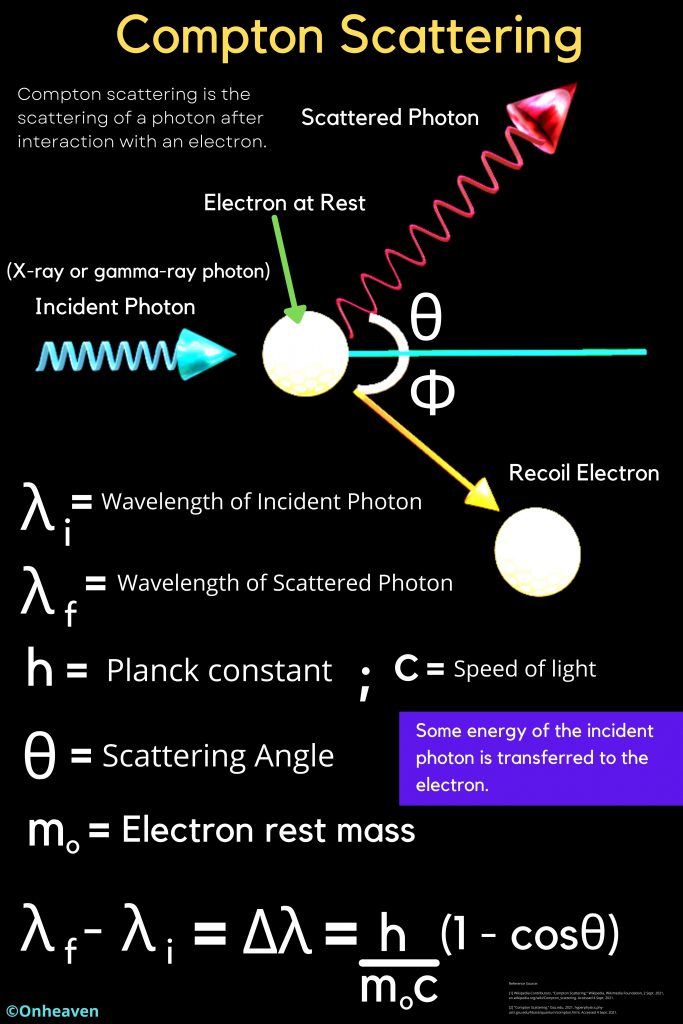
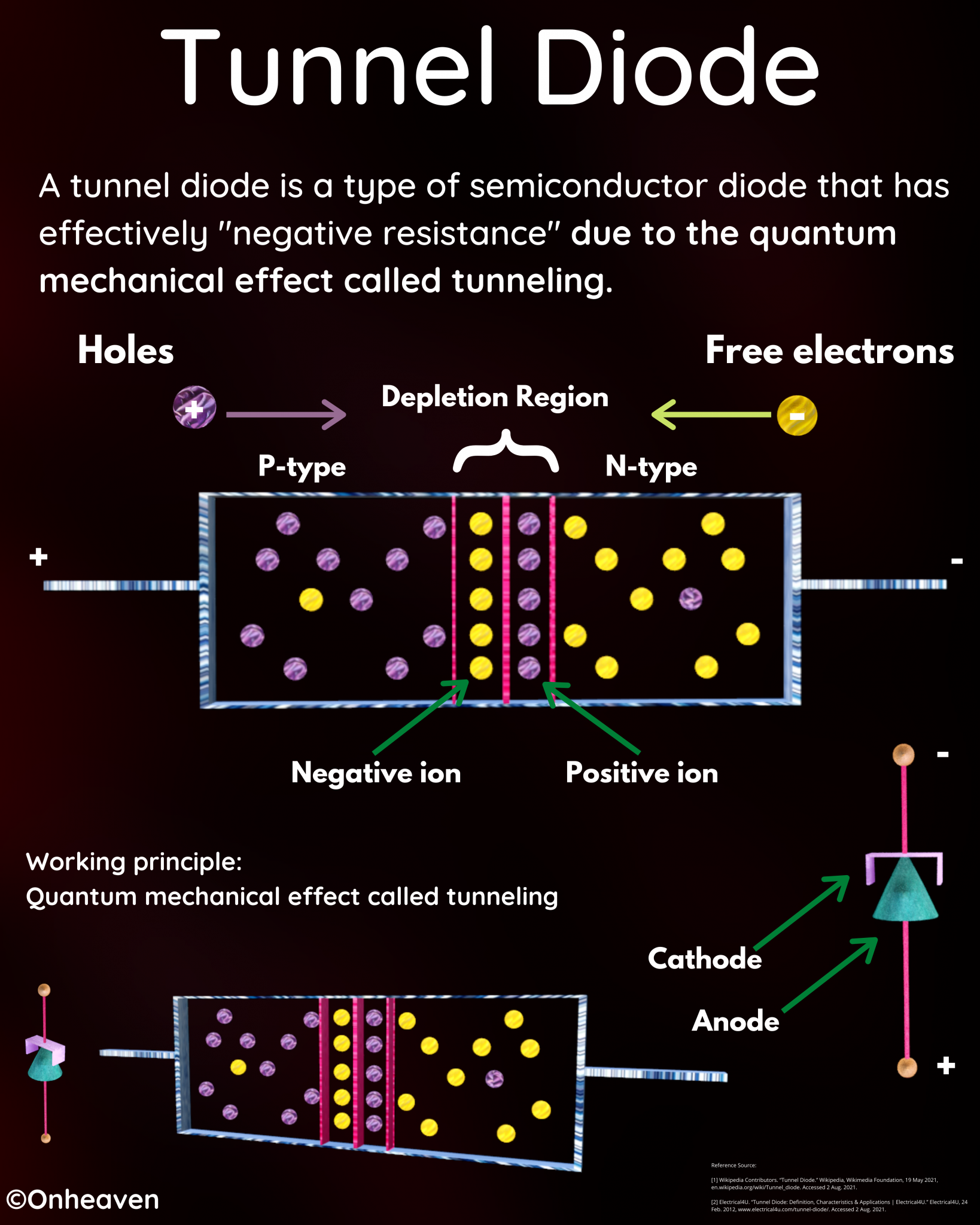
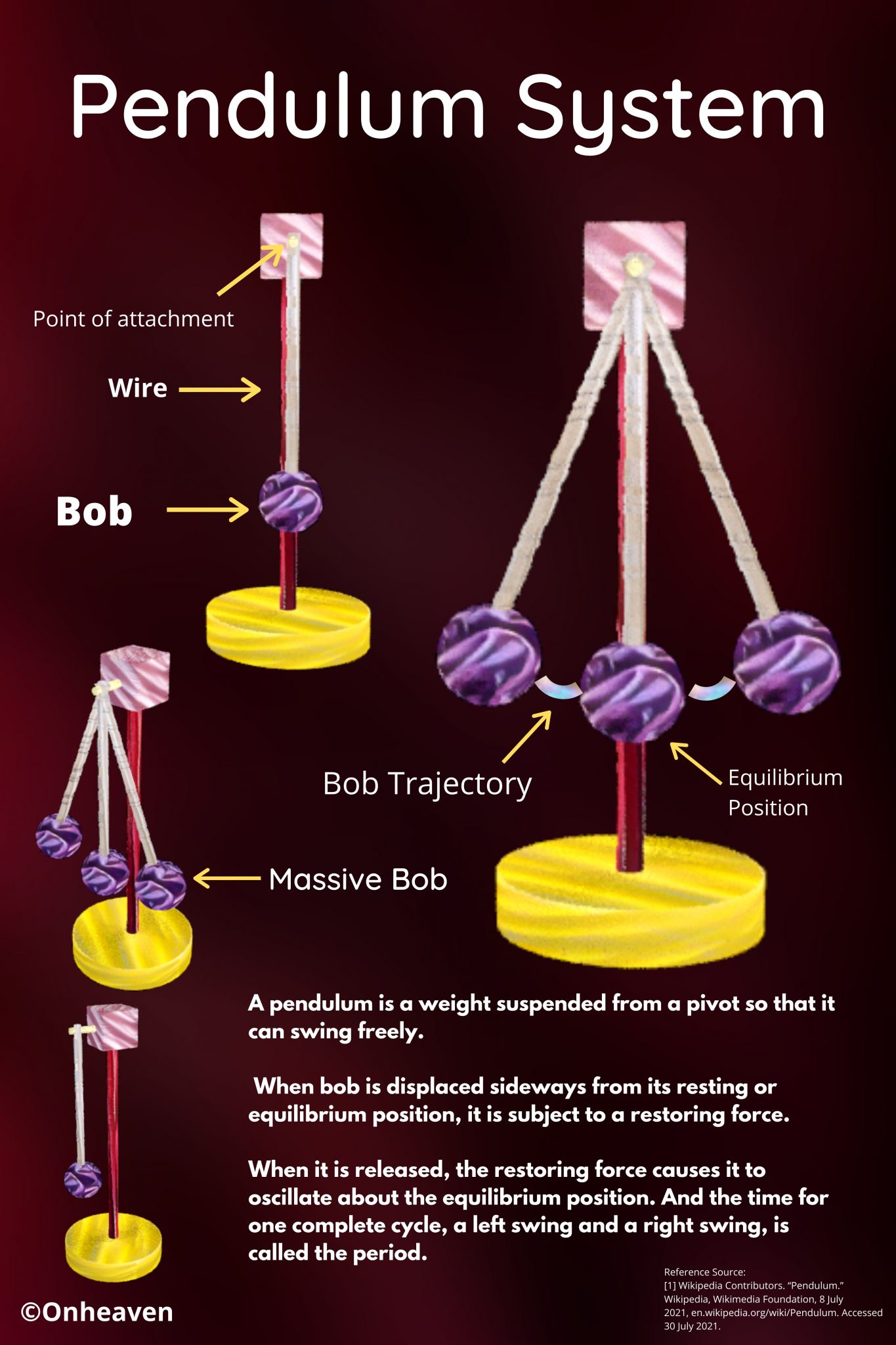
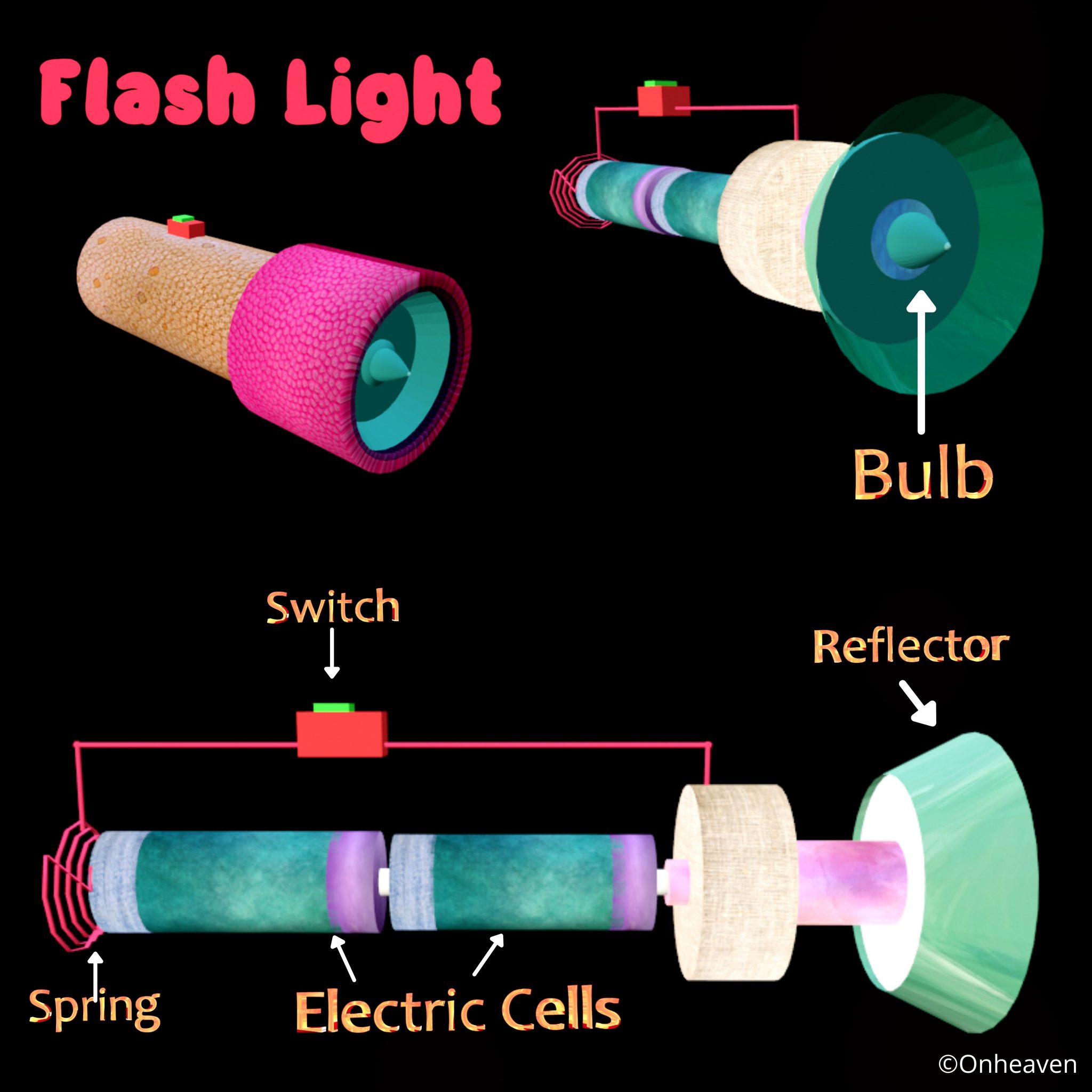
