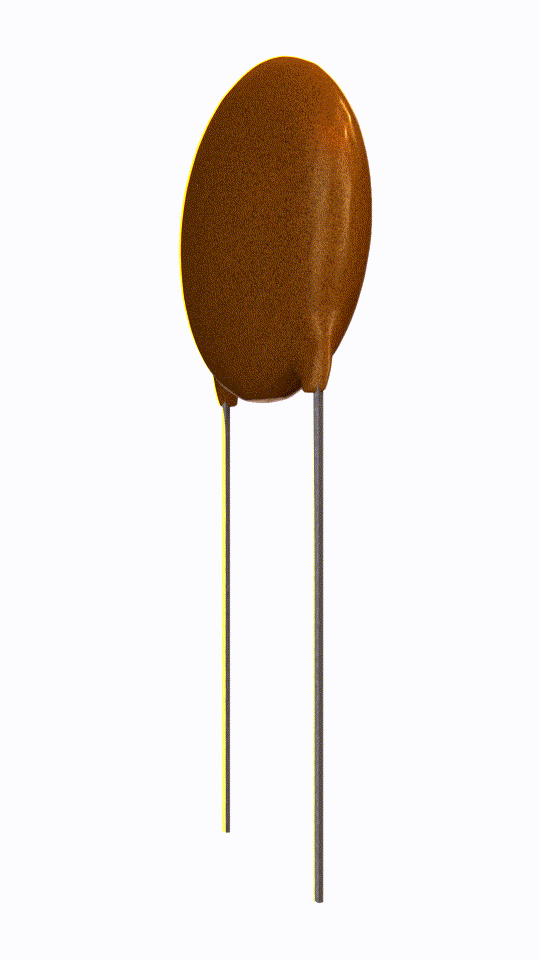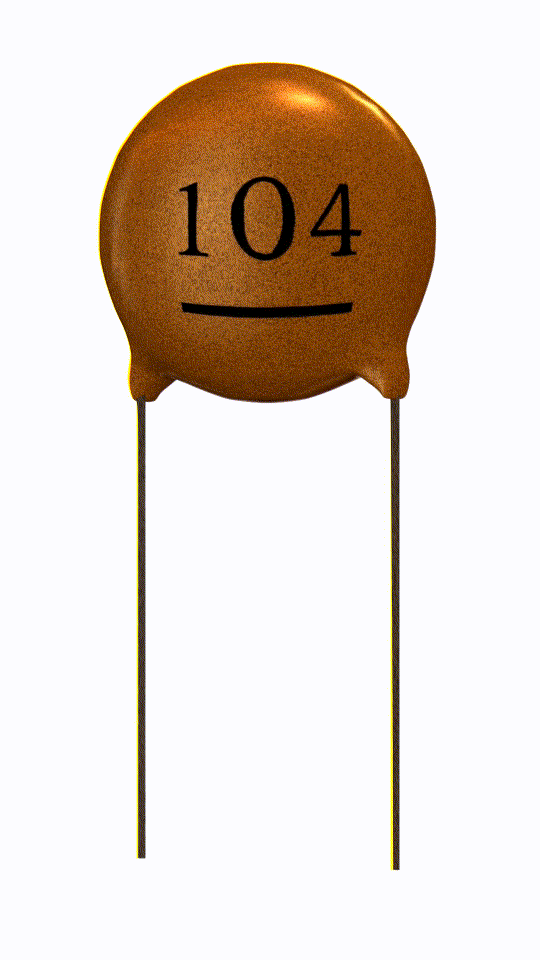
Ceramic Capacitor
Ceramic capacitor is a passive electronic device which uses ceramic material as its dielectric medium.
Ceramic capacitor is non-polarized.
In this capacitor ceramic material acts as a dielectric