D orbitals contain two angular nodes. Nodal Plane contains the nucleus and has no electron density. Radial Node is the spherical surface region in which… Read More »D orbital
Quantum
In the year 1860, James Clerk Maxwell published equations that describe how charged particles give rise to electric and magnetic force per unit charge. Maxwell’s… Read More »What are Maxwell’s Equation
What are Maxwell’s Equation
In physics, a sinusoidal plane wave is a wave whose value varies as a sinusoidal function of time and of the distance from some fixed… Read More »What is Sinusoidal plane wave: Explanation and Diagram
What is Sinusoidal plane wave: Explanation and Diagram
The shape of p orbital is in a dumbbell shape. There is three p orbital that differs in orientation along a three-dimensional axis. P orbitals… Read More »P Orbital: Explanation and Diagram
P Orbital: Explanation and Diagram
The Principal quantum number (symbolized ‘n’) is one of the four quantum numbers assigned to each electron in an atom to describe the electron’s state.… Read More »What is Principal Quantum Number: Explanation and Diagram
What is Principal Quantum Number: Explanation and Diagram
Arthur Holly Compton was a physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his 1923 discovery of the Compton effect, which demonstrated… Read More »What is Compton Scattering: Explanation and Diagram
What is Compton Scattering: Explanation and Diagram
OLED stands for organic light-emitting diode. OLED is a light-emitting diode in which an emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compounds that emits… Read More »What is Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLED)
What is Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLED)
The spin quantum number describes the intrinsic angular momentum of an electron or other particle. Spin quantum number is proposed by George Uhlenbeck and Samuel… Read More »What is Spin quantum number of an Electron
What is Spin quantum number of an Electron
Tunnel diode was invented in August 1957 by Leo Esaki, Yuriko Kurose, and Takashi Suzuki. A tunnel diode is a type of semiconductor diode that… Read More »What is Tunnel Diode
What is Tunnel Diode
He is best known for his “Schrödinger ’s cat” thought experiment. In the year 1926, Schrödinger published the “Schrödinger equation”. Reference Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors.… Read More »What is Schrödinger Equation: Explanation and Diagram
What is Schrödinger Equation: Explanation and Diagram
Theodore Maiman invented the world’s first laser which was ruby laser on May 16, 1960. Ruby Laser is a solid-state laser that uses a synthetic… Read More »What is Ruby Laser: Explanation and Diagram
What is Ruby Laser: Explanation and Diagram
He earned a Ph.D. degree at the age of 23. He is best known for his “Schrödinger ’s cat” thought experiment. In 1926, Schrondinger published… Read More »Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger
Coulomb’s law is published in 1785 by the physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. COULOMBS’S LAW STATES THAT THE ELECTRIC FORCE BETWEEN THE TWO CHARGES IS DIRECTLY… Read More »Coulomb’s law
Coulomb’s law