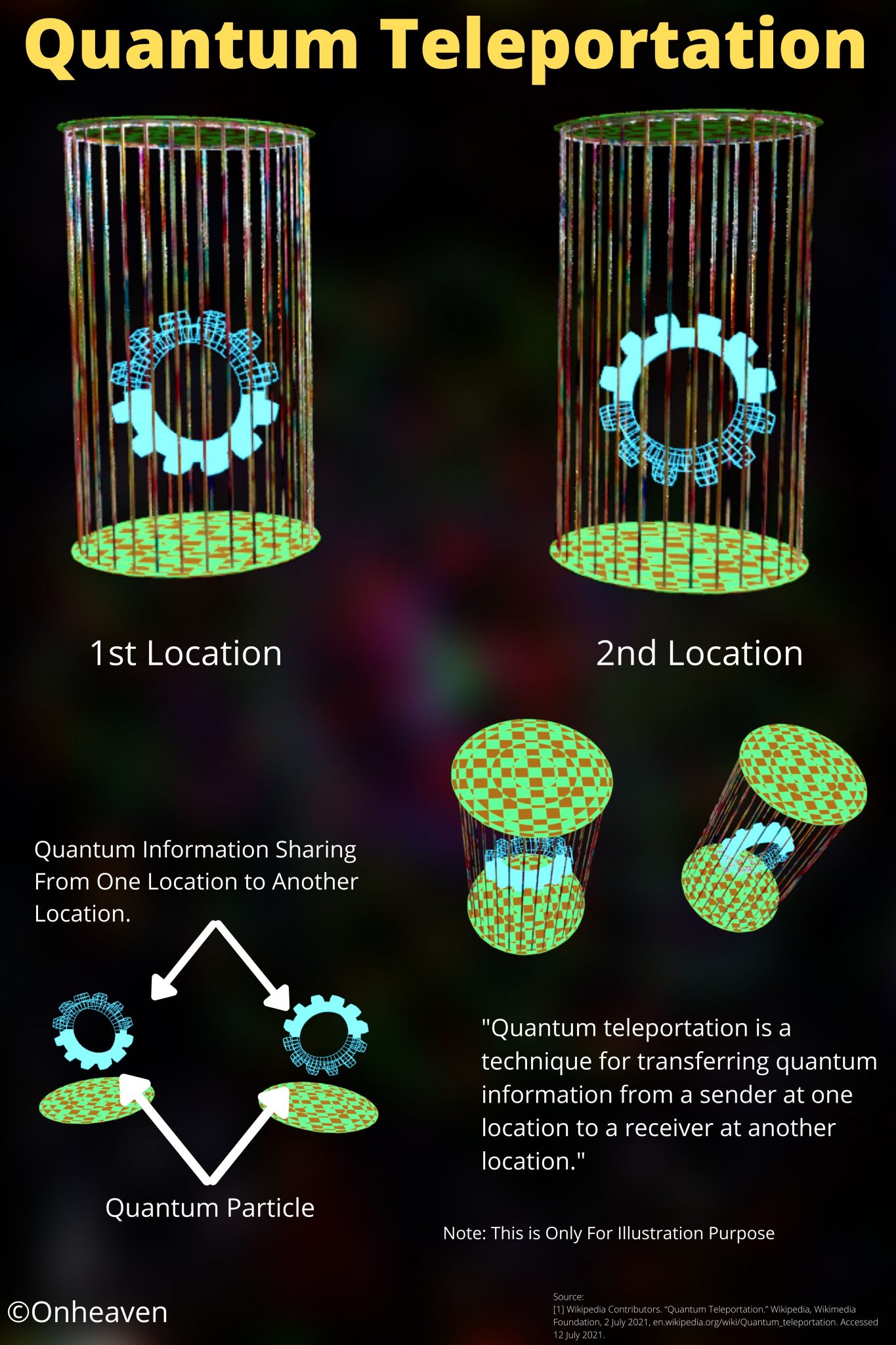
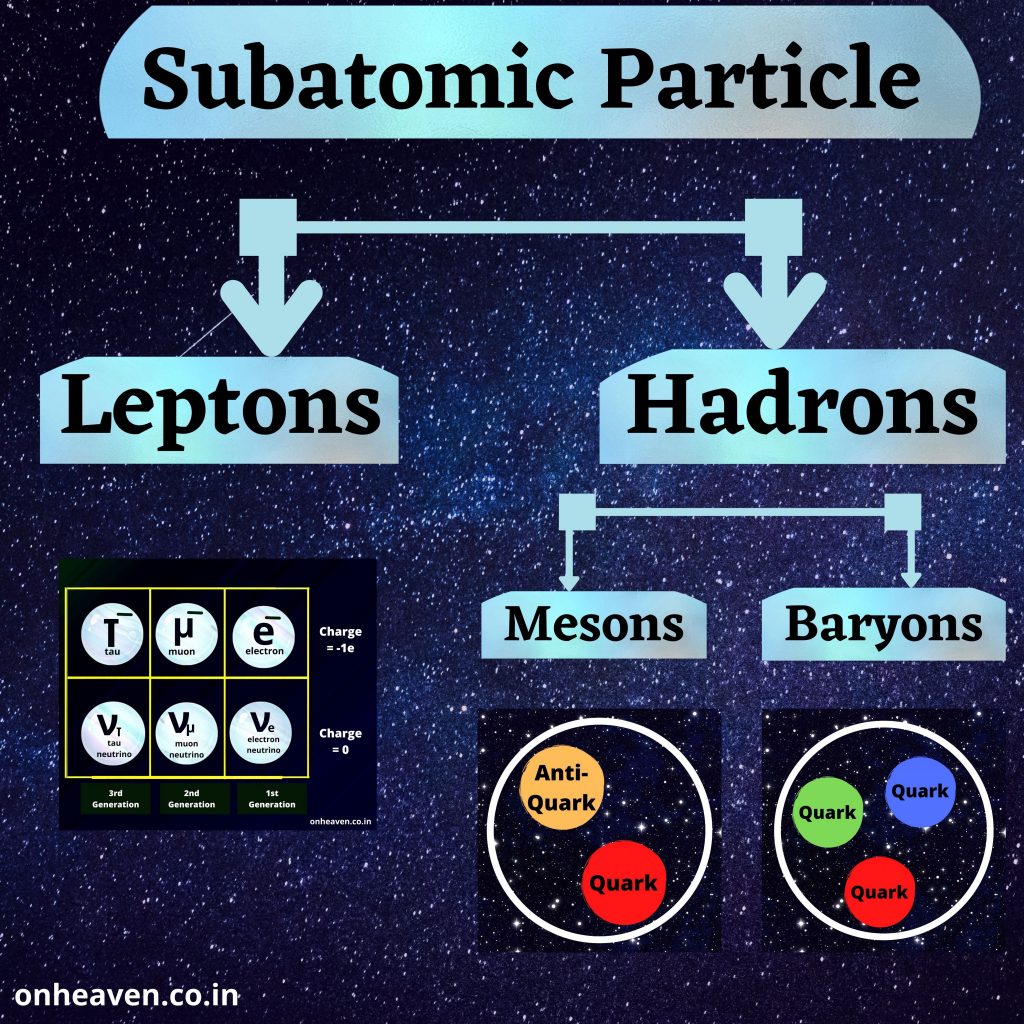
Illustration Video of Van De Graaff Generator:
