Extrinsic semiconductors are impure semiconductors that are doped with impurities in order to enhance their conductivity.
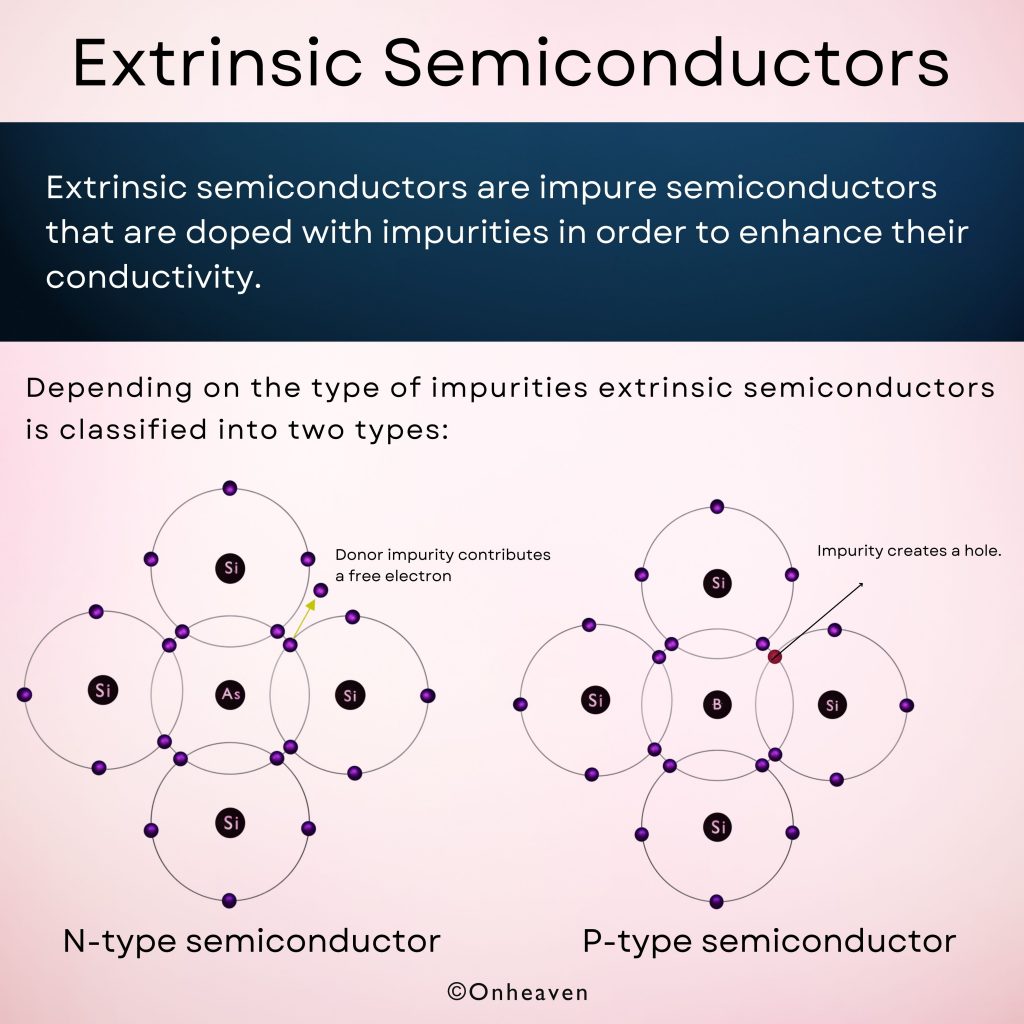
Depending on the type of impurities extrinsic semiconductors is classified into two types:
N-type semiconductor:
When tetravalent atom semiconductors like silicon or germanium are doped with the pentavalent atom impurities like Phosphorous (P), Arsenic (As), Antimony(Sb).
Four electrons of pentavalent impurities form a covalent bond with the silicon atom, and the fifth electron is loosely bonded and works as the current carrier.
In N-type semiconductors, the free electron is the majority charge carrier and the hole is the minority charge carrier.
P-type semiconductor:
When tetravalent atom semiconductors like silicon or germanium are doped with the trivalent atom impurities like Boron (B) or Indium (In).
Three electrons of trivalent impurities form a covalent bond with the valence electron of the silicon atom, and in the fourth covalent bond only one electron is available and there is a deficiency of one electron called a hole.
In a p-type semiconductor, a hole is the majority charge carrier and electrons are the minority charge carriers.
Reference Source:
[1] Extrinsic Semiconductor. Self Study Point. Published February 2, 2018. Accessed February 18, 2022. https://selfstudypoint.in/extrinsic-semiconductor/
[2] Extrinsic Semiconductors – Definition, Types and Properties | BYJU’S. BYJUS. Published August 29, 2018. Accessed February 18, 2022. https://byjus.com/physics/extrinsic-semiconductors/
[3] For an n-type semiconductor, the ratio of number of electron. Testbook. Published 2014. Accessed February 18, 2022. https://testbook.com/question-answer/for-an-n-type-semiconductor-the-ratio-of-number-o–603b20444fcf12768bdb2e96