Max Born shared the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1954 with Walther Bothe for his probabilistic interpretation of quantum mechanics. Reference Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors.… Read More »MAX BORN
MAX BORN
Newton’s law of universal gravitation is published in the year 1687. NEWTON’S LAW OF UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION STATES THAT EVERY OBJECT ATTRACTS EACH OTHER IN THE… Read More »Newton’s law of universal gravitation
Newton’s law of universal gravitation
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM STATES THAT IN A RIGHT-ANGLED TRIANGLE THE SQUARE OF HYPOTENUSE IS EQUAL TO THE SUM OF THE SQUARE OF THE OTHER TWO SIDES… Read More »Pythagoras Theorem
Pythagoras Theorem
It is also known as Einstein’s equation. Einstein field equation is published in 1915 in the form of the tensor equation. This equation describes gravity… Read More »Einstein Field Equation
Einstein Field Equation
Robert Millikan determined the magnitude of the electron’s charge by oil-drop experiment. He was awarded The Nobel Prize in Physics in the year 1923 for… Read More »Robert Andrews Millikan, Oil drop experiment
Robert Andrews Millikan, Oil drop experiment
Michael Faraday received little formal education, yet he is one of the Most Influential Scientists in History. Galvanometer: A galvanometer is a device is used… Read More »Faraday’s Law of Induction
Faraday’s Law of Induction
He was a physical chemist and a Dean of the College of Chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley. The terms photon is coined by… Read More »Gilbert N. Lewis
Gilbert N. Lewis
18th December is the Birthday of Physicist Sir. J.J. Thomson (18 December 1856 – 30 August 1940). Physicist and 1906 Nobel Prize Winner in Physics… Read More »On this Day in Physics
On this Day in Physics
Thermionic emission is the emission of electrons from the surface of the metal when high thermal energy is applied to it. This occurs when the… Read More »Thermionic emission
Thermionic emission
The concept of the pendulum is first to come around in the year 1602, by Galileo Galilei. The pendulum clock was invented by Christiaan Huygens… Read More »Pendulum System
Pendulum System
On December 14, 1900, Plack published his findings on Quantum theory in the German Physical Society. His study on black-body radiation shows that the radiation… Read More »Max Planck
Max Planck
Self-inductance is the property of the coil to resist change in the current flowing through it. When the current changes in the coil, an EMF… Read More »Self Inductance
Self Inductance
David Bohm made a significant contribution to physics, particularly quantum mechanics. He developed the theory of plasma, his book “Quantum Theory” is published in the… Read More »David Bohm
David Bohm
Newton’s cradle is based on the principle of conservation of energy and conservation of momentum. When a ball from one end is lifted in the… Read More »Newton’s Cradle
Newton’s Cradle
In the year 1925 two physicists, Samuel Goudsmit and George Uhlenbeck proposed the concept of Electron Spin. The spin quantum number (ms) describes the angular… Read More »Electron Spin
Electron Spin