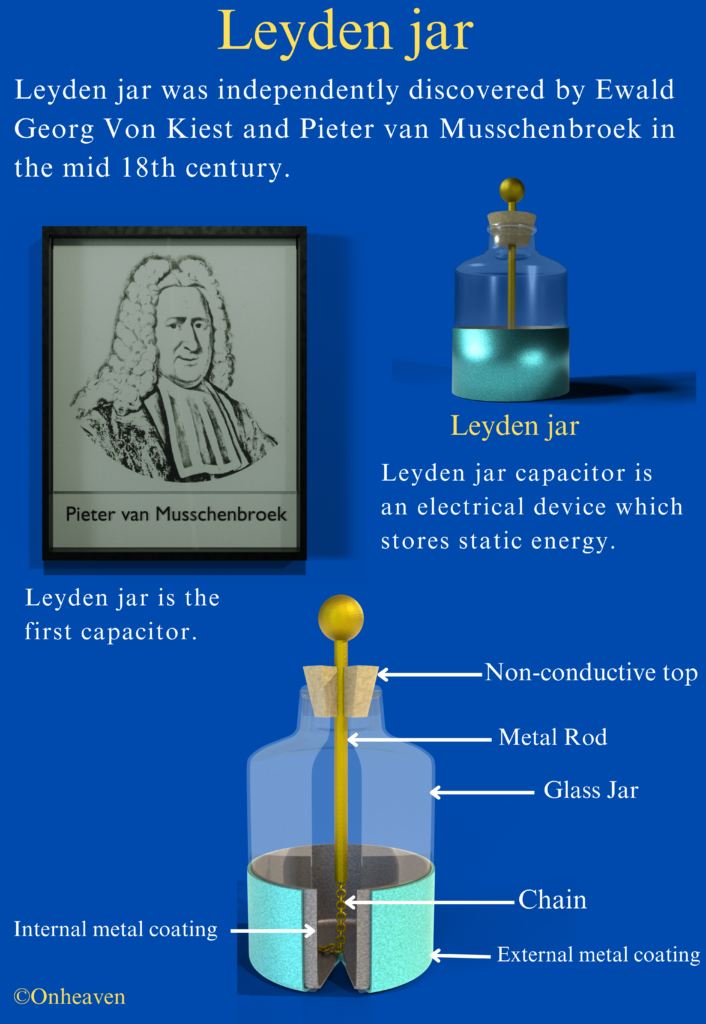
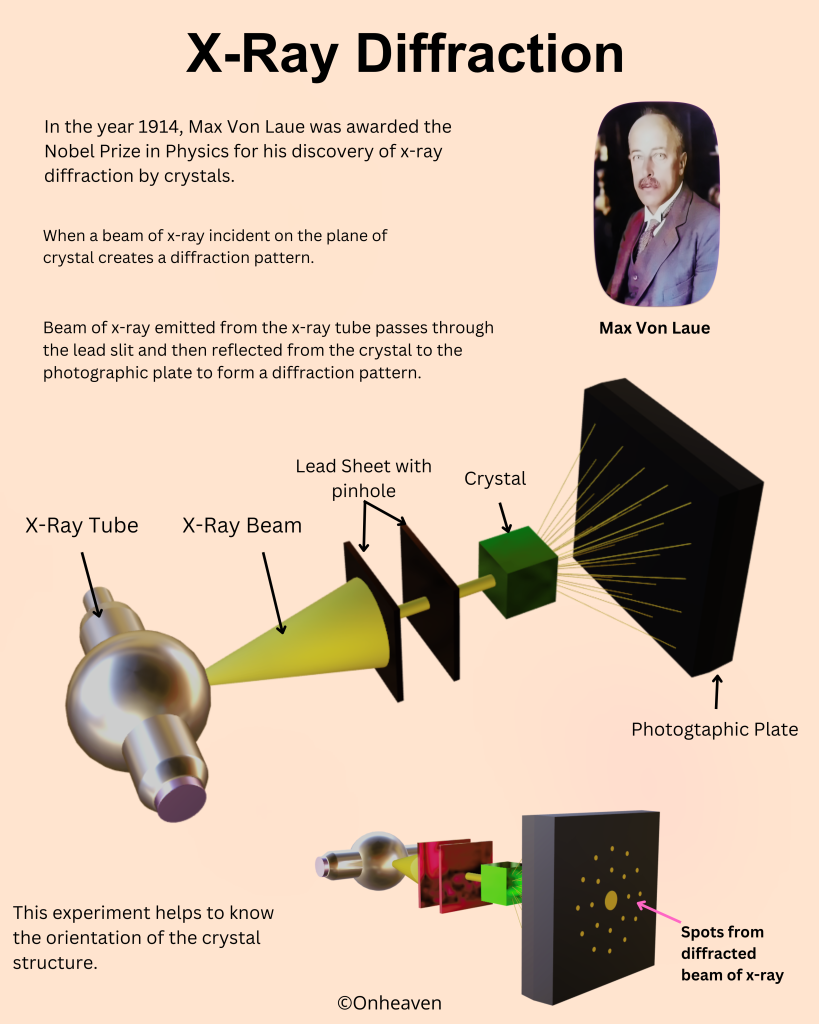
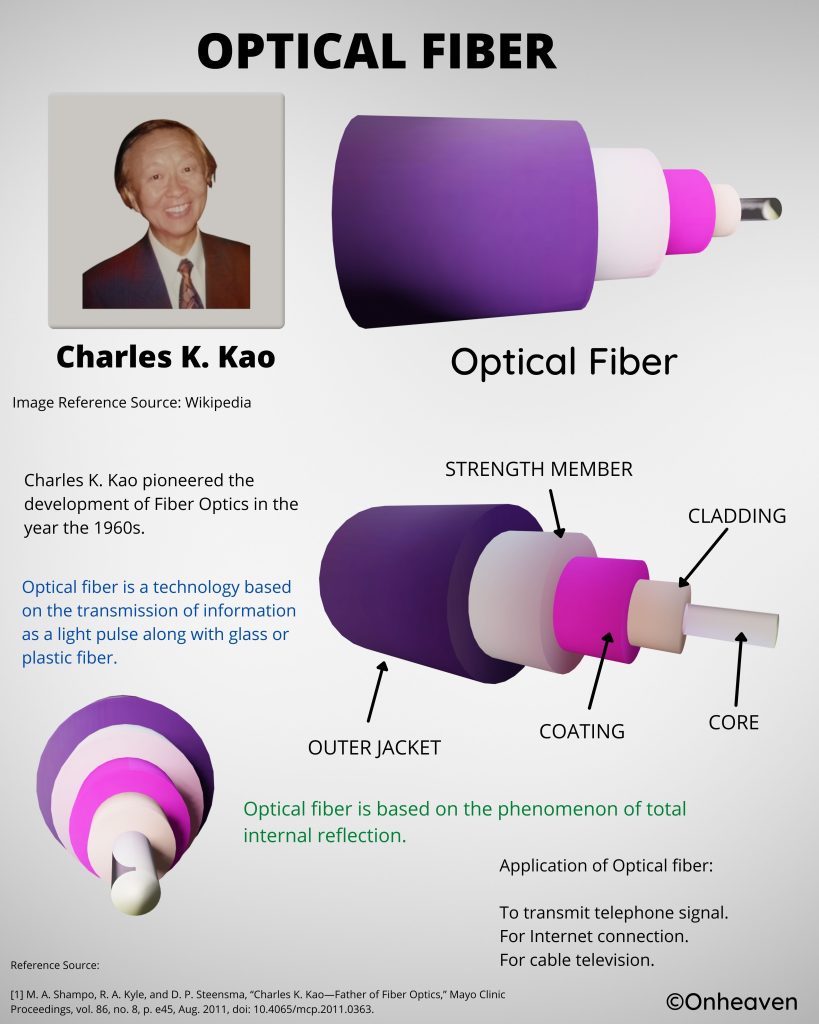
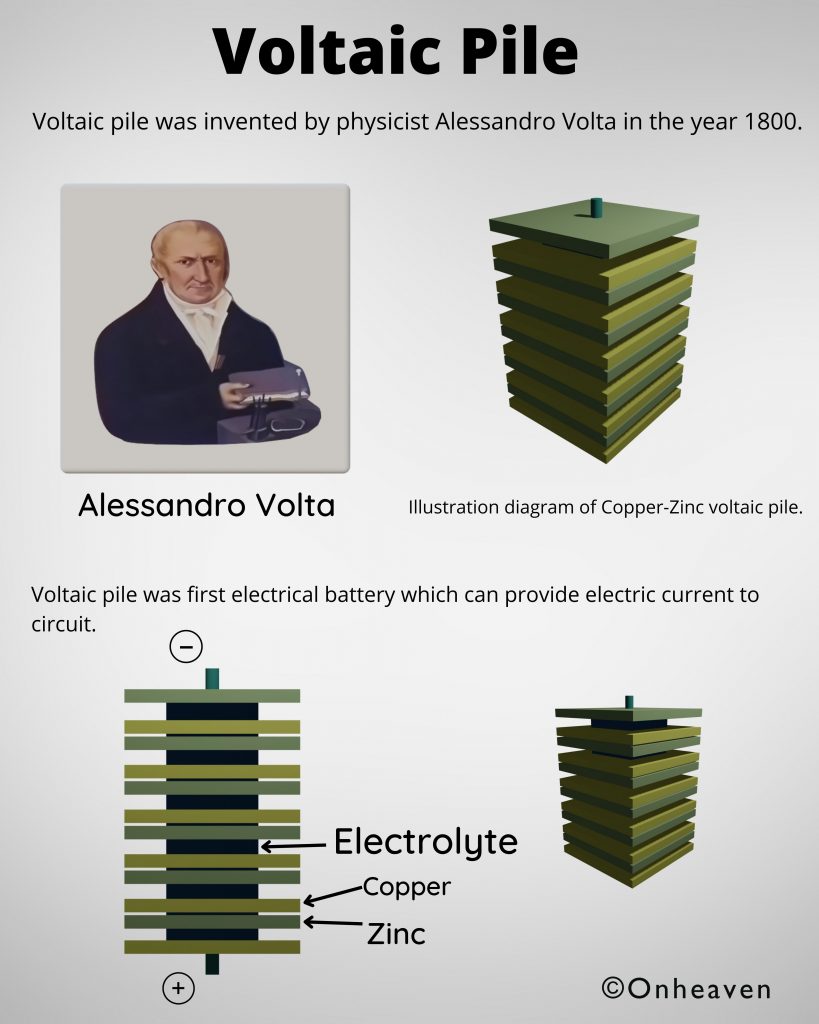
