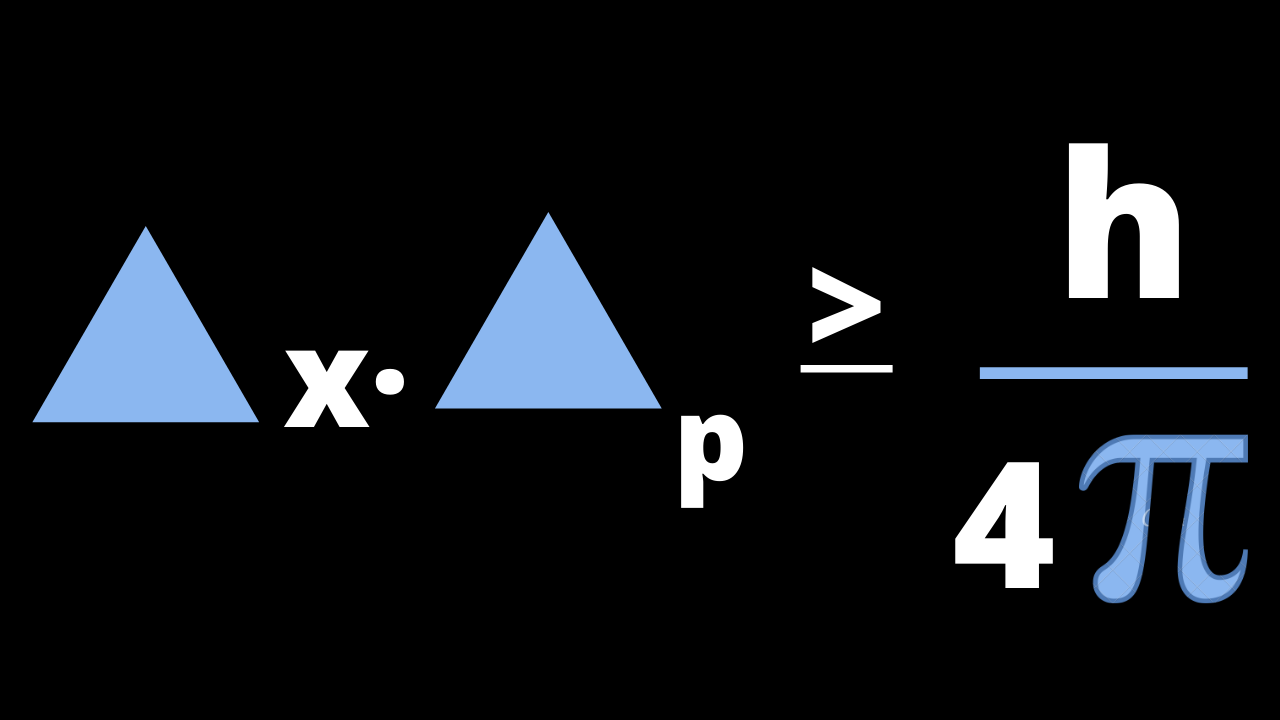Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor particles a few nanometres in size, having optical and electronic properties that differ from larger particles due to quantum mechanics.… Read More »Quantum dots (QDs) are highly regarded as the smallest particles in the world
Quantum
The idea that matter consists of smaller particles has existed in natural philosophy at least since the 6th century BC. The concept of “elementary particle”… Read More »Quantum Mechanics: Subatomic Particles Background
Quantum Mechanics: Subatomic Particles Background
Quantum Tunneling: Quantum mechanical phenomenon where wave-function can propagate through the potential barrier. Transmission through the barrier can be finite and depends exponentially on barrier… Read More »Quantum Tunneling occurs with barriers of thickness around 1–3 nm and smaller
Quantum Tunneling occurs with barriers of thickness around 1–3 nm and smaller
A quantum bit or “qubit” can represent “1” AND “0” at the same time, unlike the classical processor’s. the bit is binary and point-like but… Read More »What makes Quantum Bit (Qbit) faster
What makes Quantum Bit (Qbit) faster
Quantum mechanics has held up to rigorous and extremely precise tests in an extraordinarily broad range of experiments. There exist a number of contending schools… Read More »Interpretation of “Quantum Mechanics” in Brief
Interpretation of “Quantum Mechanics” in Brief
Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons. The most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. There are six… Read More »The Generation of Quark: Quantum World