material which separates the two plates (electrode) inside the capacitor.
It has a great frequency response due to low parasitic inductance effect.
Application:
- Resonant Circuit.
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB).
- Navigation System.
- Power Supplies.
- Absorb Voltage Strike.
- Microwave Oven.
- Reduce Noise.
- Automotive.

Inside Ceramic Capacitor:
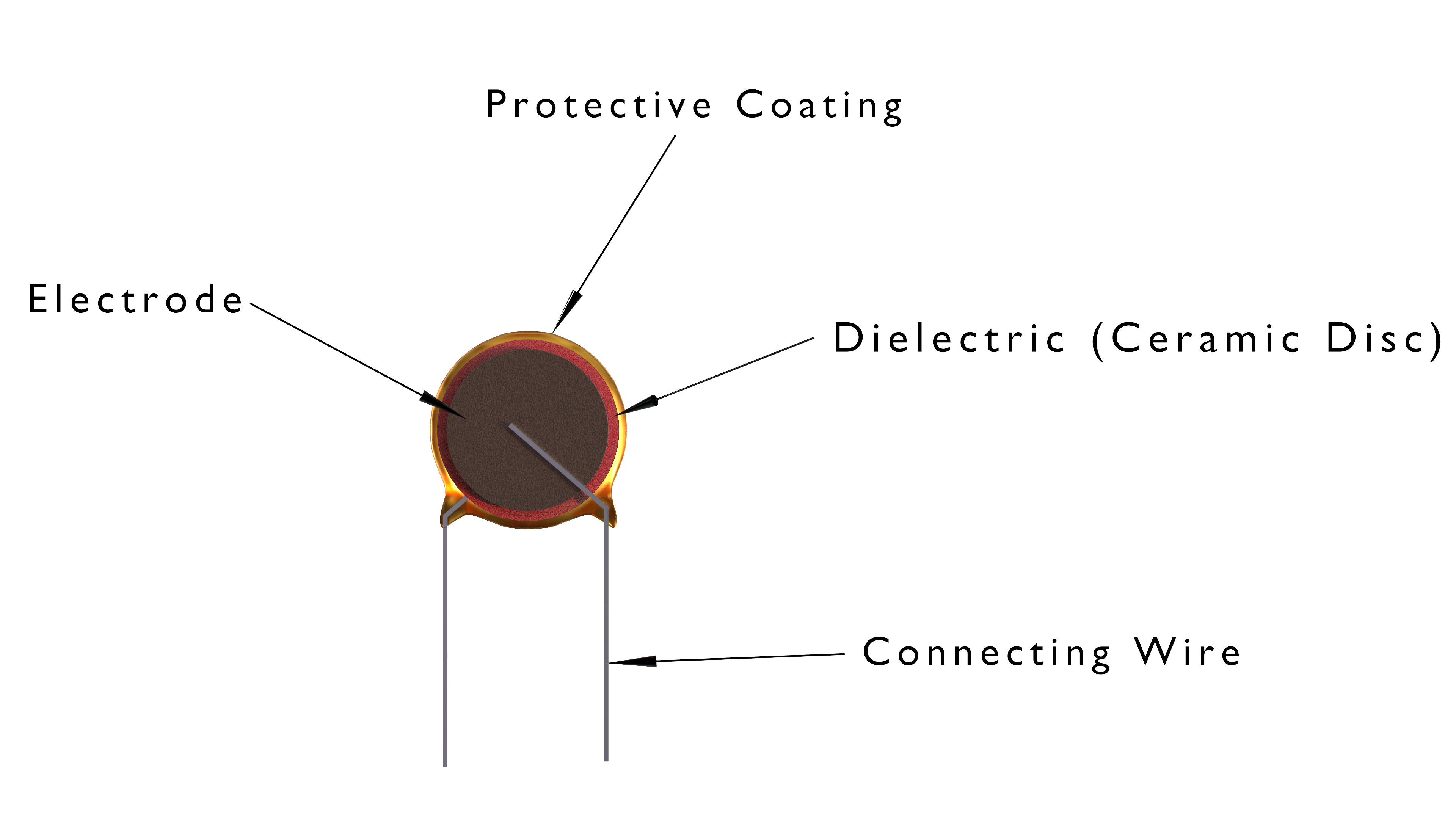
Ceramic Capacitor (3D Viewer)
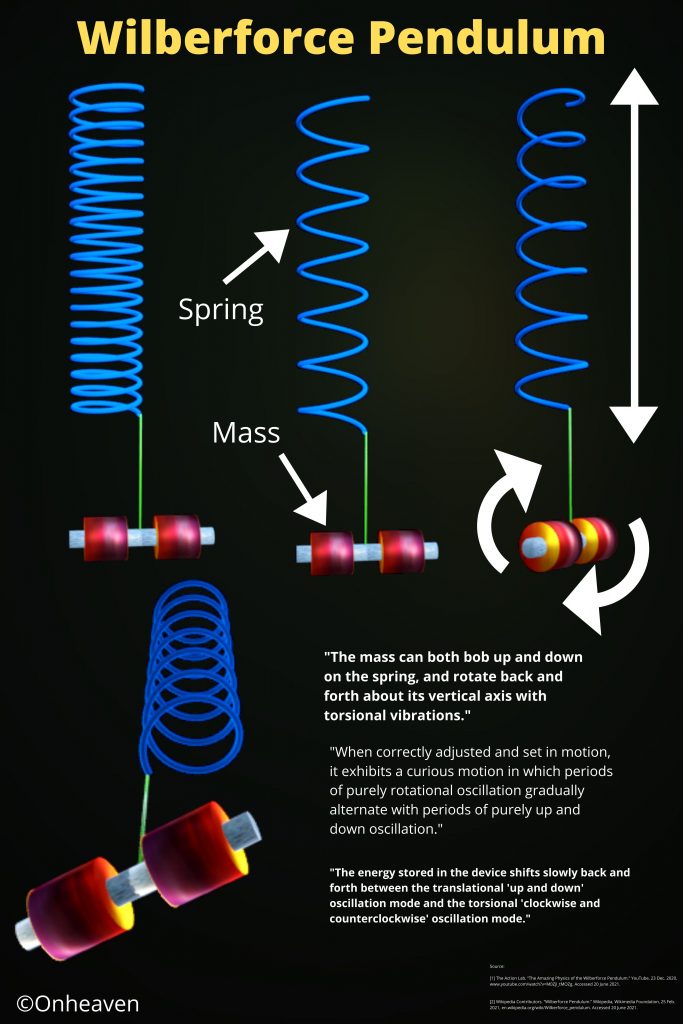
Linear Type Rheostat
3D Viewer
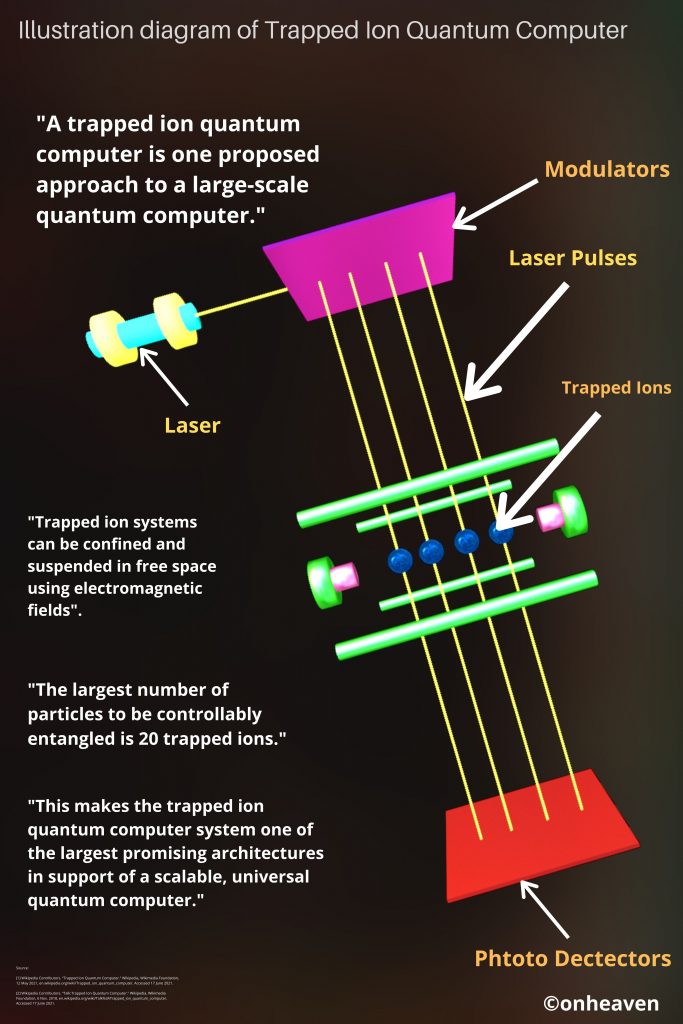
Tesla Coil
3D Viewer