Archimedes’ principle states that any object completely or partially submerged in a fluid at rest is acted upon by an upward force or buoyant force… Read More »Archimedes’ Principle
Archimedes’ Principle
Archimedes’ principle states that any object completely or partially submerged in a fluid at rest is acted upon by an upward force or buoyant force… Read More »Archimedes’ Principle
Archimedes’ Principle
If you placed the current carrying conductor in the magnetic field, then force acts on the conductor is perpendicular to both direction of magnetic field… Read More »Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
Boyle’s law states that the pressure exerted by the given mass of the gas is inversely proportional to the volume occupied by it if the… Read More »Boyle’s law
Boyle’s law
Reference Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. Julius von Mayer. Wikipedia. Published August 21, 2021. Accessed November 28, 2021. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Julius_von_Mayer. [2] Wikipedia Contributors. Mayer’s relation. Wikipedia. Published… Read More »Mayer’s Relation for an Ideal gas.
Mayer’s Relation for an Ideal gas.
Charles’s law explains how gas expand when heated. At, fixed pressure volume and temperature of a gas is directly proportional to each other. V1/T1 =… Read More »Jacques Charles
Jacques Charles
Raman Effect: When the light is deflected through the molecule, it scatters with the change in wavelength and frequency. C.V. Raman received Nobel Prize in… Read More »C.V. Raman
C.V. Raman
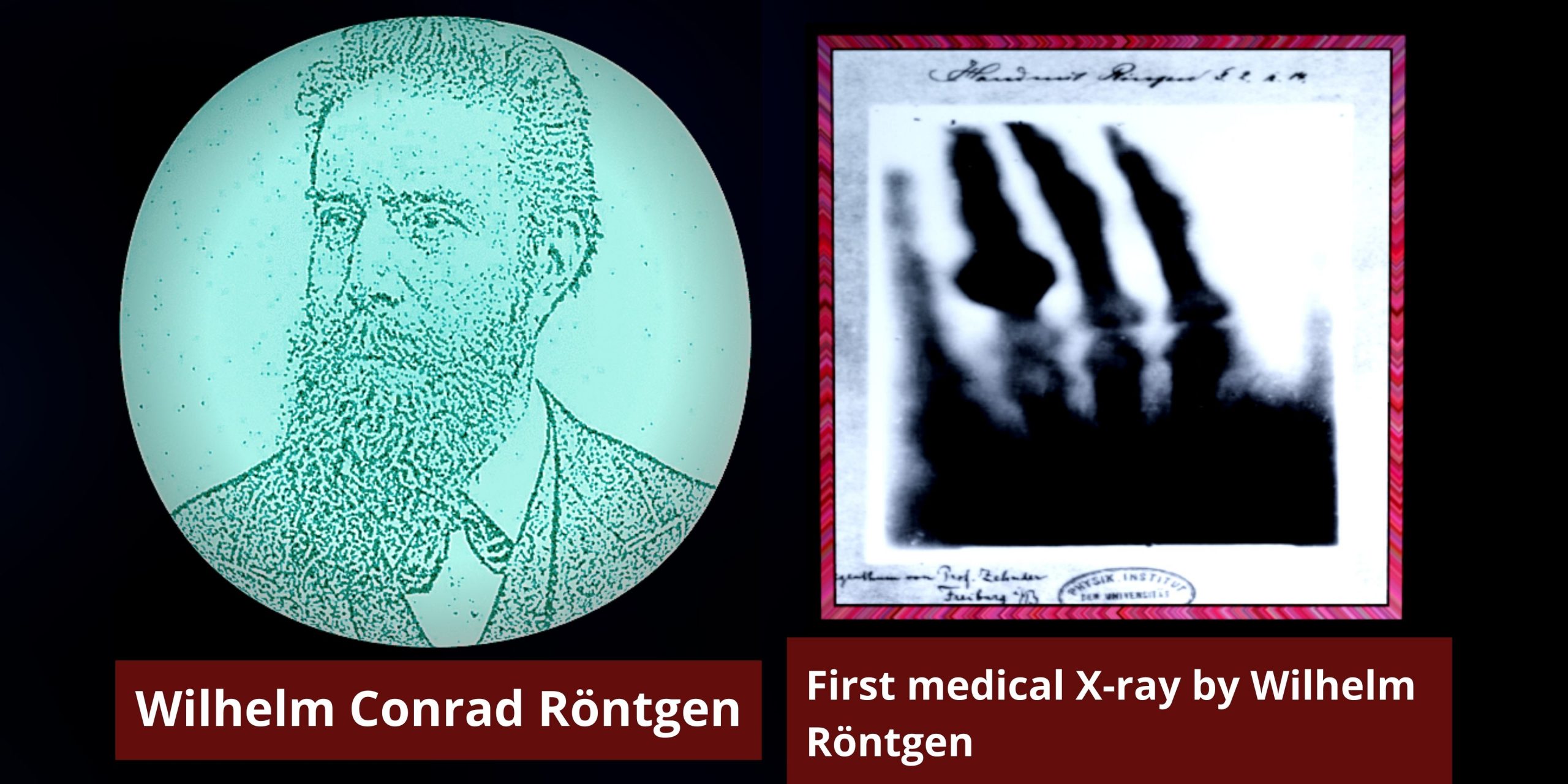
On this Day in Physics (Discovery of X-Ray) In 8th November 1895 German Physicist Wilhelm Röntgen discovered X-rays. By this achievement, he earned the First… Read More »On this Day in Physics (Discovery of X-Ray)
On this Day in Physics (Discovery of X-Ray)
Most Notable achievement: Classical theory of Electromagnetic Radiation. He calculated that the speed of propagation of the electromagnetic wave is approximately equal to the speed… Read More »James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell
He is the inventor of Solenoid. The S.I. unit of electric current is Ampere (A) is named after him. Reference Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “André-Marie… Read More »André-Marie Ampère
André-Marie Ampère
The uncertainty principle states that the position and momentum of a particle cannot be simultaneously measured with absolute precision.
HEISENBERG’S UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE
He is most commonly recognized for the Hubble Space Telescope, which is named in his honor. Reference Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Edwin Hubble.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation,… Read More »Edwin Hubble: The Person who revolutionized astronomy.
Edwin Hubble: The Person who revolutionized astronomy.
The nucleus of an atom is the small dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. Reference Source: [1] Wikipedia… Read More »Discovery of an Atomic Nucleus
Discovery of an Atomic Nucleus
Jupiter has a mass more than two and a half times that of the combined mass of all other planets in the solar system. As… Read More »Jupiter’s Fact
Jupiter’s Fact
His most notable work is on the nature of chemical bonding.
