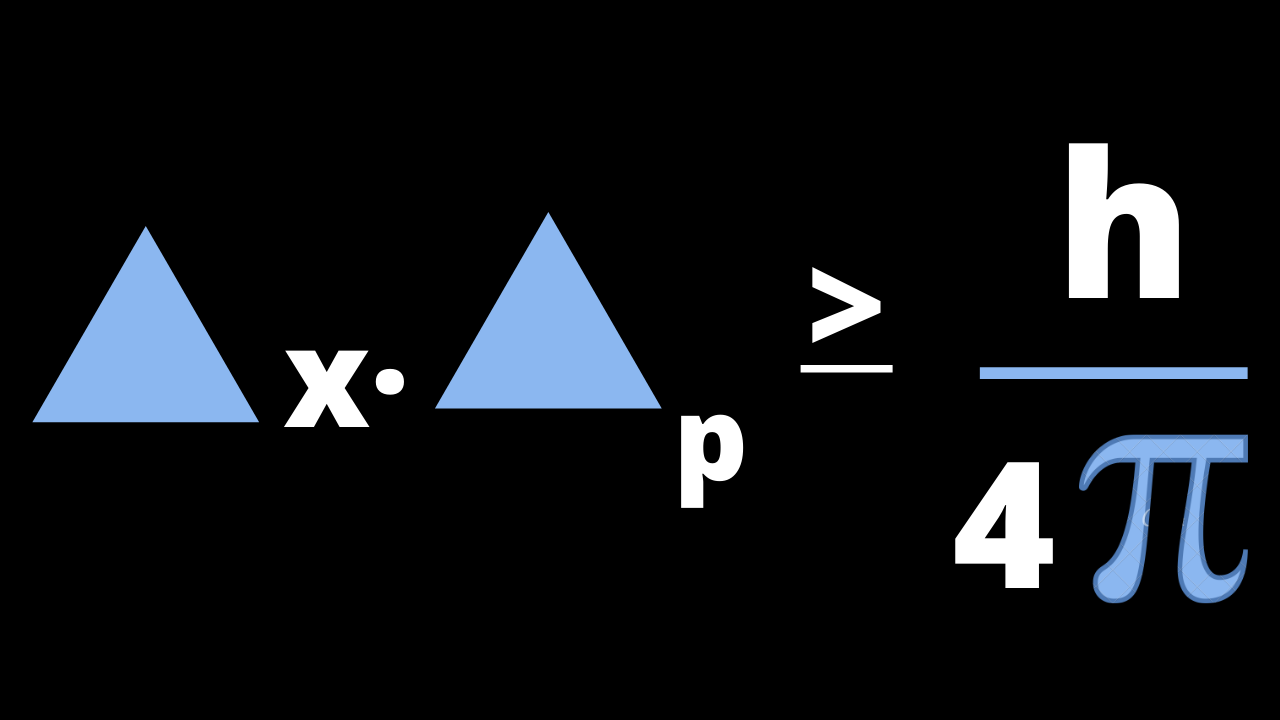“In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called strings. String theory describes how these… Read More »String Theory Visualization
Physics
Plasma is one of the four fundamental states of matter, and was first define by chemist Irving Langmuir in the 1920s. The Earth’s ionosphere is… Read More »Visualizing the Formation of Plasma State
Visualizing the Formation of Plasma State
With the beginning of modern physics, about a hundred years later, it was realized light could in fact show behavior characteristic of both waves and… Read More »Double Slit Experiment Visualization
Double Slit Experiment Visualization
Here is the some good points about atomic nucleus Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Atomic Nucleus.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 4 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atomic_nucleus. Accessed 19 Nov. 2020.… Read More »Some Points about Atomic nucleus
Some Points about Atomic nucleus
The Brief Introduction of the Standard Model Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Standard Model.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 15 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_Model. Accessed 19 Nov. 2020. [2] WikiImages.… Read More »The Higgs boson plays a unique role in the Standard Model
The Higgs boson plays a unique role in the Standard Model
Types of Quarks Types of Quarks Generation Name Symbol Antiparticle Spin Charge(e) 1 up u u 1⁄2 +2⁄3 down d d 1⁄2 −1⁄3 2… Read More »Types of Quarks(Subatomic Particles)
Types of Quarks(Subatomic Particles)
In particle physics, a lepton is an elementary particle of half-integer “1/2” spin that does not undergo strong interactions. Two main classes of leptons exist,… Read More »Brief Introduction of Lepton
Brief Introduction of Lepton
A quark is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. •Quarks own various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, mass, color charge,… Read More »Some Points about Quark
Some Points about Quark
“The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons.” Click on the “FREE PREVIEW” button… Read More »An Idea about Photoelectric Effect
An Idea about Photoelectric Effect
Source: [1] Wikipedia Contributors. “Photoelectric Effect.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 8 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photoelectric_effect. Accessed 16 Nov. 2020. [2] Khan Academy Organic Chemistry. “Photoelectric Effect | Electronic Structure of… Read More »Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect
Key Idea: When light radiation of a certain frequency incident on the surface of the metal plate, causing the emission of electron from that surface… Read More »Introduction to PhotoElectric Effect
Introduction to PhotoElectric Effect
In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called strings. •String theory… Read More »Brief Introduction of String Theory
Brief Introduction of String Theory
Key Idea: The Quantum particle is living in all possible states simultaneously until it is observed by an observer. During the observing period, the quantum… Read More »Quantum Superposition: Understanding
Quantum Superposition: Understanding
Key Idea: We can’t measure the exact position and momentum at the same time of any particle. Representation of the formula of the Heisenberg’s uncertainty… Read More »Introduction of Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
Introduction of Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
According to the Relative Mass equation, in the special theory of relativity, “ the mass of any object is increase with the increase in speed… Read More »Why we can’t go faster than the speed of Light
Why we can’t go faster than the speed of Light
The main Idea behind the holographic principle is that the whole universe is Hologram. This idea is first introduced by the Stephen Hawking, ‘ As… Read More »Understanding the Holographic Principle
Understanding the Holographic Principle
Key Idea: That Gravitational Field effects Time. General relativity also predicts novel effects of gravity, such as gravitational waves, gravitational lensing and an effect of… Read More »An Idea about General Relativity
An Idea about General Relativity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. 😊It… Read More »Some Points about Superconductivity
Some Points about Superconductivity
According to the spin-statistics theorem in relativistic quantum field theory, particles with integer spin are bosons, while particles with half-integer spin are fermions. 😊Fermions are… Read More »Some Points about Fermions
Some Points about Fermions
The weak interaction participates in nuclear fission, and the theory describing it in terms of both its behavior and effects is sometimes called quantum flavourdynamics.… Read More »Understanding Weak Interaction
Understanding Weak Interaction
The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. 😊The neutrino… Read More »Some Points about Neutrinos
Some Points about Neutrinos