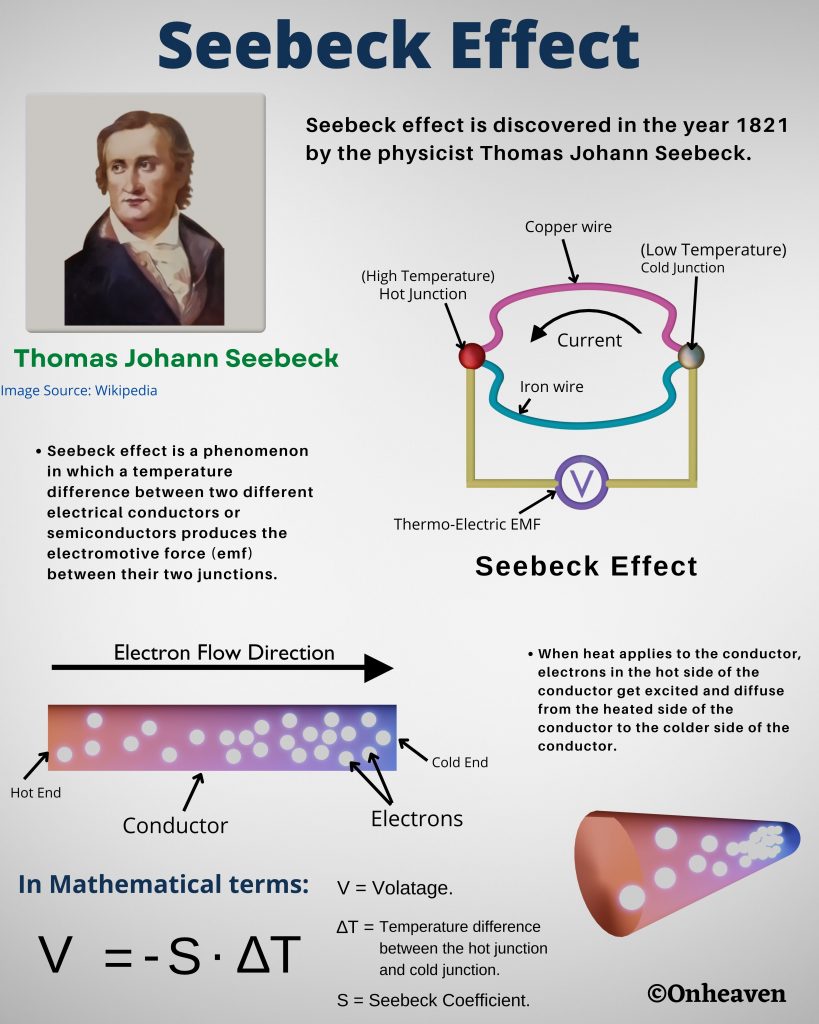
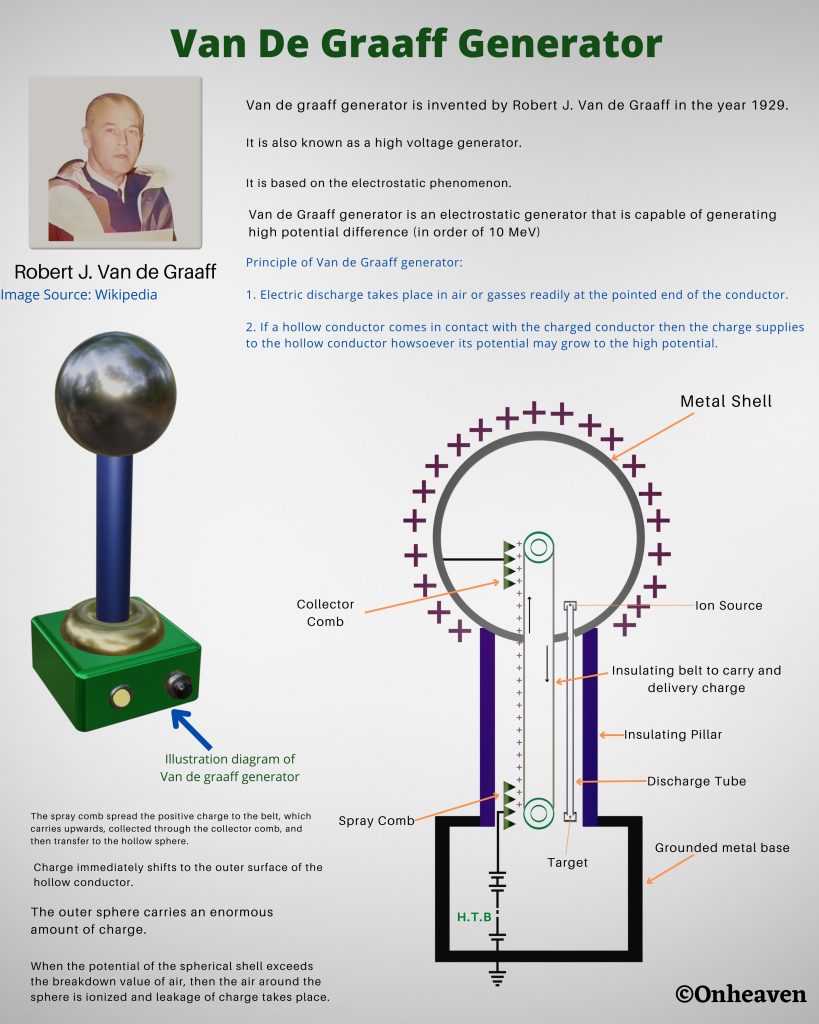
Van de graaff generator is invented by Robert J. Van de Graaff in the year 1929.