Linus Pauling
“His experiments about energy transformations were first published in 1843.” Reference Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “James Prescott Joule.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 19 Sept. 2021, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_Prescott_Joule. Accessed… Read More »James Prescott Joule
James Prescott Joule
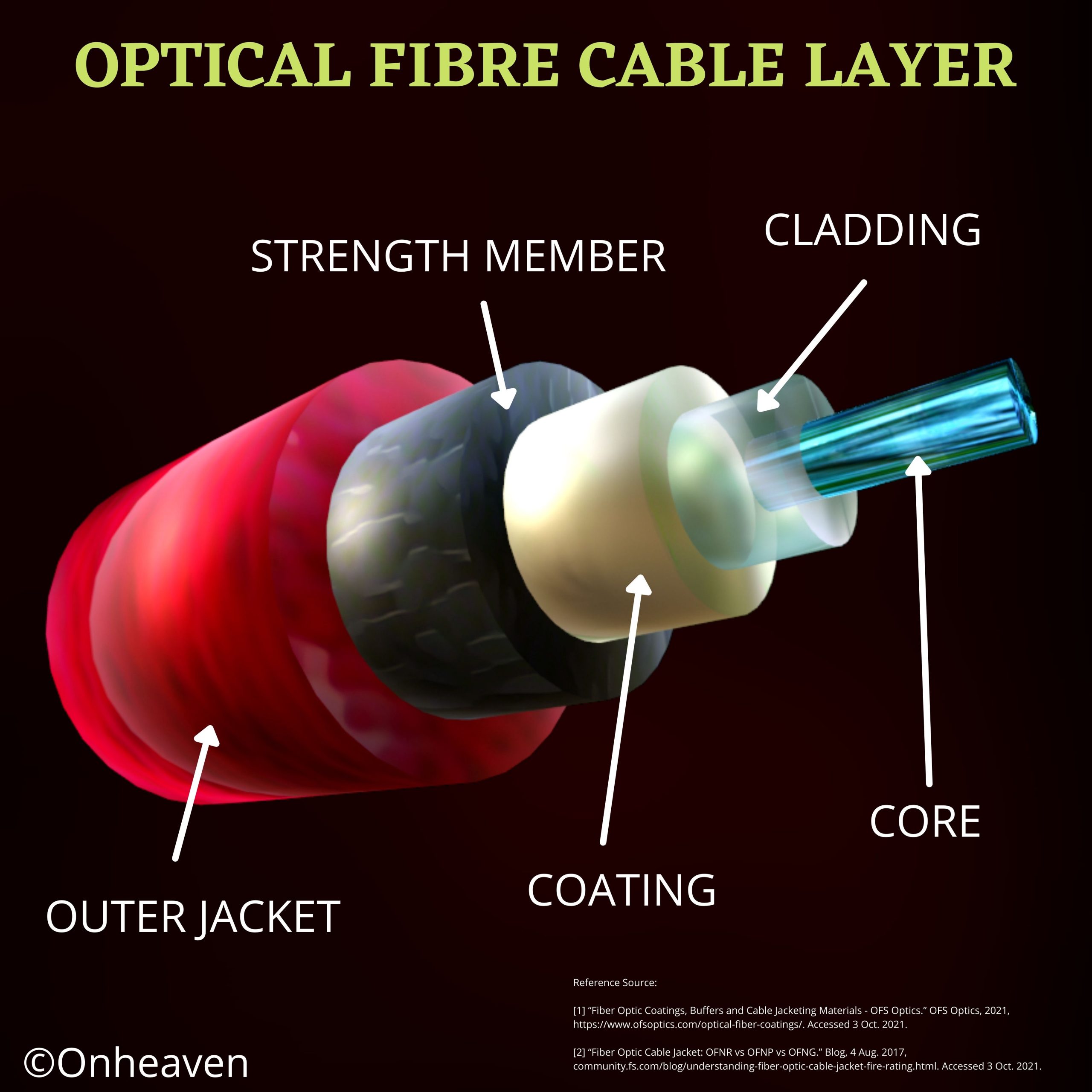
An optical fiber is a flexible fiber, it is generally used for long-distance and high-performance data networking. Optical Fiber is used most often as a… Read More »OPTICAL FIBRE CABLE LAYER