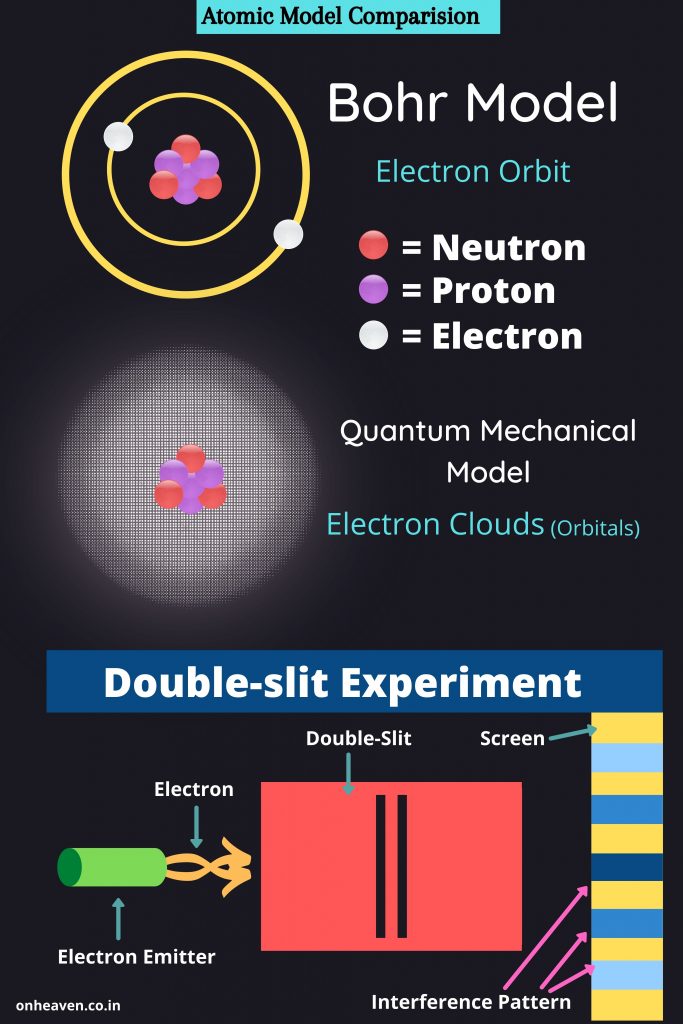
Permanent Magnet Moving Coil (PMMC)
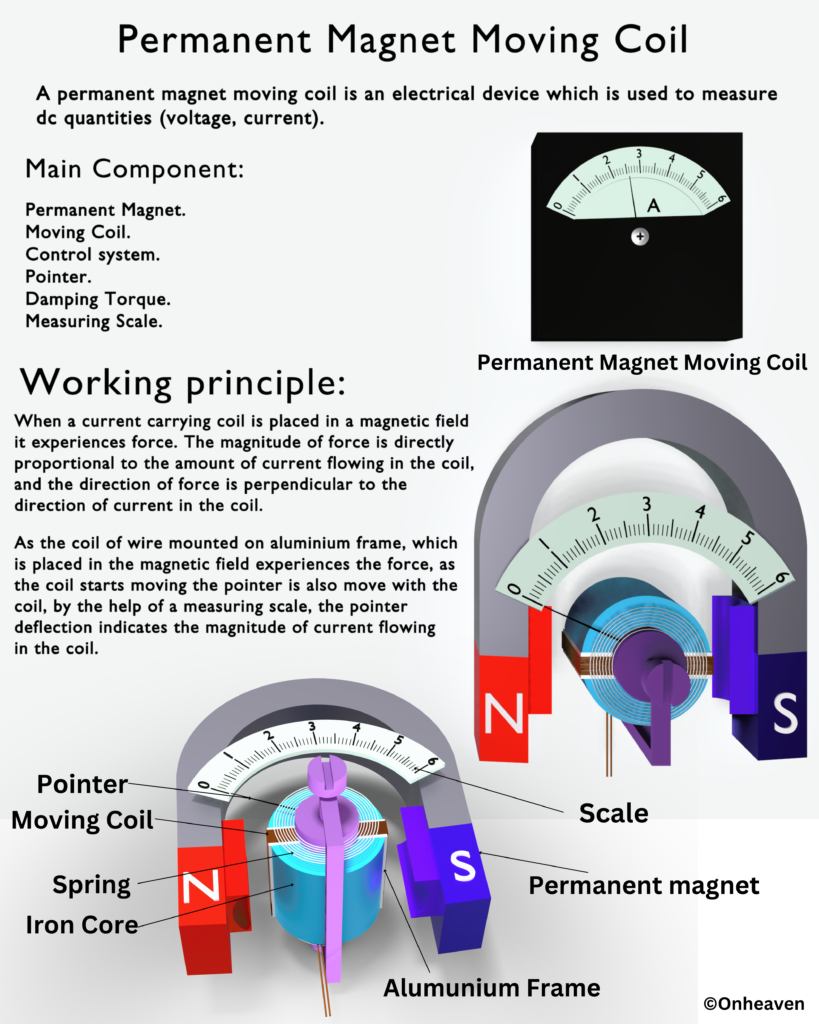
3D Viewer
Tank Circuit
3D Viewer
Electromechanical Relay
3D Viewer
Magnetic Coupler
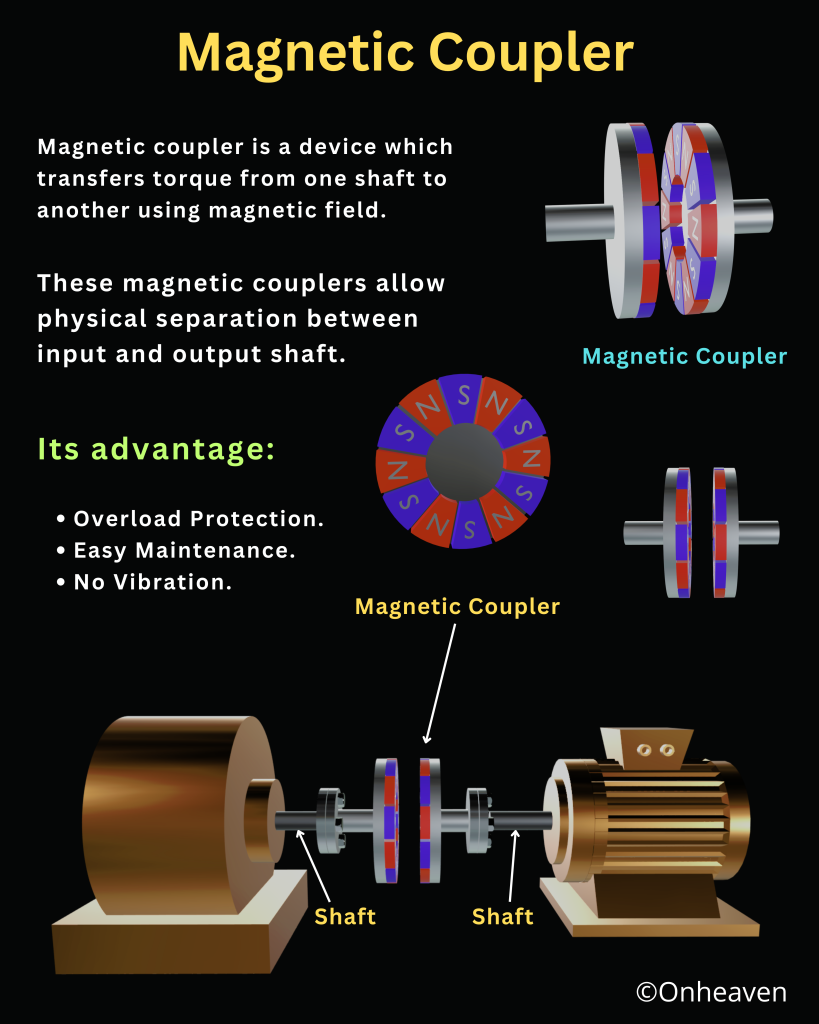
3D Viewer
Air Quality Sensor