The Generation of Quark: Quantum World
Virtual particle is a transient quantum fluctuation that exhibits some of the characteristics of an ordinary particle. The concept of virtual particles arises in perturbation… Read More »Virtual particles are excitations of the underlying quantum fields, but are “temporary”
Virtual particles are excitations of the underlying quantum fields, but are “temporary”
Quantum field theory emerges from Newton’s law of universal gravitation. The force of gravity as described by Newton is an “action at a distance” it… Read More »Background of Quantum Field Theory (QFT)
Background of Quantum Field Theory (QFT)
Quantum field theory (QFT) is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles. QFT treats particles as excited states (also called quanta)… Read More »How Quantum Field Theory(QFT) Used in Particle Physics
How Quantum Field Theory(QFT) Used in Particle Physics
Quantum physics encompasses any discipline concerned with quantum-mechanical effects. Applications of quantum mechanics include explaining phenomena found in nature and developing technologies that rely upon… Read More »Application of Quantum Mechanics
Application of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics was developed in the early decades of the 20th century. scientists proposed a wave theory of light based on experimental observations, in 1803… Read More »Background of Quantum Mechanics
Background of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics. It describes the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles, compared to… Read More »Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics
This is the Simulation of Emission of Particle (Just a Fun Visualization)
Simulation of Emission of Particle
Particle in Quantum Mechanics: Source: [1] Gam-Ol. “Abstract Cosmos Space – Free Photo on Pixabay.” Pixabay.com, 8 June 2018, pixabay.com/photos/abstract-cosmos-space-particle-3460328/. Accessed 1 Dec. 2020.
Particle in Quantum Mechanics
Generation of Gravitational wave by the interaction of two Neutron Star. Generation of Gravitational wave by the interaction of two Black Holes. (This Gif file… Read More »Generation of Gravitational Wave (Quantum World)
Generation of Gravitational Wave (Quantum World)
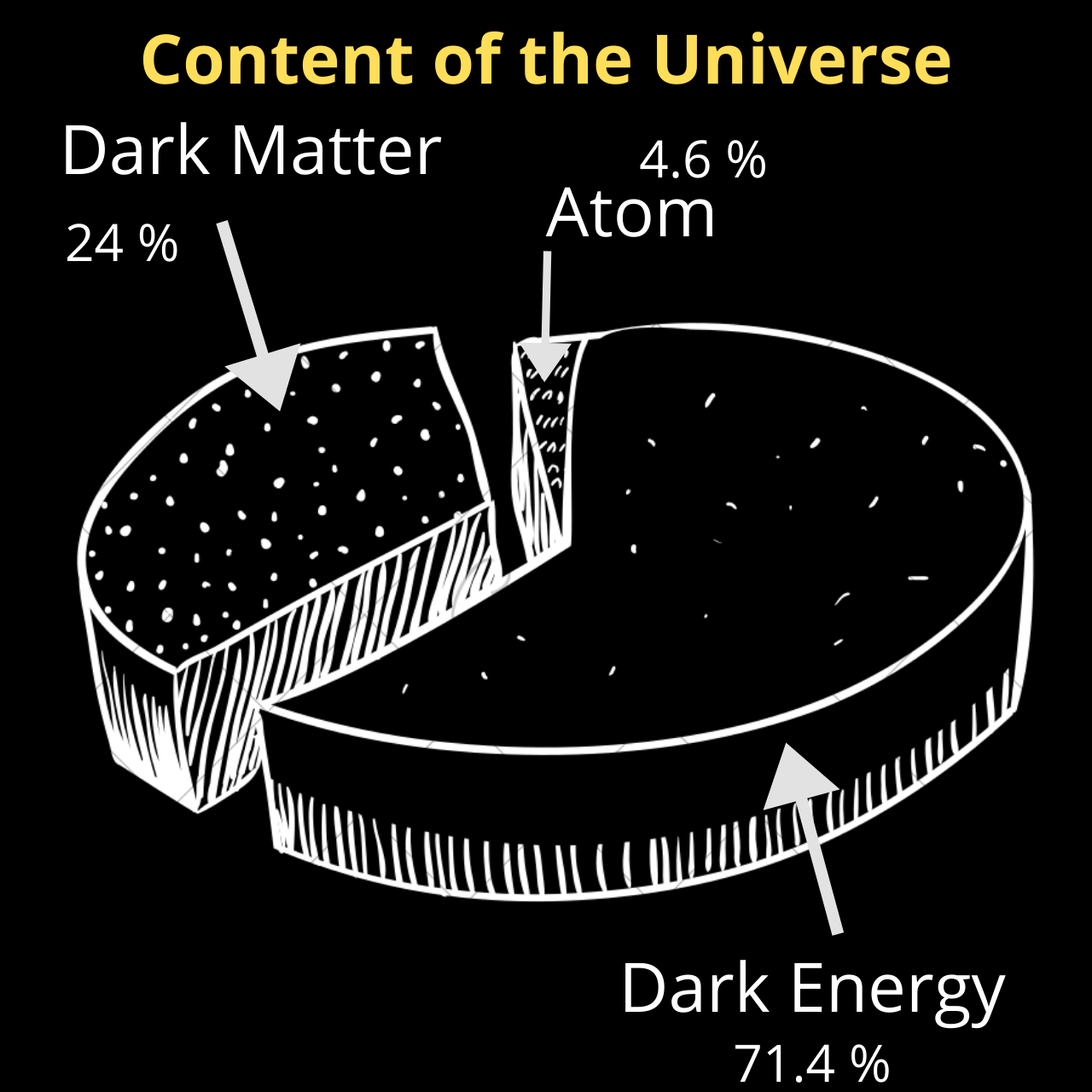
This is the representation of the content of the universe in the Pie- Chart Format. Reference Source: [1] Fermilab. “What Is Dark Matter and Why… Read More »Content of The Universe (Quantum World)
Content of The Universe (Quantum World)
When two Hadrons collide, nearly at the speed of light, at Large Hadron Collider then Higgs Boson particle comes to existence, with the confirmation of… Read More »Generation of The Higgs Boson (Quantum World)
Generation of The Higgs Boson (Quantum World)
The more particle interacts in the Higgs field the more mass it, gets, As you saw this, the less mass particles move faster, in comparison… Read More »Interaction of Particle in Higgs Field (Quantum World)
Interaction of Particle in Higgs Field (Quantum World)
