Compton scattering is the scattering of a photon after interaction with an electron. Compton effect is discovered in the year 1923 by scientist Arthur Holly… Read More »Compton Scattering: Definition and Diagram
Physics
Total internal reflection is an optical phenomenon in which a light ray is completely reflected under certain conditions. Total internal reflection is discovered in the… Read More »What is Total Internal Reflection: Explanation and Diagram
What is Total Internal Reflection: Explanation and Diagram
Let us consider two charges ‘+q’ and ‘-q’ which are separated from each other with a distance ‘2a’ are placed in a uniform electric field… Read More »Torque on an electric dipole in a uniform electric field:
Torque on an electric dipole in a uniform electric field:
Hooke’s law states that the length of extension or compression of spring done by the force is directly proportional to it. This law is also… Read More »What is Hooke’s law
What is Hooke’s law
This post on Muon Decay is only for the purpose of a basic understanding of Muon Decay. “The muon is an elementary particle similar to… Read More »What is Muon Decay
What is Muon Decay
Seebeck effect is a phenomenon in which a temperature difference between two different electrical conductors or semiconductors produces the electromotive force (emf) between them between… Read More »What is Seebeck Effect: Explanation
What is Seebeck Effect: Explanation
The Glass Cartridge fuse is the safety device that is used to protect electrical systems against overload, overcurrent, and short circuits. The main function of… Read More »What is Glass Cartridge Fuse: Explanation and Application
What is Glass Cartridge Fuse: Explanation and Application
Electrical power is defined as the rate at which electrical energy is consumed in an electrical circuit. The SI unit of electrical power is watt(W).… Read More »What is Electric Power: Definition and Diagram
What is Electric Power: Definition and Diagram
Joule heating is the process in which electric current passes through a conductor and produces heat. Joule’s law of heating was first published in the… Read More »What is Joule Heating
What is Joule Heating
Windmill is a machine that converts wind energy into mechanical energy then mechanical energy into electrical energy. Rotor blades mounted with rotor. Wind rotates the… Read More »What is Windmill
What is Windmill
Armand Hippolyte Louis Fizeau: Hippolyte Fizeau measures the speed of light in the year 1849, in his Fizeau Experiment. This post is just for an… Read More »Measurement Speed of Light
Measurement Speed of Light
In linear polarization of light, light is transformed from unpolarized light into linear polarized light. The term “Linear Polarization” was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in… Read More »Linear Polarization of Light: Explanation and Diagram
Linear Polarization of Light: Explanation and Diagram
When two or more resistors connected end to end in a single branch such that the same current flows through the resistors, then resistors are… Read More »Resistor in Series: Explanation through Visuals
Resistor in Series: Explanation through Visuals
Avogadro’s law was hypothesized in the year 1811, by the Amedeo Avogadro. Avagadro hypothesized that, at equal volume of different gasses at the same temperature… Read More »What is Avogadro’s law: Explanation
What is Avogadro’s law: Explanation
Drift velocity of an electron per unit applied electric field is called electron mobility. Mobility of an electron (μ) = Vd/E Where drift velocity of… Read More »What is mobility of an electron: Explanation