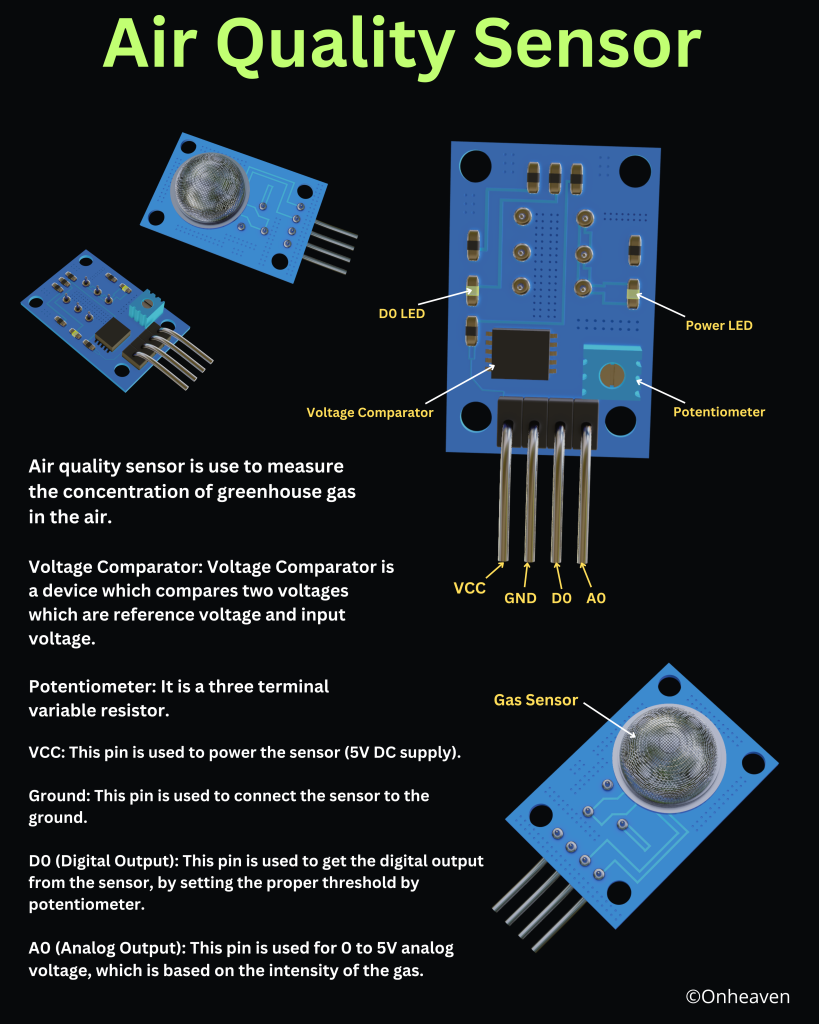
3D Viewer
Altimeter

3D Viewer
Venturimeter
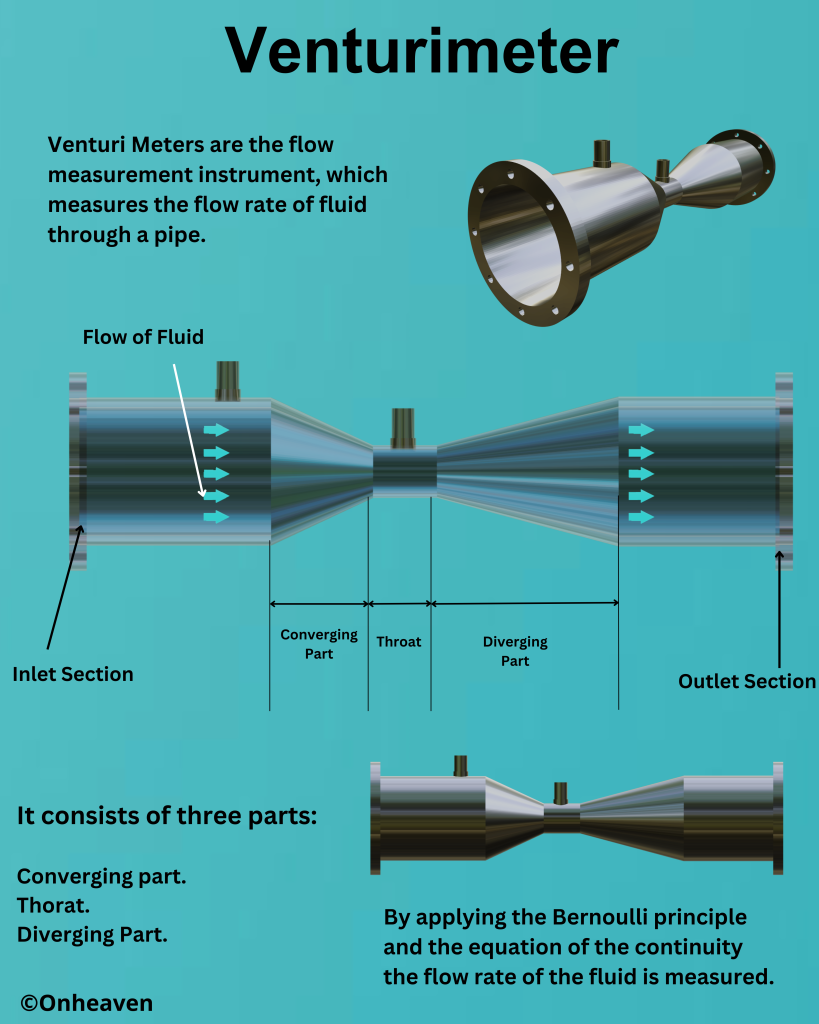
3D Viewer
Transformer
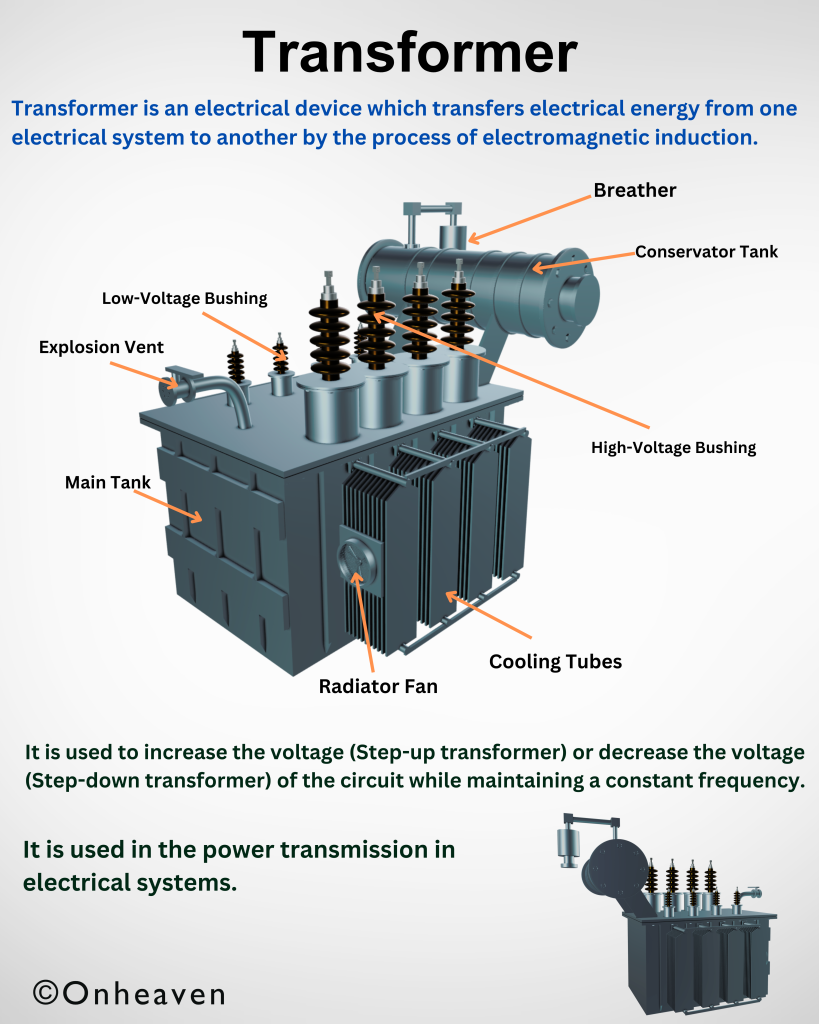
3D Viewer
Waveform of 3-Phase AC System
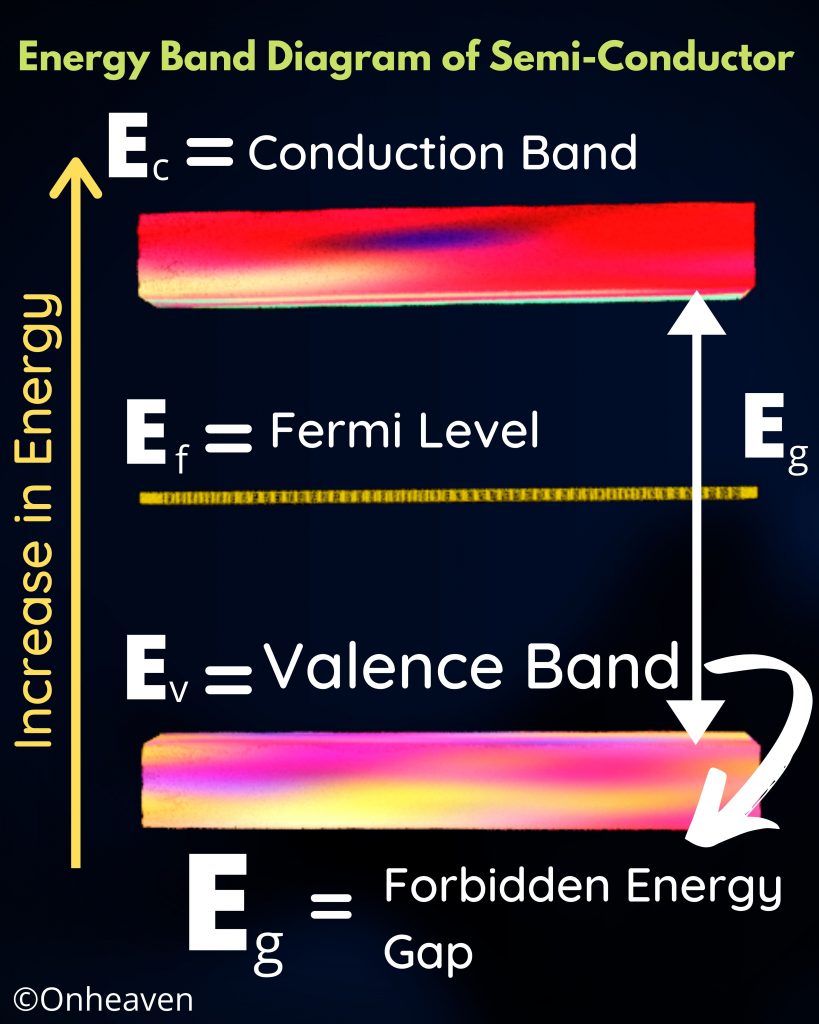
Hall Effect
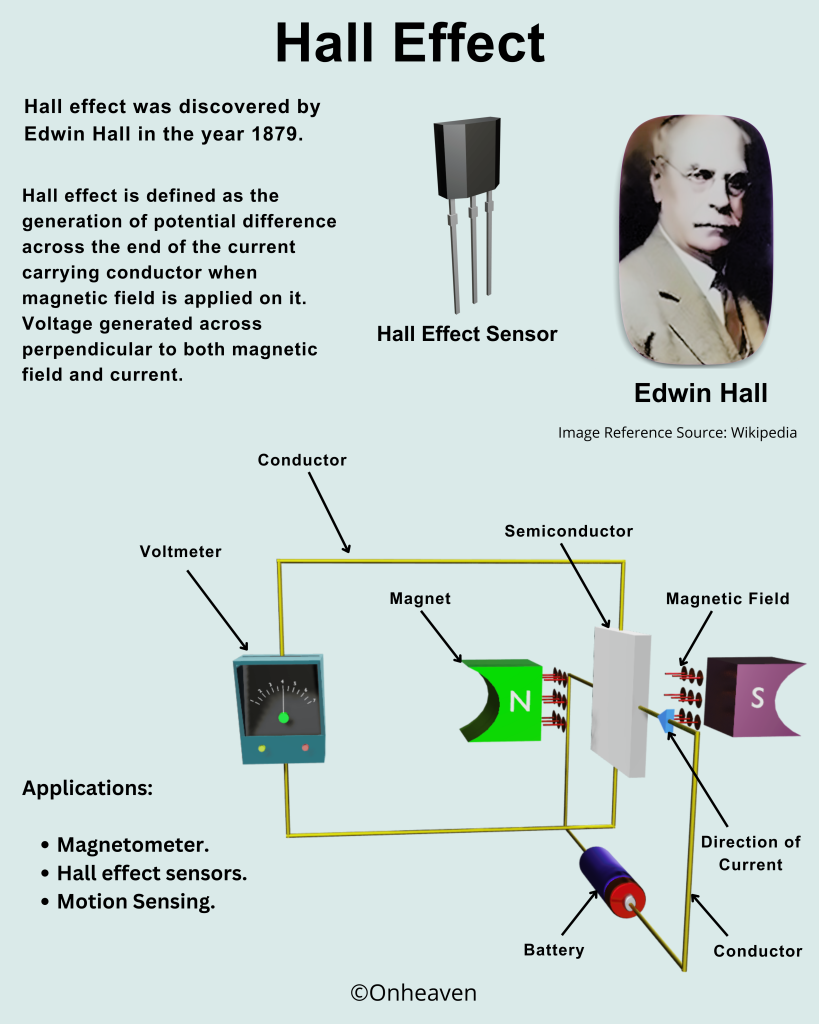