A wormhole could connect extremely long distances such as a billion light years or additional, short distances such as a hardly any meters, different universes,… Read More »Particle in a Wormhole (Quantum World)
Particle in a Wormhole (Quantum World)
Hydrogen Atom (Quantum Mechanics), Here is the pictorial representation, Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Hydrogen Atom.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 15 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_atom#/media/File:Hydrogen_GIF.gif. Accessed 29 Nov. 2020.… Read More »Hydrogen Atom (Quantum Mechanics)
Hydrogen Atom (Quantum Mechanics)
Visualization of Virtual Particle ( an interaction of matter and anti-matter). Virtual Particles can be generated and then annihilated in a Vacuum without breaking the… Read More »Virtual Particle (Quantum Mechanics)
Virtual Particle (Quantum Mechanics)
The more particle interact in the Higgs Field the more mass it gets, How it looks GO to Home page for more Illustrations
Deep Understanding of The Higgs Mechanism
“Quantum entanglement is a physical phenomenon that occurs when a pair or group of particles are generated, interact, or share spatial proximity in a way such that the quantum… Read More »Quantum Entanglement Process
Quantum Entanglement Process
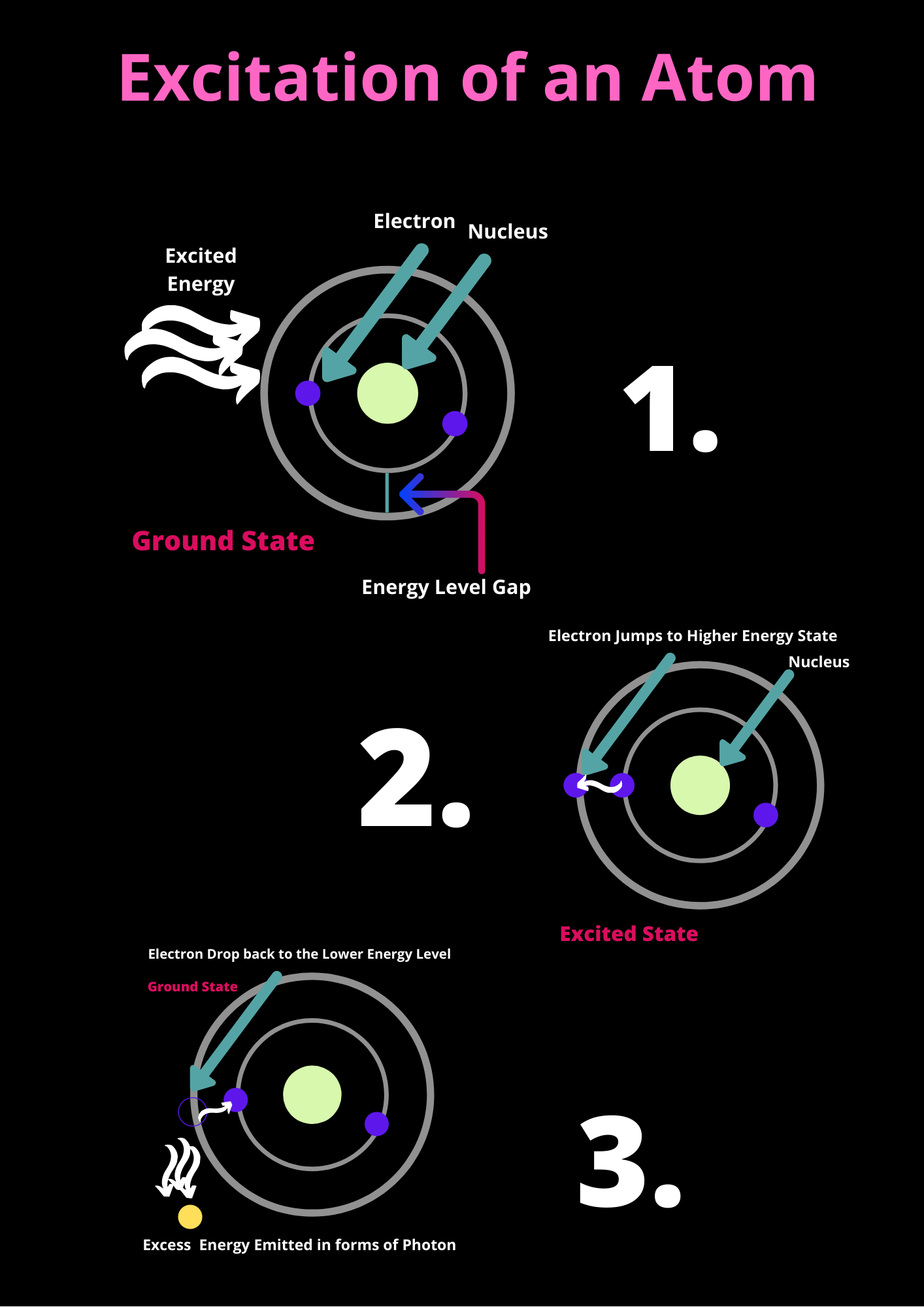
Excitation of an Atom by getting an External Energy Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Photon.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 8 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photon. Accessed 23 Nov. 2020.