What is mobility of an electron: Explanation
The drift velocity of free electrons is defined as the average velocity by which the free electrons are drifted towards the positive end of the… Read More »What is Drift Velocity: Explanation
What is Drift Velocity: Explanation
Electrical conductivity is the ability to conduct electric current. The electrical conductivity of different materials is different. Electrical conductivity (σ ) = 1/ρ = l/RA.… Read More »What is Electrical Conductivity
What is Electrical Conductivity
Current density or electric current density is defined as the amount of electric current that passes through the unit cross-sectional area of the conductor. Current… Read More »What is Current Density: Definition and Diagram
What is Current Density: Definition and Diagram
The rate of flow to charge through any conductor is called electric current. Electric Current, I = Q/t. I = Electric Current. Q = Charge.… Read More »What is Electric Current: Definition and Diagram
What is Electric Current: Definition and Diagram
Meter Bridge is the simplest practical application of Wheatstone Bridge. Construction: AC is the wire which is made up of manganin or constantan and has… Read More »What is Meter Bridge: Construction Diagram
What is Meter Bridge: Construction Diagram
A potentiometer is a device that is used to measure potential differences accurately. Principle: The working principle is that when a current flows through a… Read More »Potentiometer
Potentiometer
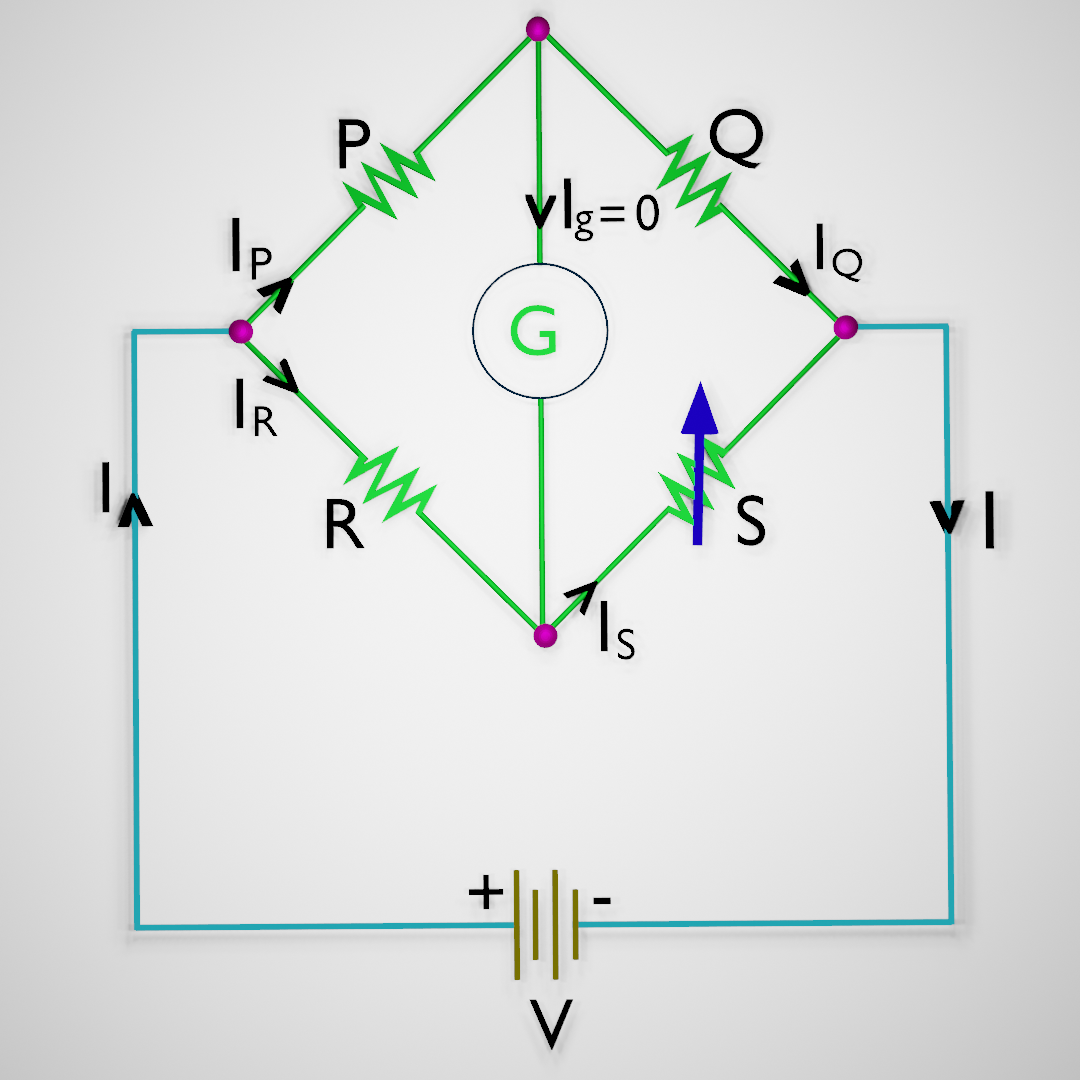
The Wheatstone bridge was invented by Samuel Hunter Christie in the year 1833 and was improved and popularized by Sir Charles Wheatstone in the year… Read More »What is Wheatstone Bridge: Explanation and Construction
What is Wheatstone Bridge: Explanation and Construction
Let us suppose capacitors of capacitance C1 and C2 are connected in parallel and voltage ‘V’ is applied across it. The net charge flowing through… Read More »Capacitor connected in parallel
Capacitor connected in parallel
Let us suppose, capacitors of capacitance C1 and C2 are connected in series and voltage ‘V’ is applied across it. The voltage across capacitor C1… Read More »Capacitors connected in Series
Capacitors connected in Series
This is the illustration diagram for the calculation of the capacitance of a spherical conductor. Let us consider a spherical conductor of radius R, which… Read More »Capacitance of a spherical conductor
Capacitance of a spherical conductor
Let us consider an infinite charged plane sheet with the surface charge density σ. Surface charge density, σ = charge/Area = q/A. σ is the… Read More »Electric field due to an infinite plane sheet of charge
Electric field due to an infinite plane sheet of charge
Electric field lines are the way to visualization of electric fields. Properties of electric field lines. • Electric field lines never intersect each other. •… Read More »What is Electric field lines: Explanation, Properties, Diagram
What is Electric field lines: Explanation, Properties, Diagram
This is the illustration diagram for the calculation of electric field due to line charge at point P. Let us consider a charge is uniformly… Read More »Electric field due to line charge
Electric field due to line charge
When a positive and negative charge is separated by some fixed distance then it is called an electric dipole. Electric Dipole moment is defined as… Read More »What is Electric Dipole Moment
What is Electric Dipole Moment
This is the illustration diagram for the calculation of electric field due to circular loop at point P.