OPTICAL FIBRE CABLE LAYER
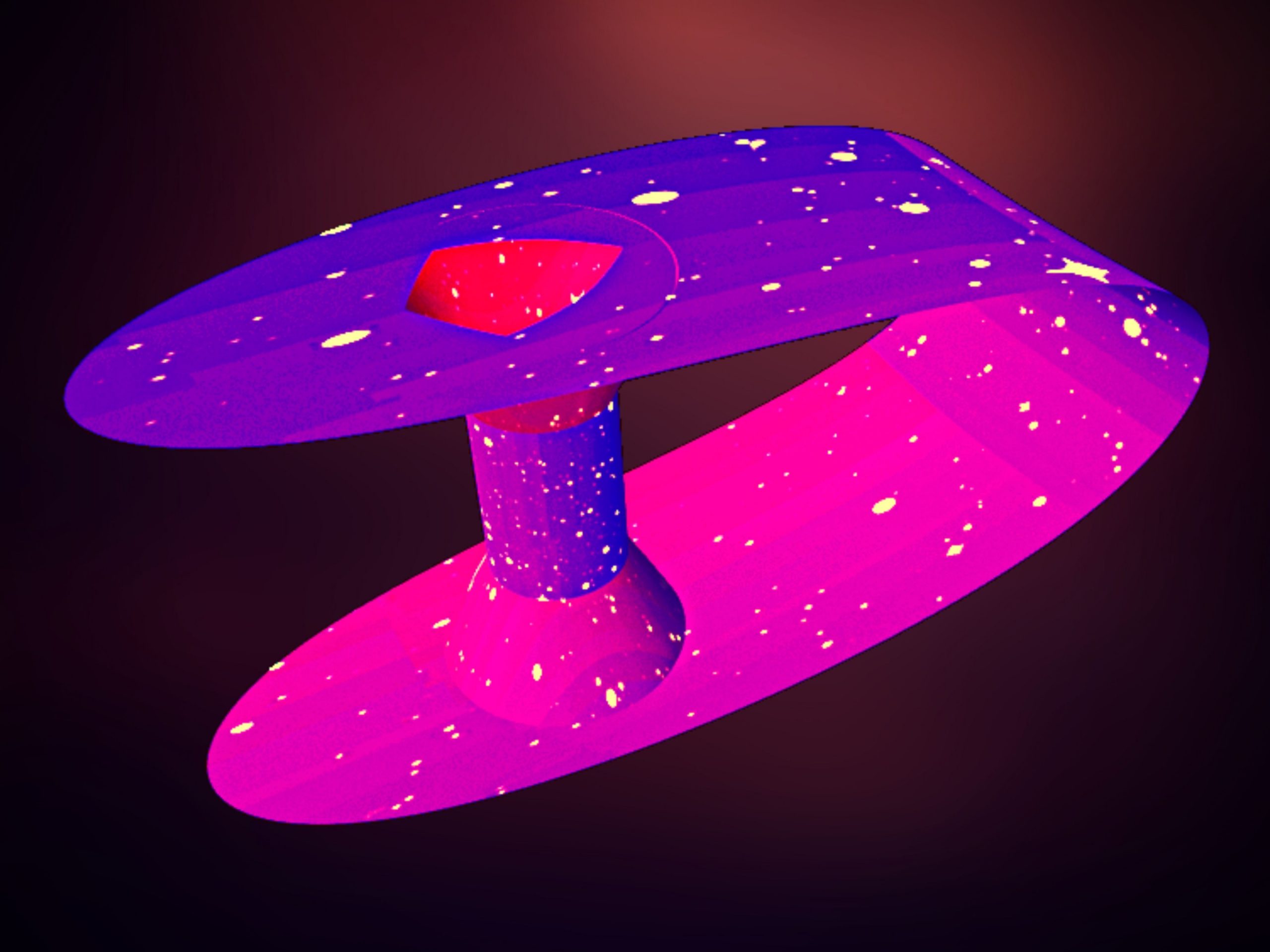
Wormhole (or Einstein–Rosen bridge or Einstein–Rosen wormhole) can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in space-time. First of all, wormhole… Read More »Wormhole (or Einstein–Rosen bridge or Einstein–Rosen wormhole) can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime.
Wormhole (or Einstein–Rosen bridge or Einstein–Rosen wormhole) can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime.