The positron has an electric charge of +1 e, a spin of 1/2 , and has the same mass as an electron. 😊 The positron… Read More »Some Points about Positron
Some Points about Positron
The topic of quantum entanglement is at the heart of the disparity between classical and quantum physics: entanglement is a primary feature of quantum mechanics… Read More »Some Points about Quantum Entanglement
Some Points about Quantum Entanglement
The old quantum theory is a collection of results from the years 1900–1925 which predate modern quantum mechanics. The theory was never complete or self-consistent,… Read More »Some Points about Old Quantum Theory
Some Points about Old Quantum Theory
Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: they can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. 😊Electrons… Read More »Some Points about Electron
Some Points about Electron
Quantum states cannot be written as a mixture of other states are called pure quantum states, while all other states are called mixed quantum states.… Read More »Brief Introduction of Quantum State
Brief Introduction of Quantum State
According to the superposition principle of quantum mechanics, wave functions can be added together and multiplied by complex numbers to form new wave functions and… Read More »Short Notes about Wave Function
Short Notes about Wave Function
Quantum tunneling or tunneling is the quantum mechanical phenomenon where a wavefunction can propagate through a potential barrier. 😊Quantum tunneling is not predicted by the… Read More »Some Points about Quantum Tunneling
Some Points about Quantum Tunneling
The application of quantum mechanics to chemistry is familiar as quantum chemistry. 😊Quantum mechanics is also critically important in support of understanding how individual atoms… Read More »Some Applications of Quantum Mechanics
Some Applications of Quantum Mechanics
Throughout the nineteenth century, some scientists had cautioned the evidence in support of atoms was indirect, and therefore atoms might not actually be real, only… Read More »Some Points about historical models of an Atomic Theory
Some Points about historical models of an Atomic Theory
An atom is composed of a positively-charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively-charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. 😊Protons and neutrons are… Read More »Brief Introduction to Atomic Nucleus
Brief Introduction to Atomic Nucleus
[A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing—no particles or even electromagnetic radiation such as light—can escape from it.] [A black hole occurs when additional than a certain amount… Read More »Brief Introduction to Hawking Radiation
Brief Introduction to Hawking Radiation
In vacuum, when free electrons are present, a sufficiently slow proton may pick up a single free electron, becoming a neutral hydrogen atom, which is… Read More »Some Concepts about Proton
Some Concepts about Proton
Assuming the lambda-CDM model of cosmology is correct, the best current measurements indicate dark energy contributes 68% of the total energy in the present-day observable… Read More »Introduction to Dark Energy
Introduction to Dark Energy
The idea of a subatomic particle was refined when experiments showed light could behave like a stream of particles as well as exhibiting wave-like properties.… Read More »Brief Introduction of Sub-Atomic Particle
Brief Introduction of Sub-Atomic Particle
Time is usual to define other quantities – such as velocity – so defining time in terms of such quantities would result in circularity of… Read More »An Idea about TIME
An Idea about TIME
Particle physics is a branch of physics studies the nature of the particles constitute matter and radiation. High energy physics compared to low energy physics… Read More »The Key Points about Particle Physics
The Key Points about Particle Physics
If there are other stars orbiting a black hole, their orbits can be usual to determine the black hole’s mass and location. 😊By absorbing other… Read More »The key points about Black Hole
The key points about Black Hole
It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Definition: Quantum mechanics is a… Read More »Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a theory useful in support of the learning of the motion of non-quantum mechanical low-energy particles in weak gravitational fields. 😊In the… Read More »Some keys about Classical Mechanics
Some keys about Classical Mechanics
Largest usually classical physics refers to pre-1900 physics while modern physics refers to post-1900 physics which incorporates elements of quantum mechanics and relativity. 😊In the… Read More »The key points about Classical Physics
The key points about Classical Physics
😊The quantum field theory of the strong nuclear force is called quantum chromodynamics and describes the interactions of subnuclear particles such as quarks and gluons.… Read More »13 things you need to know about Quantum Mechanics
13 things you need to know about Quantum Mechanics
- « Previous
- 1
- …
- 6
- 7
- 8