Electric field due to a circular loop of charge.
Oil drop experiment: “The oil drop experiment was first performed by Robert A. Millikan and Harvey Fletcher in the year 1909 in order to measure… Read More »What is Oil drop experiment: Explanation and Diagram
What is Oil drop experiment: Explanation and Diagram
A Direct Current (DC) motor is an electrical machine that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy. The electrical energy of direct current is… Read More »What is DC Motor: Definition and Diagram
What is DC Motor: Definition and Diagram
Extrinsic semiconductors are impure semiconductors that are doped with impurities in order to enhance their conductivity. Depending on the type of impurities extrinsic semiconductors is… Read More »What is Extrinsic Semiconductors: Explanation and Diagram
What is Extrinsic Semiconductors: Explanation and Diagram
Intrinsic semiconductors are pure semiconductors that are impurity-free. The most common intrinsic semiconductors are Silicon (Si) and Germanium (Ge). At room temperature, intrinsic semiconductor shows… Read More »What is Intrinsic semiconductors
What is Intrinsic semiconductors
Kirchhoff’s Current Law: The algebraic sum of all incoming current and outgoing current in a node is equal to zero. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law: The algebraic… Read More »What is Kirchhoff’s Law: Explanation and Diagram
What is Kirchhoff’s Law: Explanation and Diagram
A capacitor is an electric device that works as a charge storing device. It has two terminals. It stores the charge in the form of… Read More »What is Capacitor:Explanation
What is Capacitor:Explanation
Ideal gas equation gives expression of simultaneous effect on gas, according to its pressure, volume, temperature, and the amount of gas. The term ideal gas… Read More »What is Ideal Gas Equation: Explanation
What is Ideal Gas Equation: Explanation
The concept of zero-point energy was developed by Max Planck in the year 1911. According to quantum physics, even in vacuum space, there is some… Read More »What is Zero-point energy: Explanation
What is Zero-point energy: Explanation
Rydberg calculates the wavelength of a spectrum line in the hydrogen emission spectrum. Rydberg formula was first stated in 1888 by Physicist Johannes Rydberg. Rydberg’s… Read More »Rydberg formula for the hydrogen spectrum
Rydberg formula for the hydrogen spectrum
An electron in an atom revolves around the nucleus in those orbits in which the angular momentum of revolution of an electron is an integral… Read More »What is Bohr Second Postulate: Explanation
What is Bohr Second Postulate: Explanation
“The force that acts on an object moving in a circular path and directed towards the center, around which the object is moving.” The magnitude… Read More »What is Centripetal Force: Explanation and Diagram
What is Centripetal Force: Explanation and Diagram
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM STATES THAT IN A RIGHT-ANGLED TRIANGLE THE SQUARE OF HYPOTENUSE IS EQUAL TO THE SUM OF THE SQUARE OF THE OTHER TWO SIDES… Read More »What is Pythagoras Theorem
What is Pythagoras Theorem
Conservative Force In conservative force, the work done to move an object from one point to another is does not depend on the path. E.g.,… Read More »What is Conservative Force and Non-Conservative Force
What is Conservative Force and Non-Conservative Force
“No two-electron in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers.” The Nobel Prize in Physics in the year 1945, was awarded to Wolfgang… Read More »What is Pauli Exclusion Principle
What is Pauli Exclusion Principle
Ideal gas equation gives expression of simultaneous effect on gas, according to its pressure, volume, temperature, and the amount of gas. The term ideal gas… Read More »What is Ideal Gas Equation: Explanation
What is Ideal Gas Equation: Explanation
Magnetic levitation is a process through which a magnet is suspended in the air with the help of a magnetic field. In magnetic levitation, magnetic… Read More »What is Magnetic Levitation
What is Magnetic Levitation
The Phenomenon of self-inductance was first recognized by the Scientist Joseph Henry. The unit of inductance is the henry (H). Self-inductance is the property of… Read More »What is Self Inductance