A potentiometer is a device that is used to measure potential differences accurately.
Principle:
The working principle is that when a current flows through a wire which has the area and composition of a uniform cross-section.
And the potential difference across that wore is directly proportional to the length of that wire.
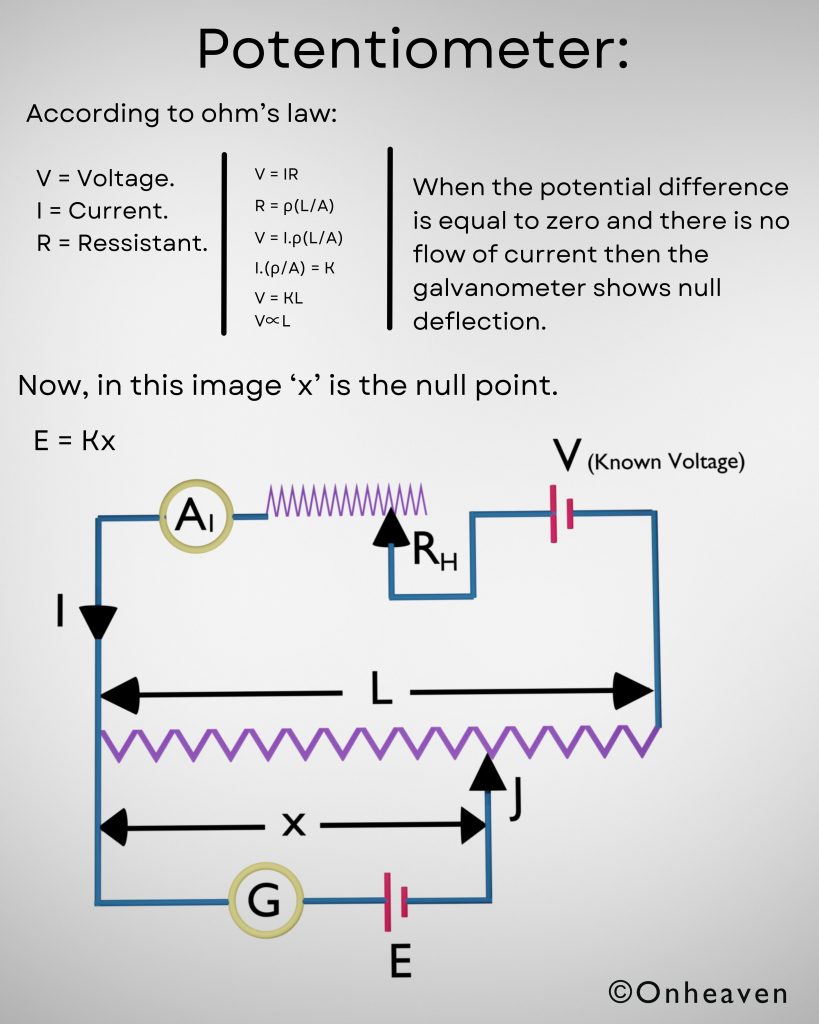
As according to ohm’s law:
V = IR
V = Voltage.
I = Current.
R = Ressistant.
R = ρ(L/A)
V = I ρ(L/A).
ρ(L/A) = K.
V = KL
V∝L
When the potential difference is equal to zero and there is no flow of current then the galvanometer shows null deflection.
Now, in this image ‘x’ is the null point.
E = Kx
Determination of emf of a cell using potentiometer:
In the case of L1 is the length of the null point for the first cell of EMF ‘E1’ and L2 is the length of the null point for the second cell EMF ‘E2’.
E = KL
E1/E2 = L1/L2
Reference Source:
[1] Potentiometer – Definition, Working Principle, Types – GeeksforGeeks. GeeksforGeeks. Published September 24, 2021. Accessed March 3, 2022. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/potentiometer-definition-working-principle-types/
[2] Potentiometer Working Principle With Their Types And Applications. BYJUS. Published February 14, 2019. Accessed March 3, 2022. https://byjus.com/physics/potentiometer-working/
[3] Bhatnagar, Nipendra. Physics handbook. Meerut, Arihant.
Also, our ebook on Quantum Physics, “Quantum Physics for beginners”, Available here: https://payhip.com/b/Y5OFx