Excitation of an Atom
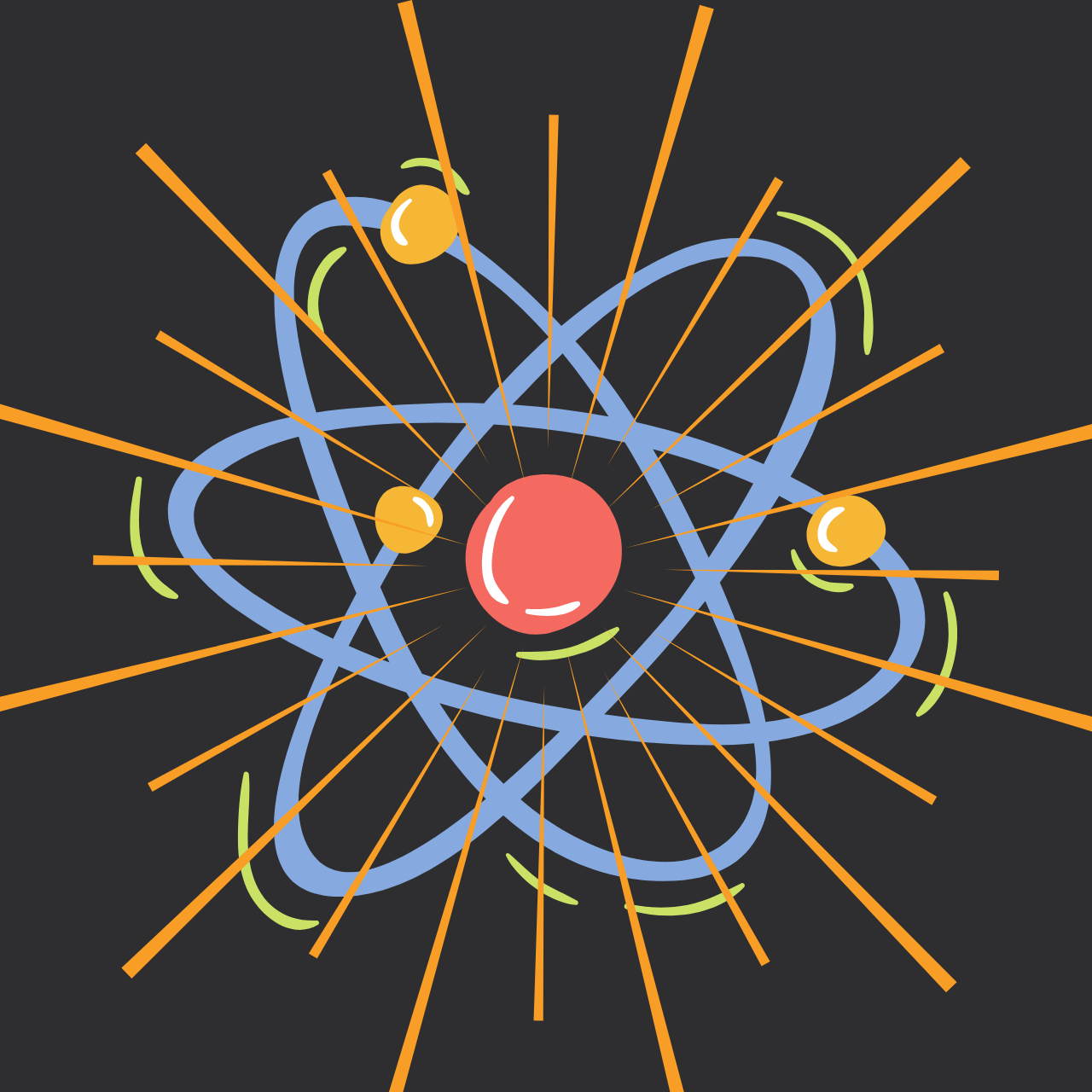
Zoom in to Deep Inside in an Atom up-to Quark. Source (Image): [1] Clker-Free-Vector-Images. “Atom Nuclear Chemistry – Free Vector Graphic on Pixabay.” Pixabay.com, 26 Apr.… Read More »Deep Inside in an Atom
Deep Inside in an Atom
Visualization of Virtual Particle ( an interaction of matter and anti-matter)
Visualization of Virtual Particle
“The photon is a type of elementary particle. It is the quantum of the electromagnetic field including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless so they always move at the speed… Read More »Visualization of Photon Generation
Visualization of Photon Generation
In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model which fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold.… Read More »Effects of Gravitational Field on Space-Time
Effects of Gravitational Field on Space-Time
The entropy of an object is a measure of the amount of energy which is unavailable to do work. •Entropy is also a measure of… Read More »Entropy Visualization Diagram
Entropy Visualization Diagram
According to Quantum Field theory, interactions between objects occur via space-filling which is known as “lines of force”. Magnetic field one of the best known… Read More »Visualization of Quantum Field Theory (QFT)
Visualization of Quantum Field Theory (QFT)
“In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called strings. String theory describes how these… Read More »String Theory Visualization
String Theory Visualization
Plasma is one of the four fundamental states of matter, and was first define by chemist Irving Langmuir in the 1920s. The Earth’s ionosphere is… Read More »Visualizing the Formation of Plasma State
Visualizing the Formation of Plasma State
With the beginning of modern physics, about a hundred years later, it was realized light could in fact show behavior characteristic of both waves and… Read More »Double Slit Experiment Visualization
Double Slit Experiment Visualization
Here is the some good points about atomic nucleus Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Atomic Nucleus.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 4 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atomic_nucleus. Accessed 19 Nov. 2020.… Read More »Some Points about Atomic nucleus
Some Points about Atomic nucleus
The Brief Introduction of the Standard Model Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Standard Model.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 15 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_Model. Accessed 19 Nov. 2020. [2] WikiImages.… Read More »The Higgs boson plays a unique role in the Standard Model