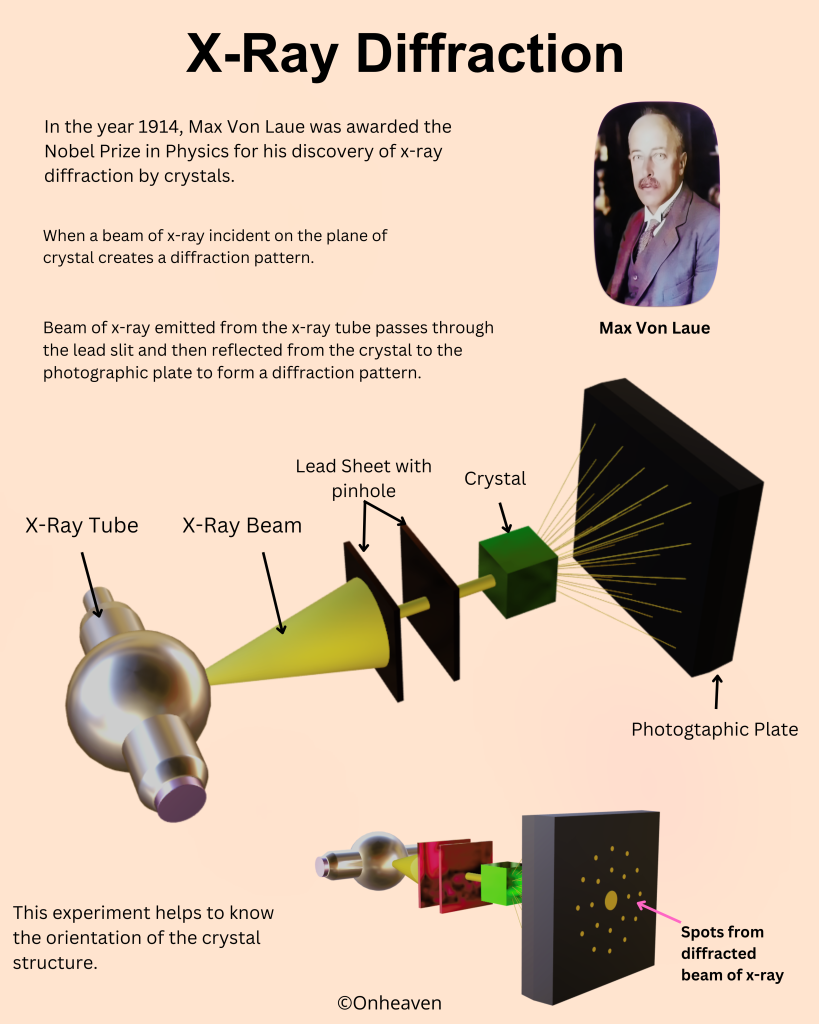
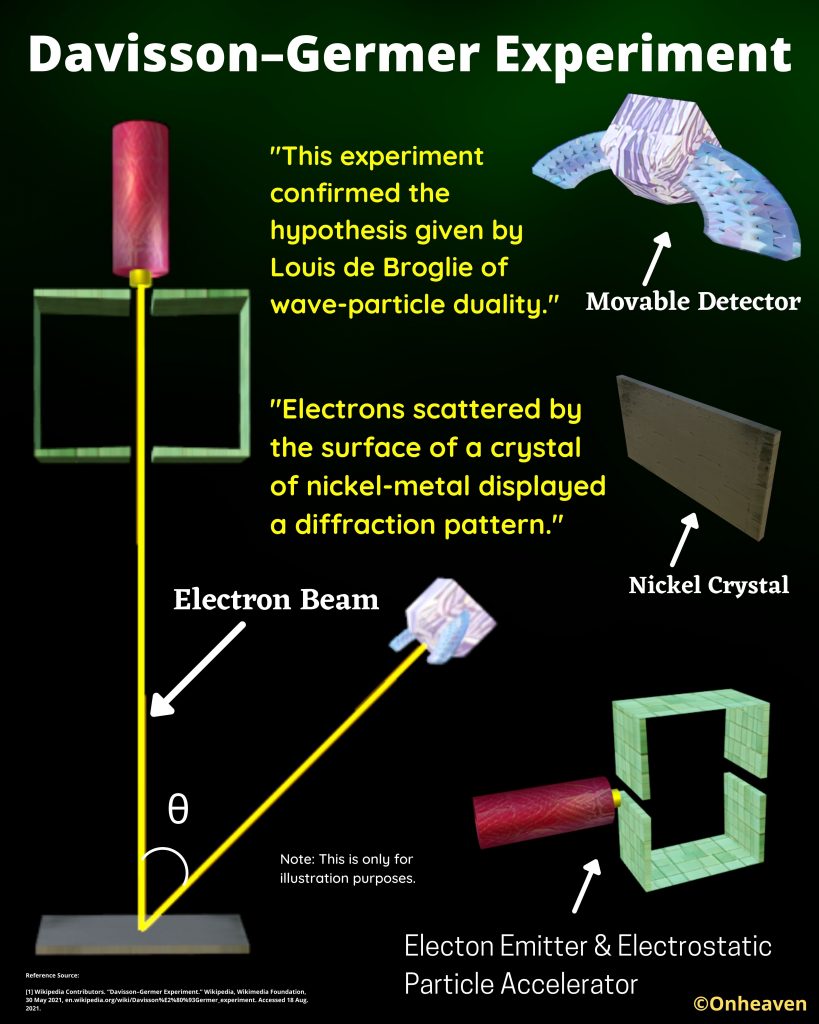
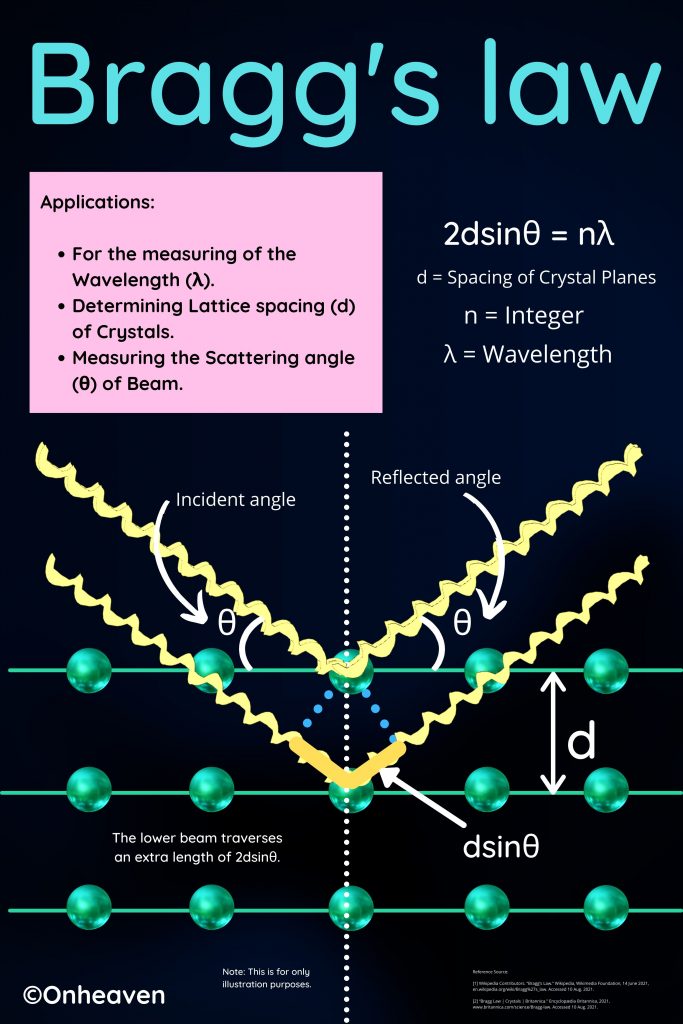
X-Ray Diffraction
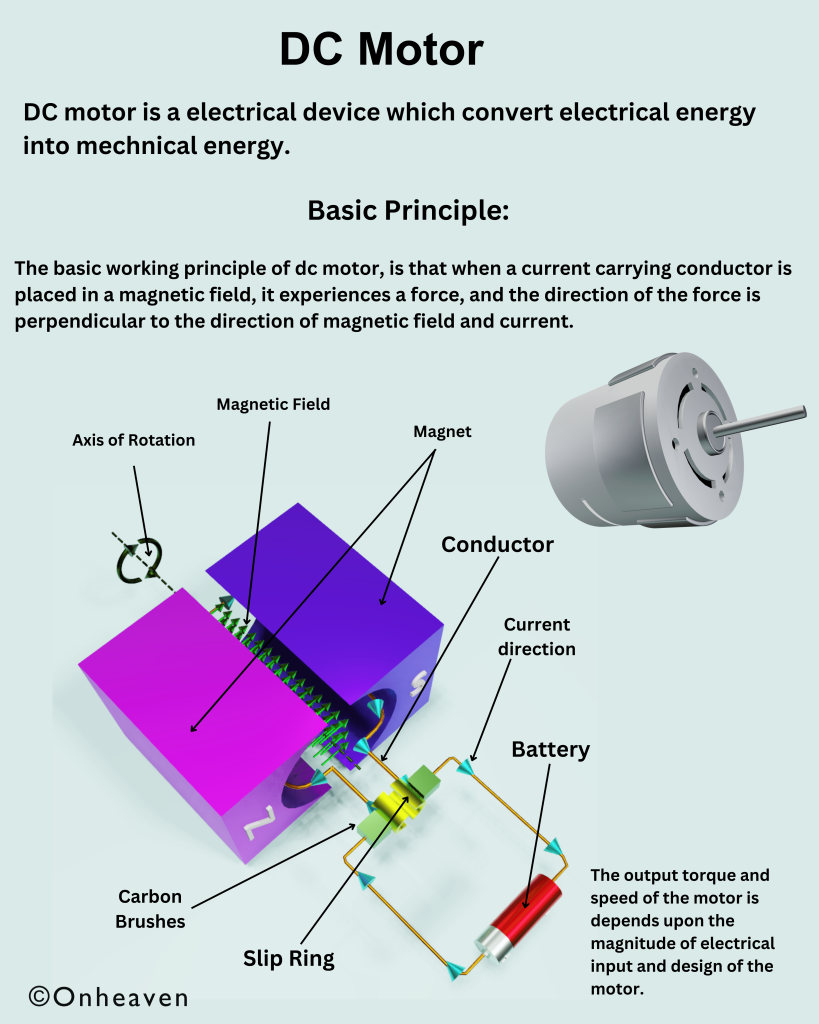
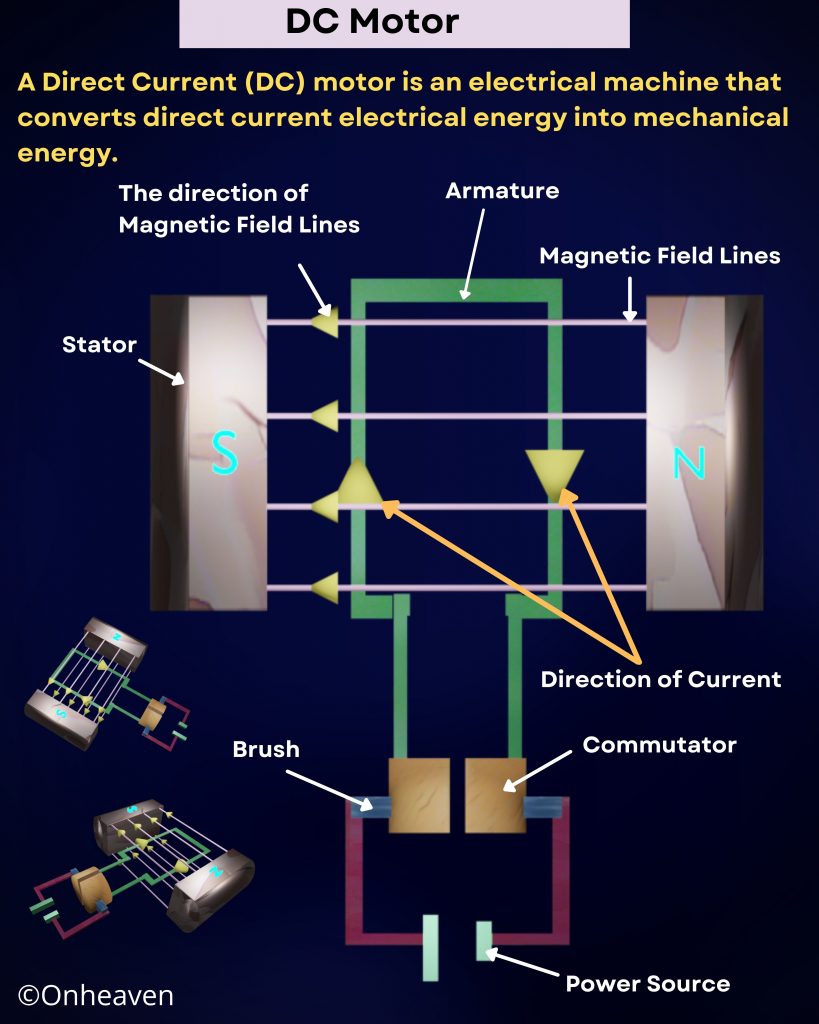
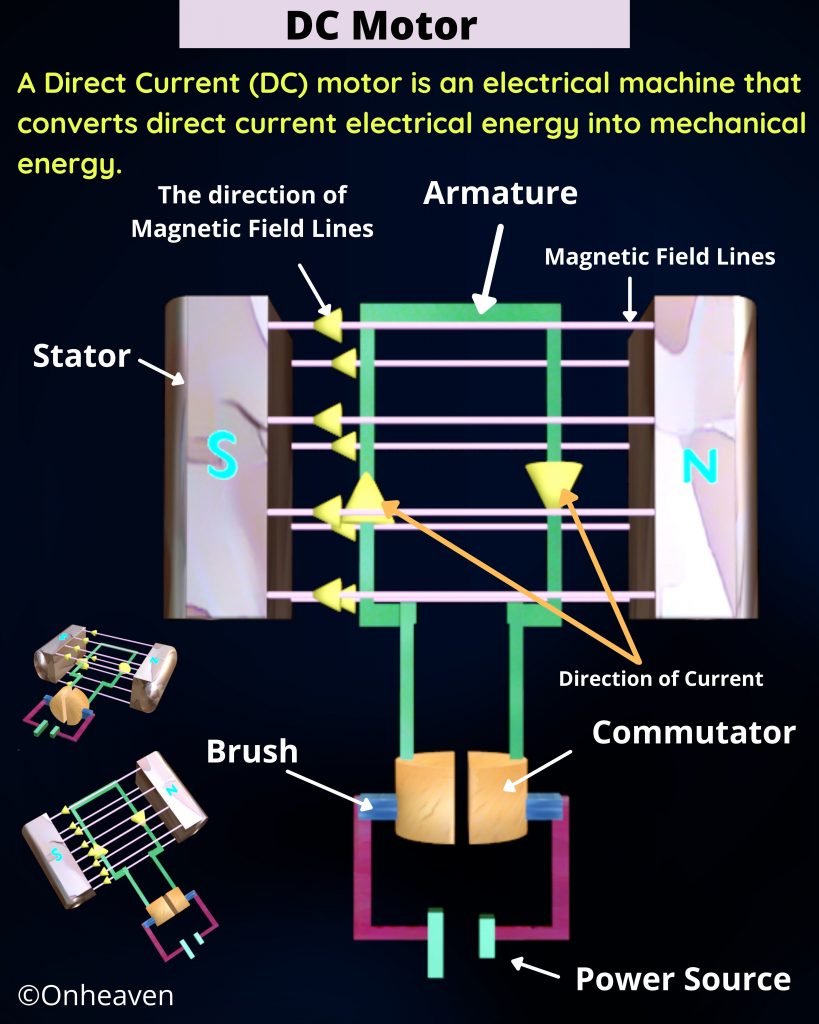
DC Motor