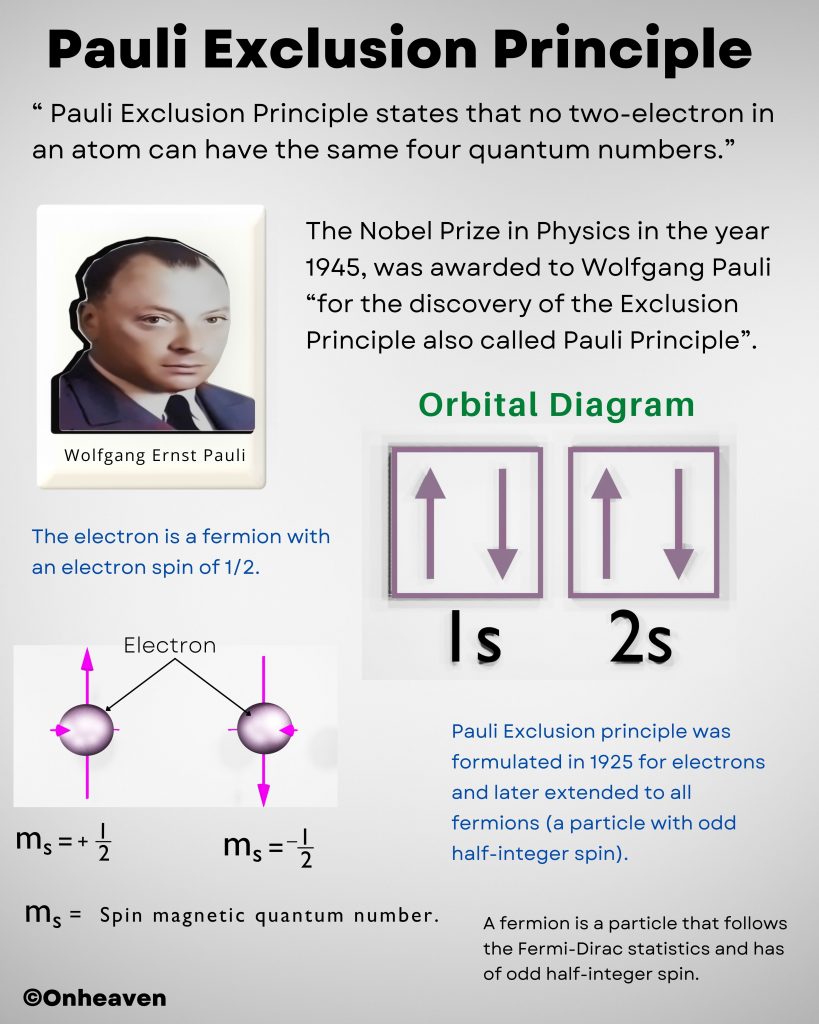
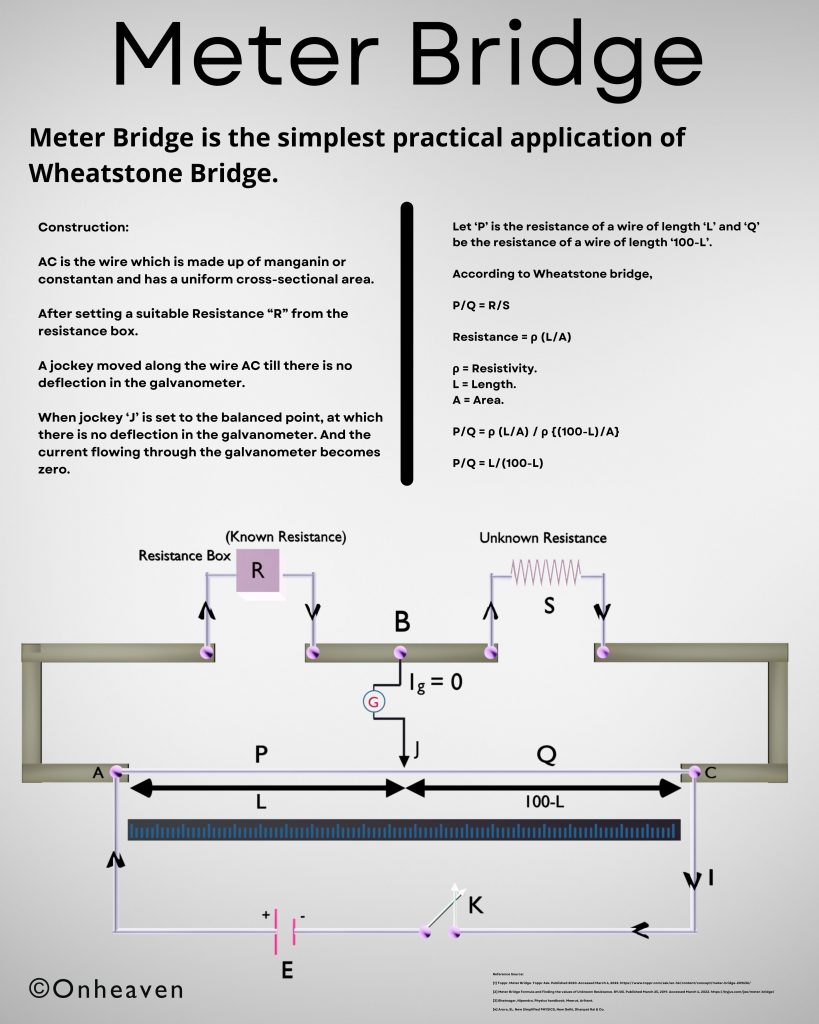
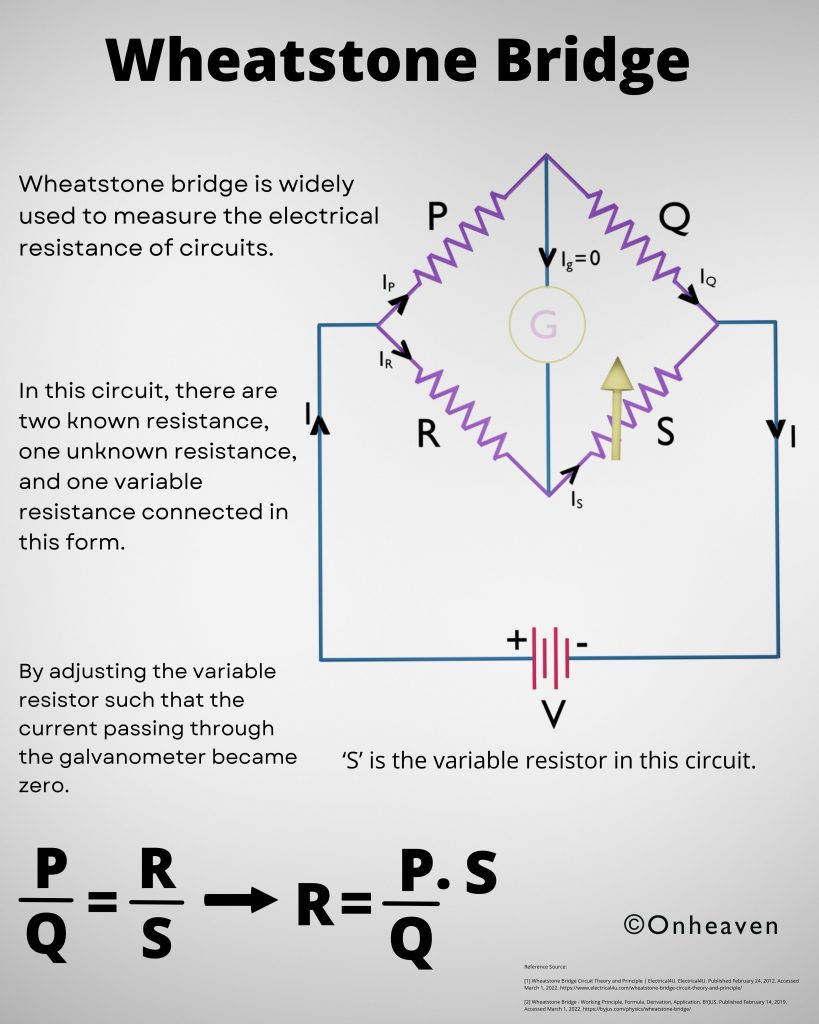
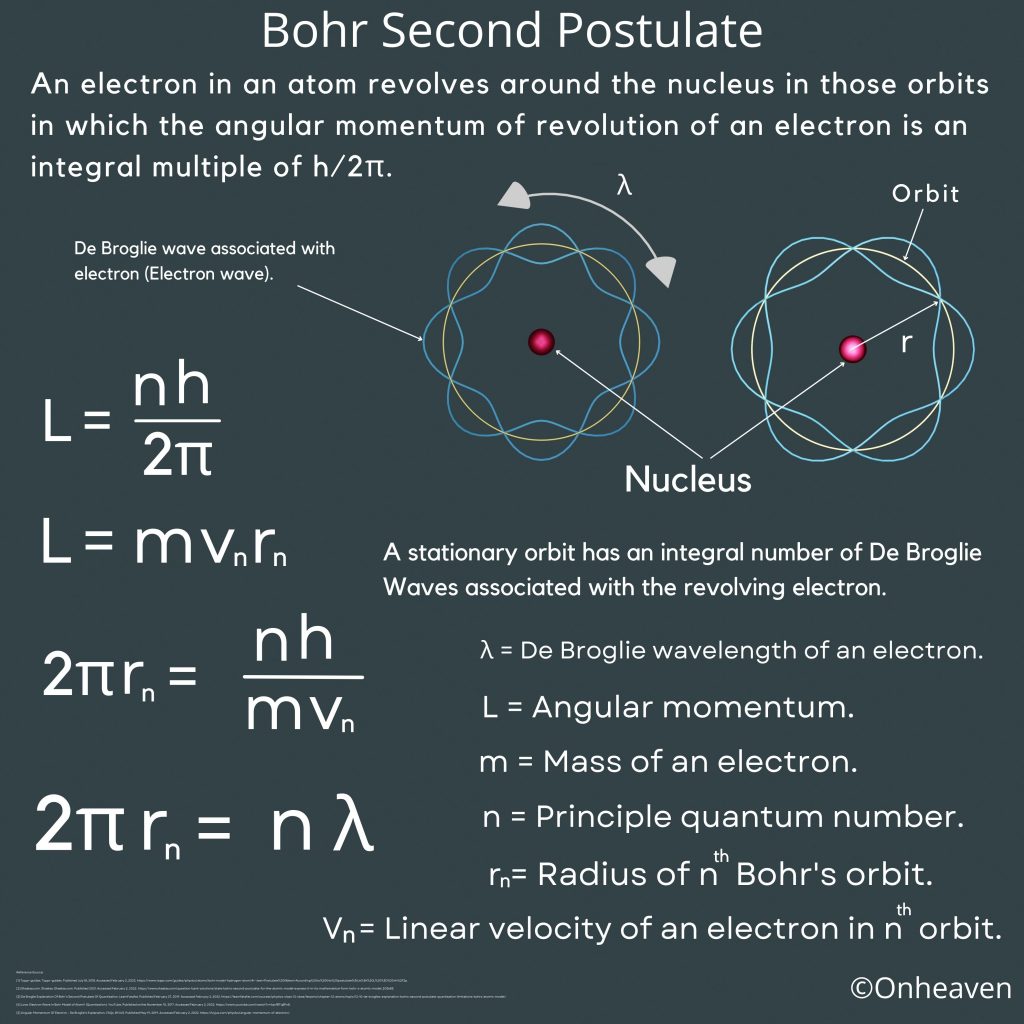
Principle of Van de Graaff generator:
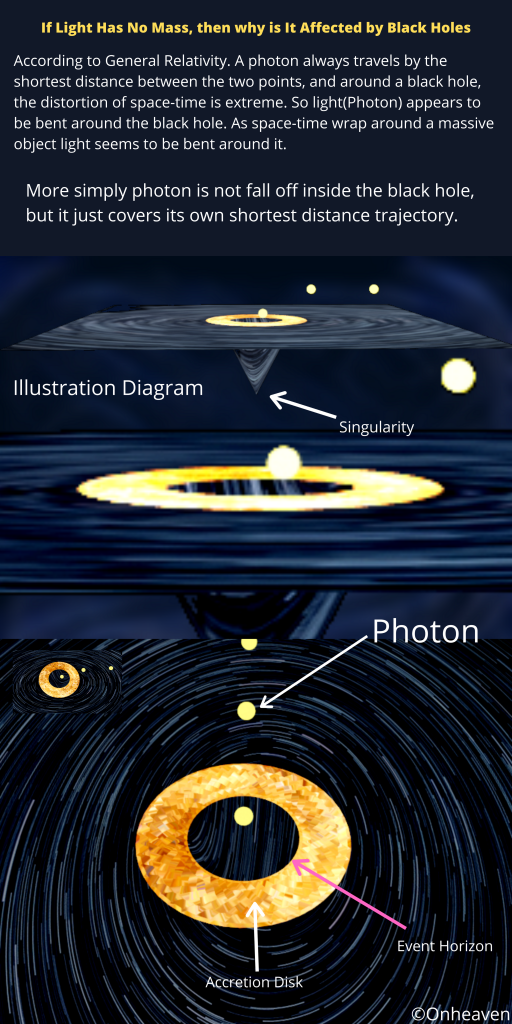
1. Electric discharge takes place in air or gasses readily at the pointed end of the conductor.
2. If a hollow conductor comes in contact with the charged conductor then the charge supplies to the hollow conductor howsoever its potential may grow to the high potential.