The Higgs boson plays a unique role in the Standard Model
Types of Quarks Types of Quarks Generation Name Symbol Antiparticle Spin Charge(e) 1 up u u 1⁄2 +2⁄3 down d d 1⁄2 −1⁄3 2… Read More »Types of Quarks(Subatomic Particles)
Types of Quarks(Subatomic Particles)
In particle physics, a lepton is an elementary particle of half-integer “1/2” spin that does not undergo strong interactions. Two main classes of leptons exist,… Read More »Brief Introduction of Lepton
Brief Introduction of Lepton
A quark is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. •Quarks own various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, mass, color charge,… Read More »Some Points about Quark
Some Points about Quark
“The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons.” Click on the “FREE PREVIEW” button… Read More »An Idea about Photoelectric Effect
An Idea about Photoelectric Effect
Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Photoelectric Effect.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 8 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photoelectric_effect. Accessed 16 Nov. 2020. [2] Khan Academy Organic Chemistry. “Photoelectric Effect | Electronic Structure of… Read More »Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect
Key Idea: When light radiation of a certain frequency incident on the surface of the metal plate, causing the emission of electron from that surface… Read More »Introduction to PhotoElectric Effect
Introduction to PhotoElectric Effect
In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called strings. •String theory… Read More »Brief Introduction of String Theory
Brief Introduction of String Theory
Key Idea: The Quantum particle is living in all possible states simultaneously until it is observed by an observer. During the observing period, the quantum… Read More »Quantum Superposition: Understanding
Quantum Superposition: Understanding
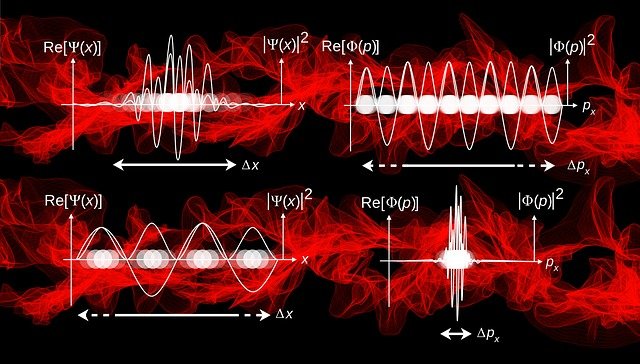
Key Idea: We can’t measure the exact position and momentum at the same time of any particle. Representation of the formula of the Heisenberg’s uncertainty… Read More »Introduction of Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
Introduction of Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
Photon energy is the energy carried by a single photon. The amount of energy is directly proportional to the photon’s electromagnetic frequency and thus, equivalently,… Read More »Understanding Photon’s Energy
Understanding Photon’s Energy
Quantum dots are semiconductor particles a hardly any nanometres in size, having optical and electronic properties differ from larger particles due to quantum mechanics. 😊When… Read More »Some Points about Quantum Dots