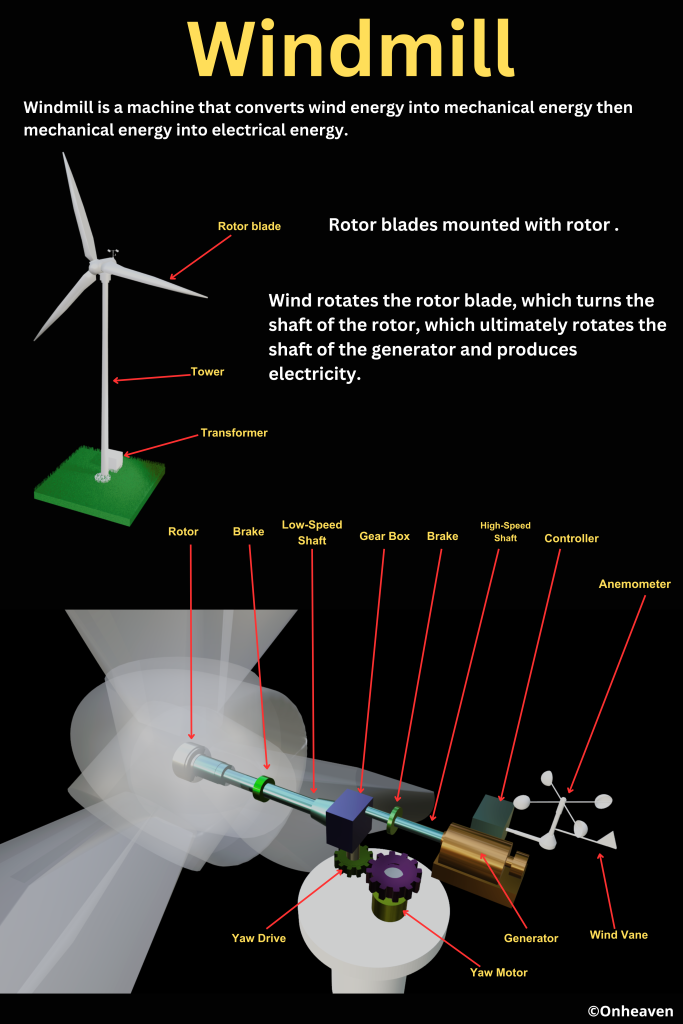
Windmill
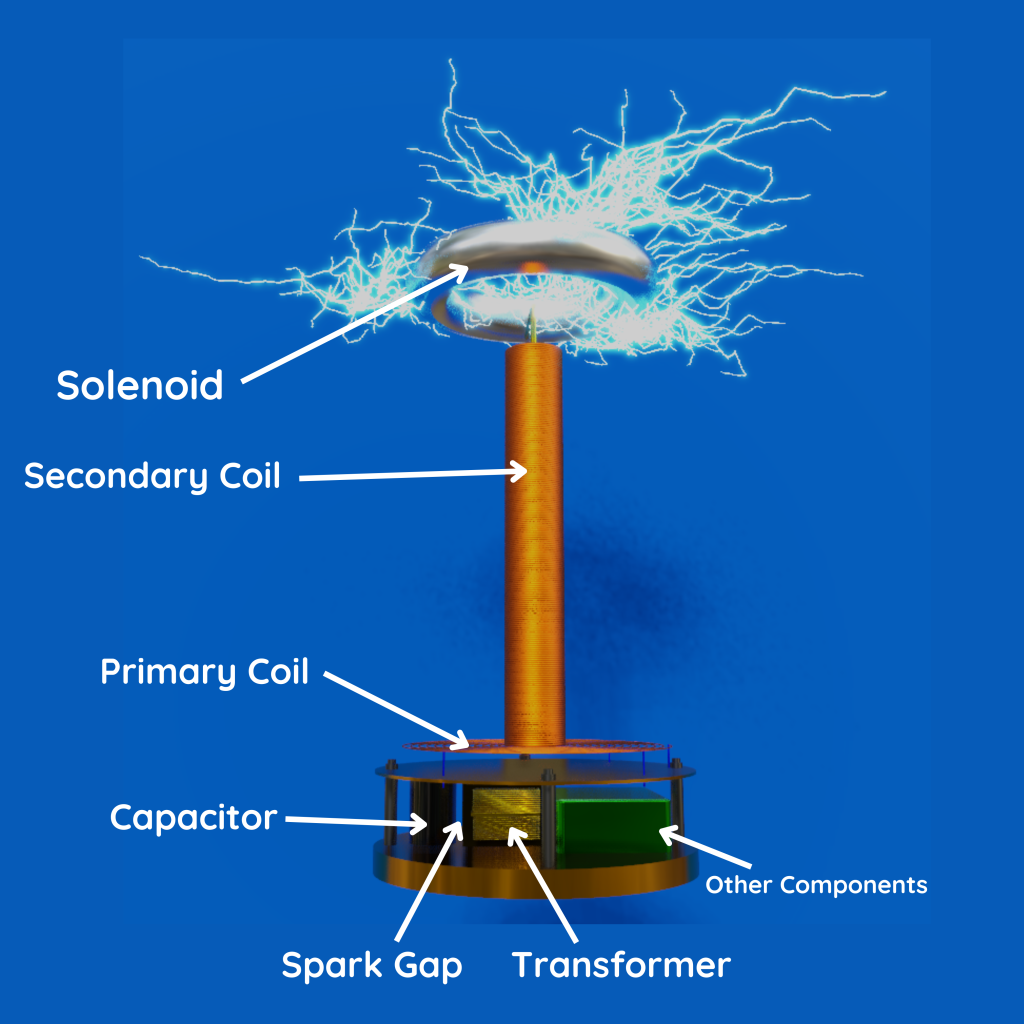
Tesla Coil

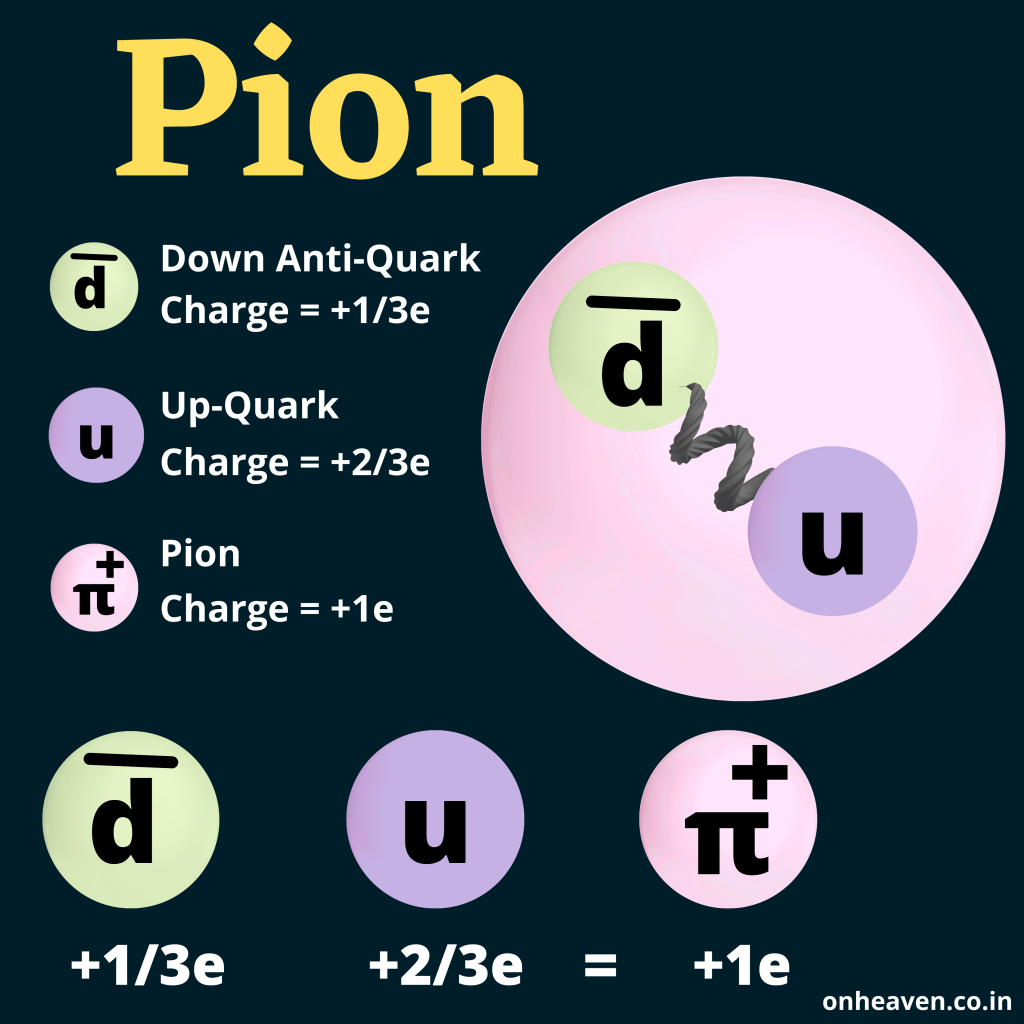
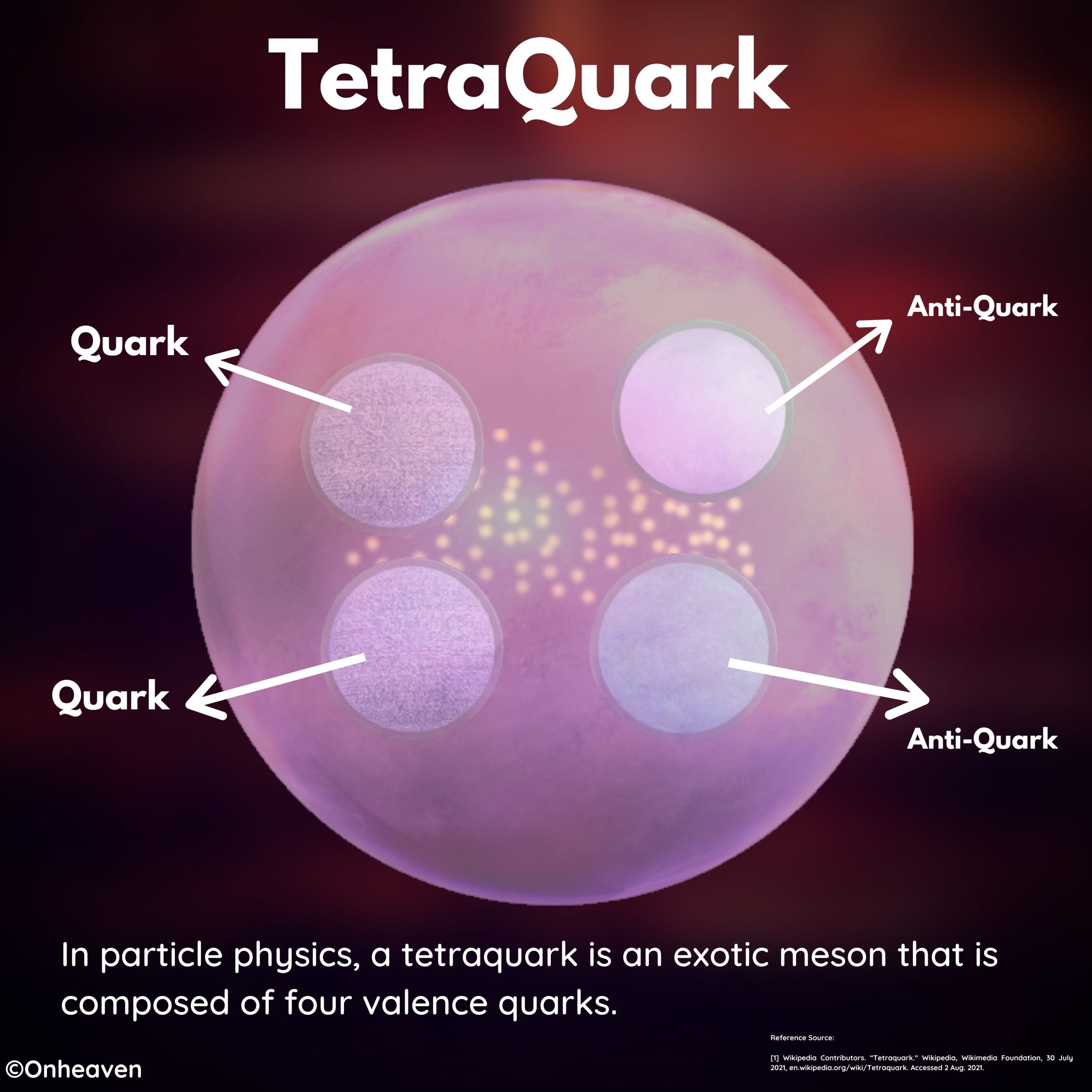
Meson

Gravitational Wave

Measurement of the Speed of Light

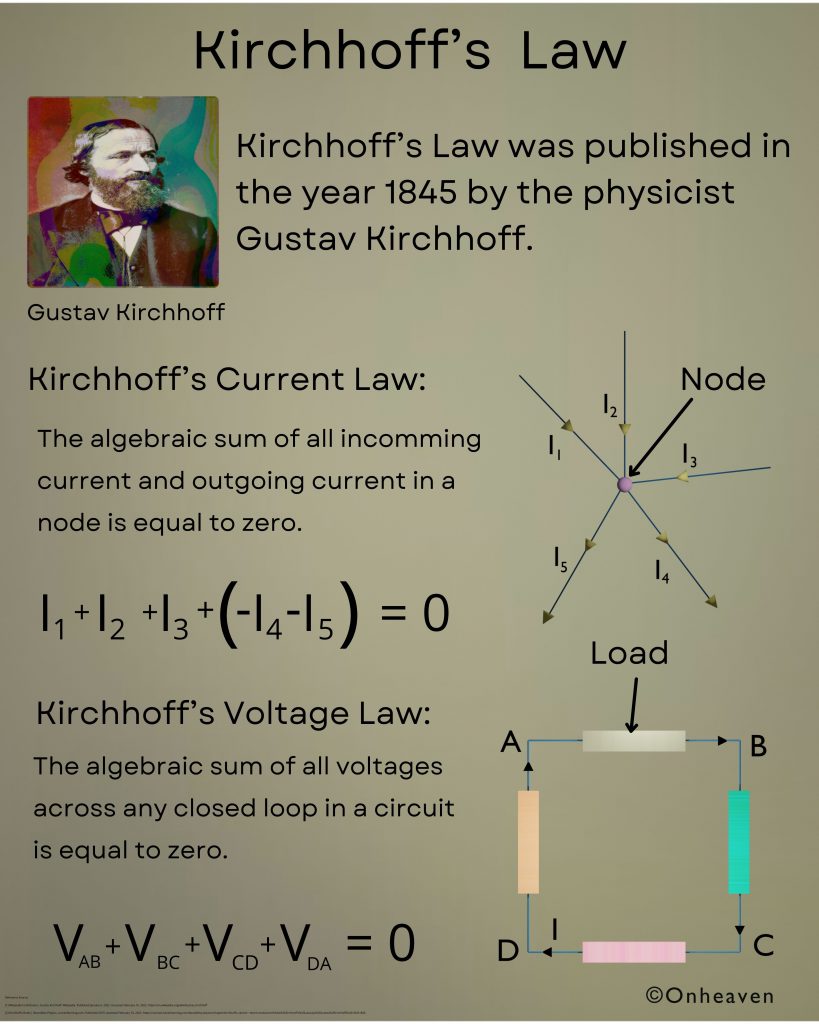