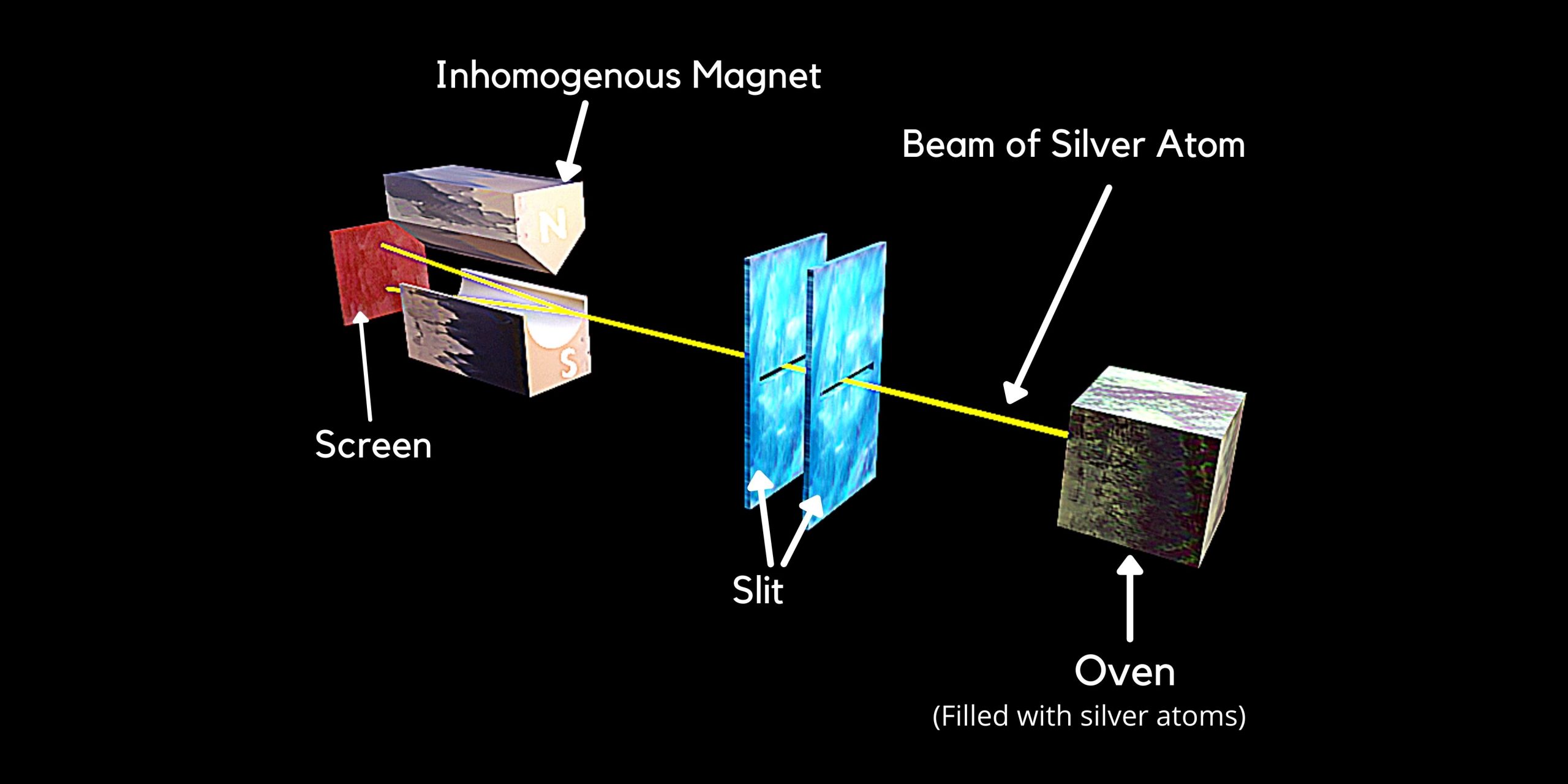
Stern–Gerlach experiment demonstrated that the spatial orientation of angular momentum is quantized. Illustration Diagram of Stern–Gerlach Experiment Reference Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Stern–Gerlach Experiment.” Wikipedia,… Read More »Stern–Gerlach experiment demonstrated that the spatial orientation of angular momentum is quantized.