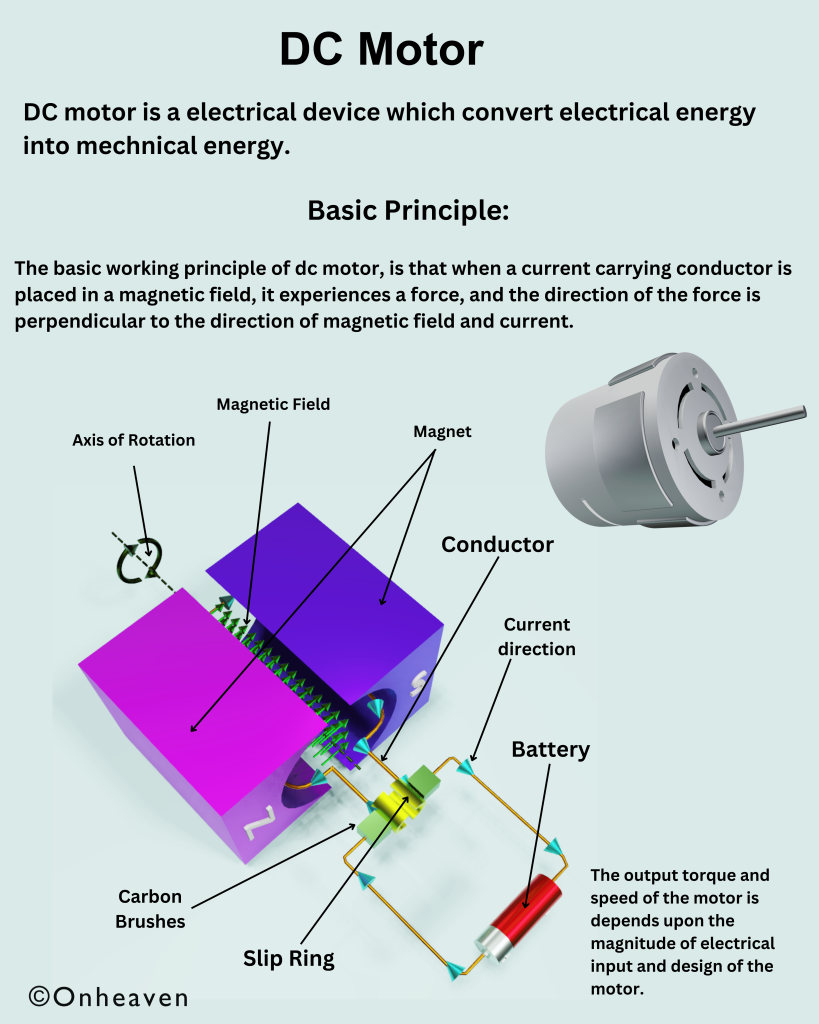
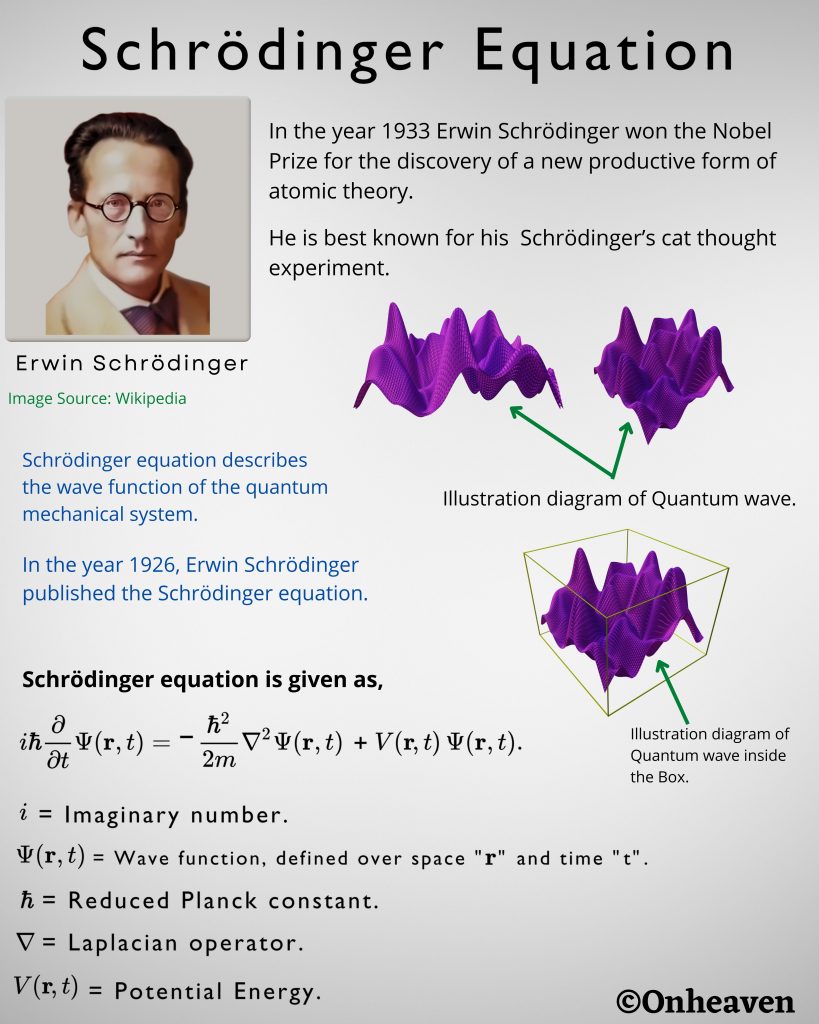
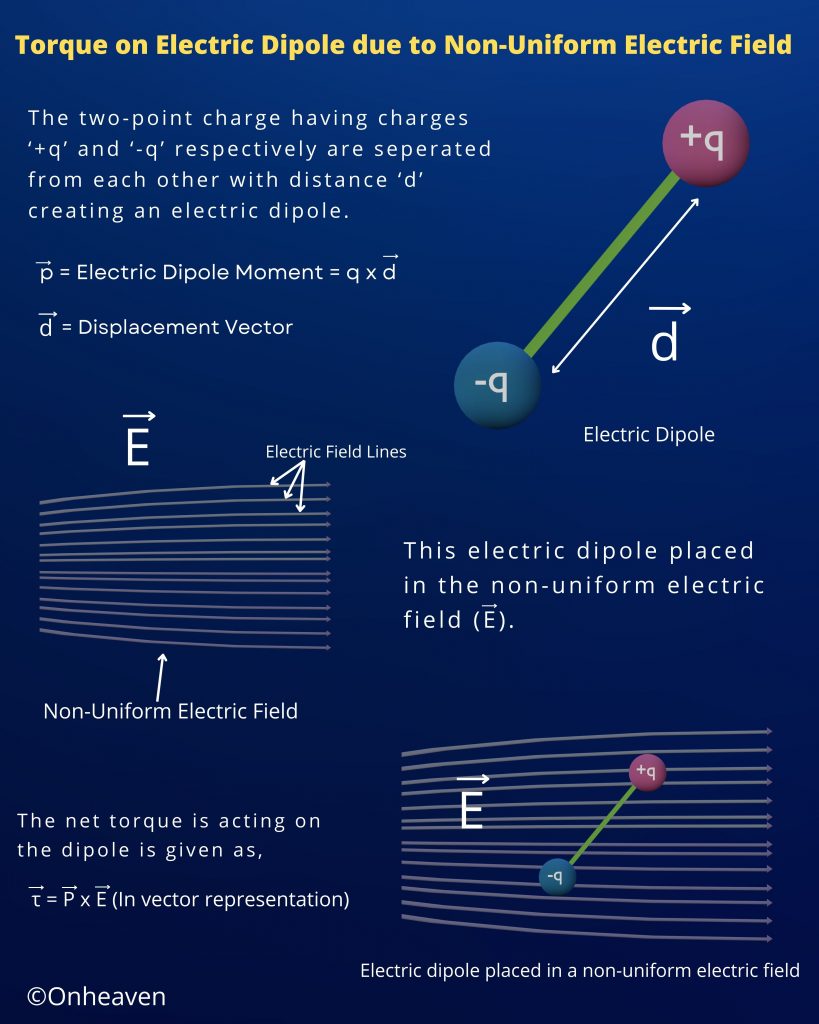