Ampere’s Circuital Law:
Rheostat:
Faraday’s Law of Induction:
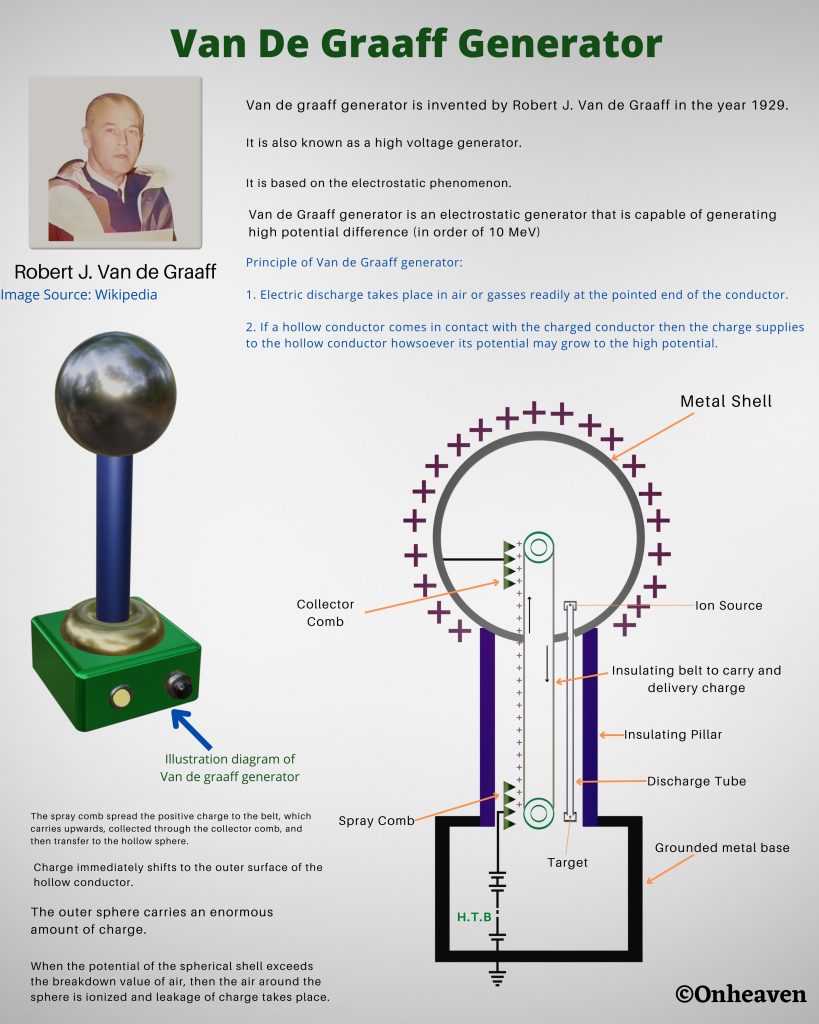
Van de Graaff Generator:
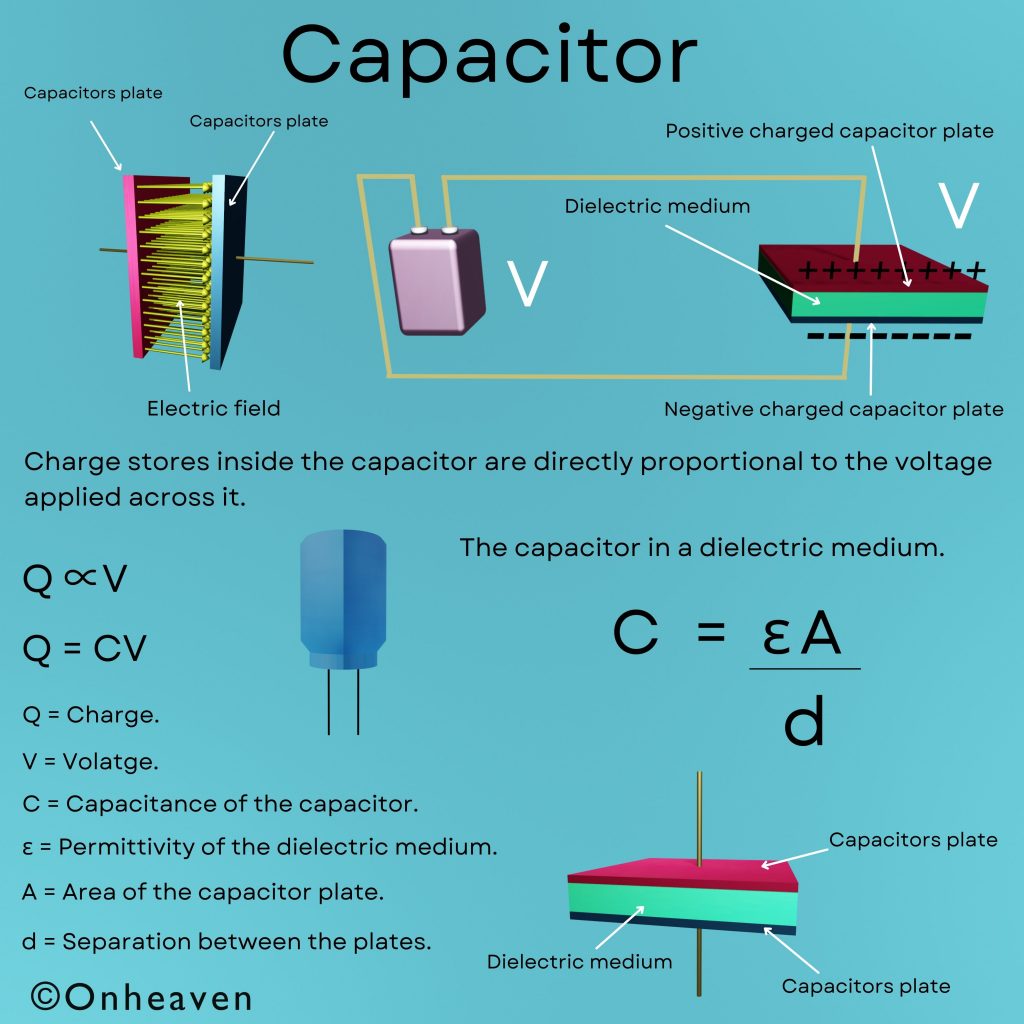
Dielectric in Capacitor:
Ohm’s Law 3D Video Illustration:


























































Advertisement