Stern–Gerlach experiment demonstrated that the spatial orientation of angular momentum is quantized.
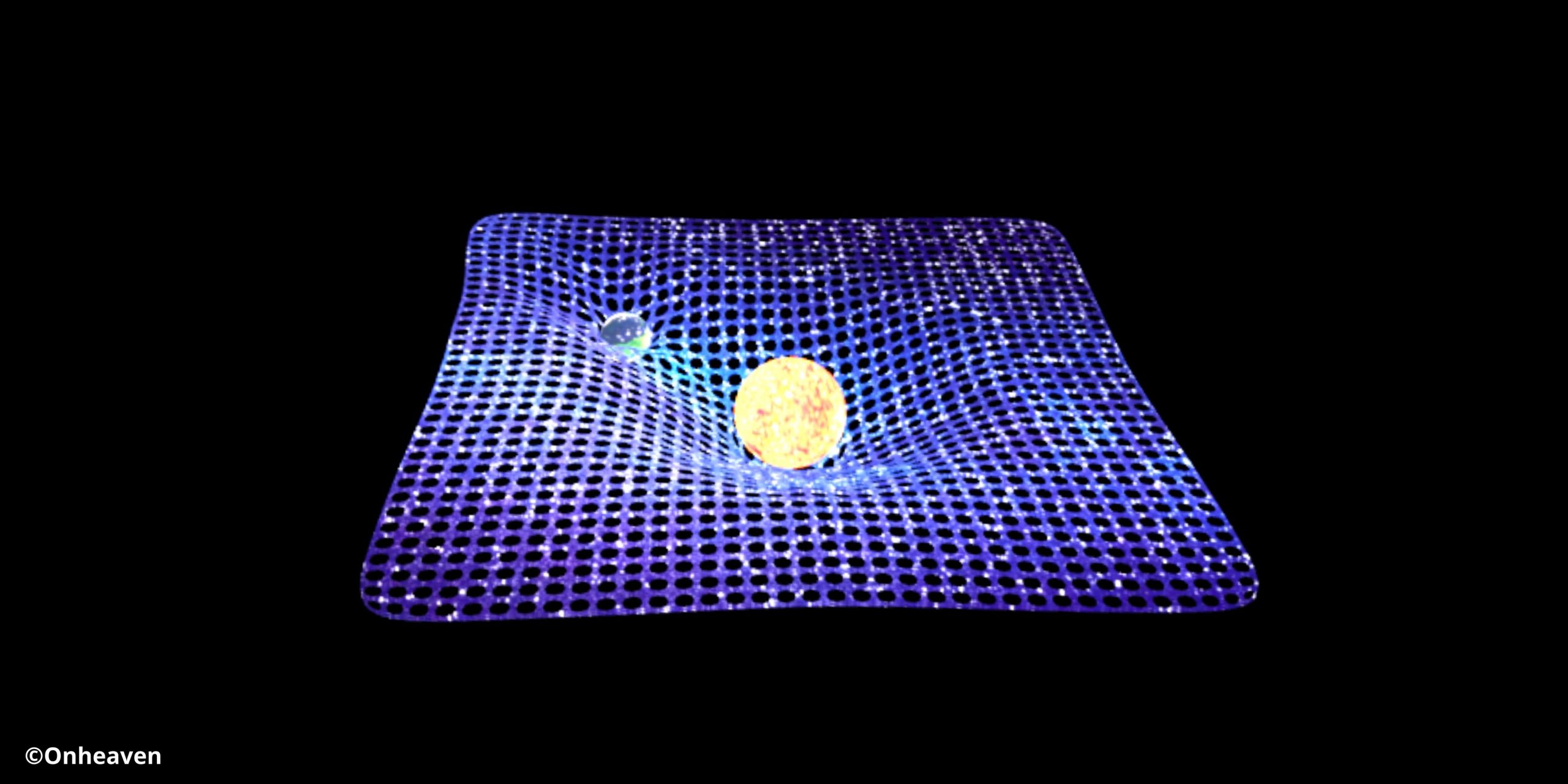
The fabric of space-time is a conceptual model combining the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time. Here is the Illustration Diagram… Read More »The fabric of space-time is a conceptual model combining the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time.