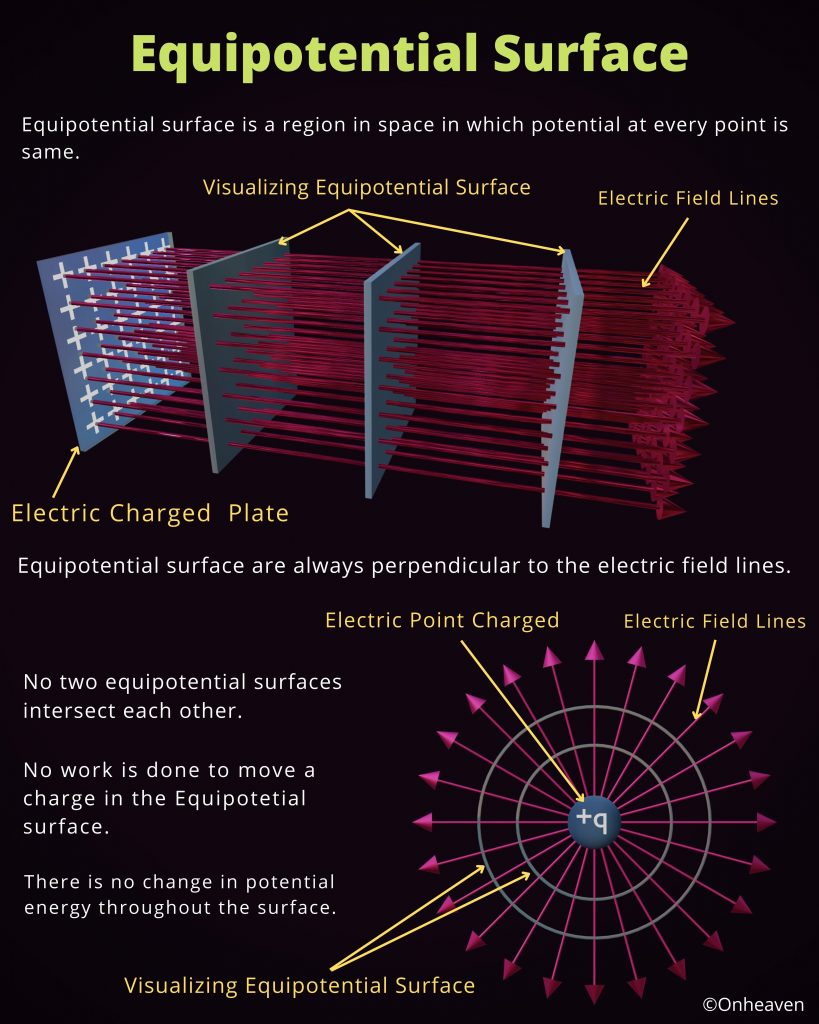
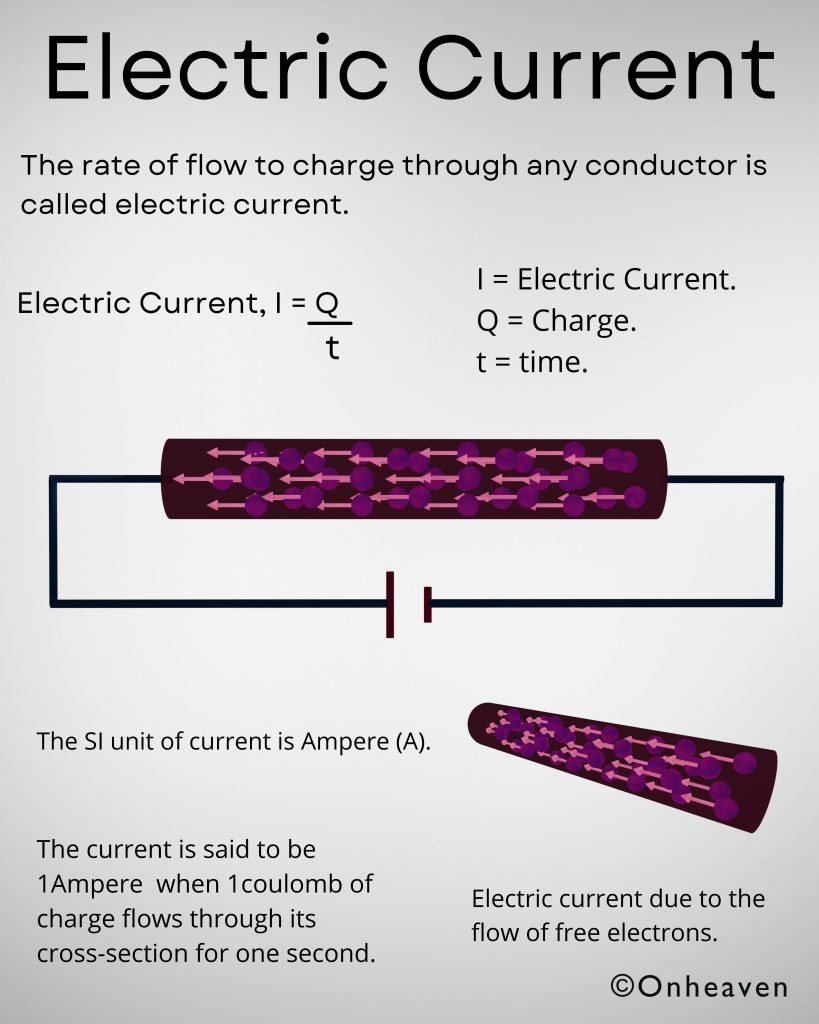
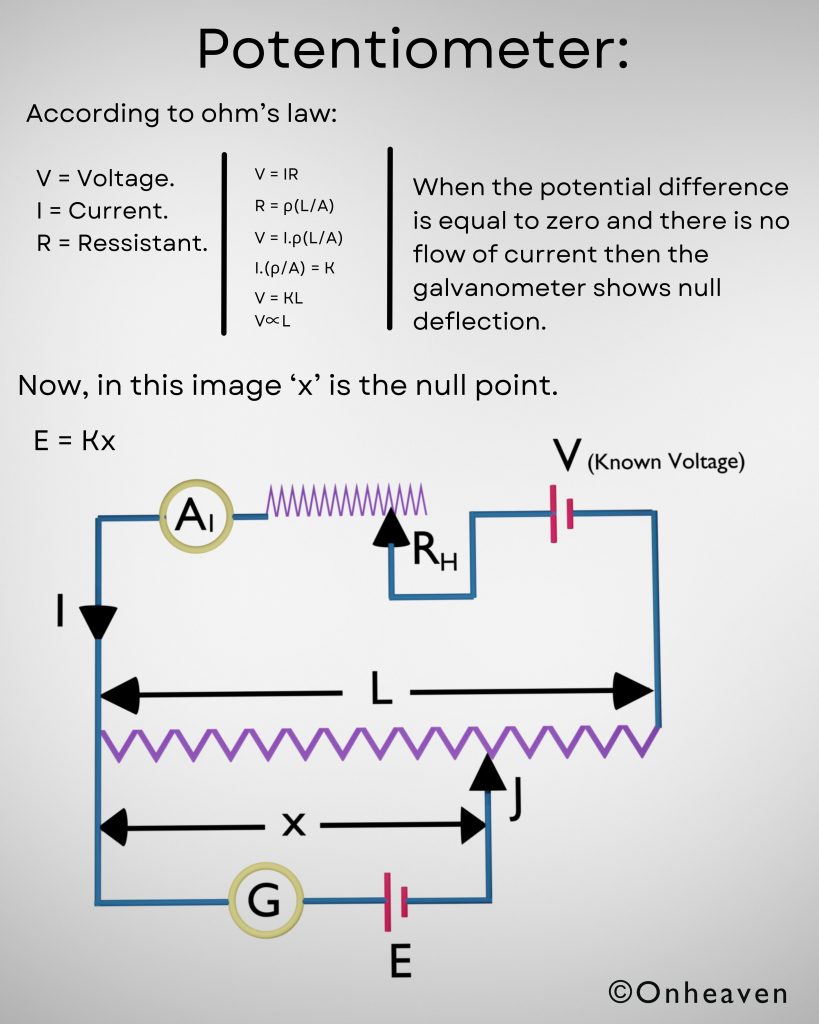
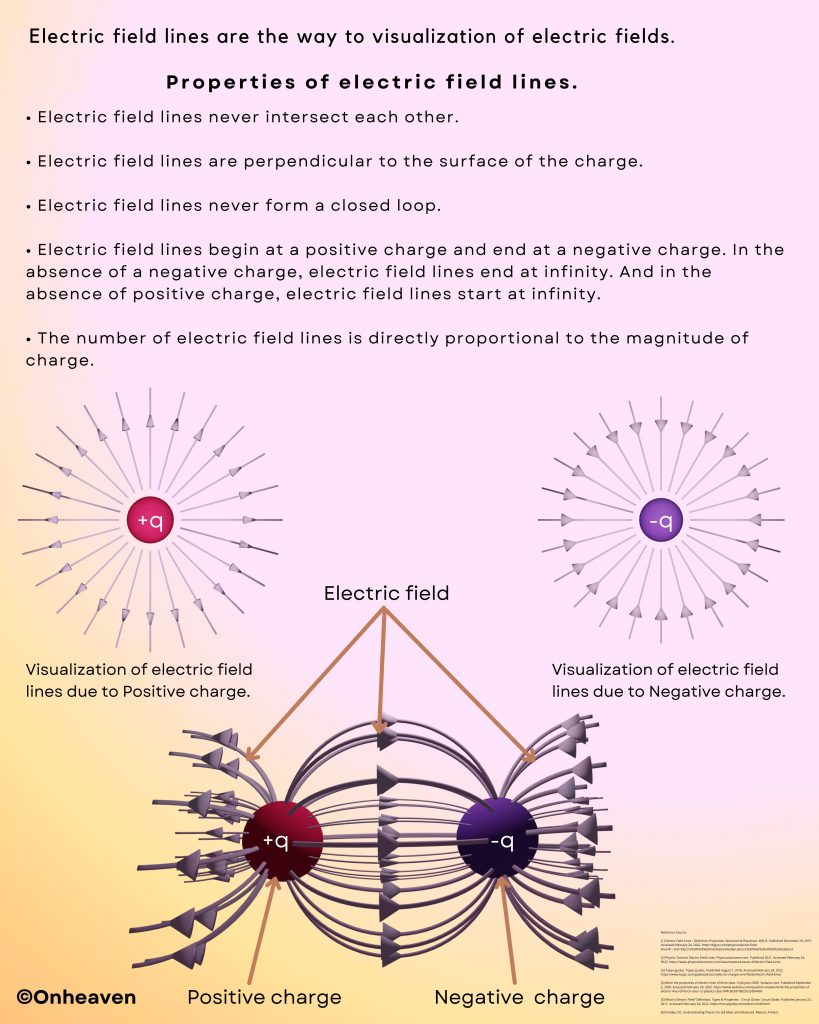
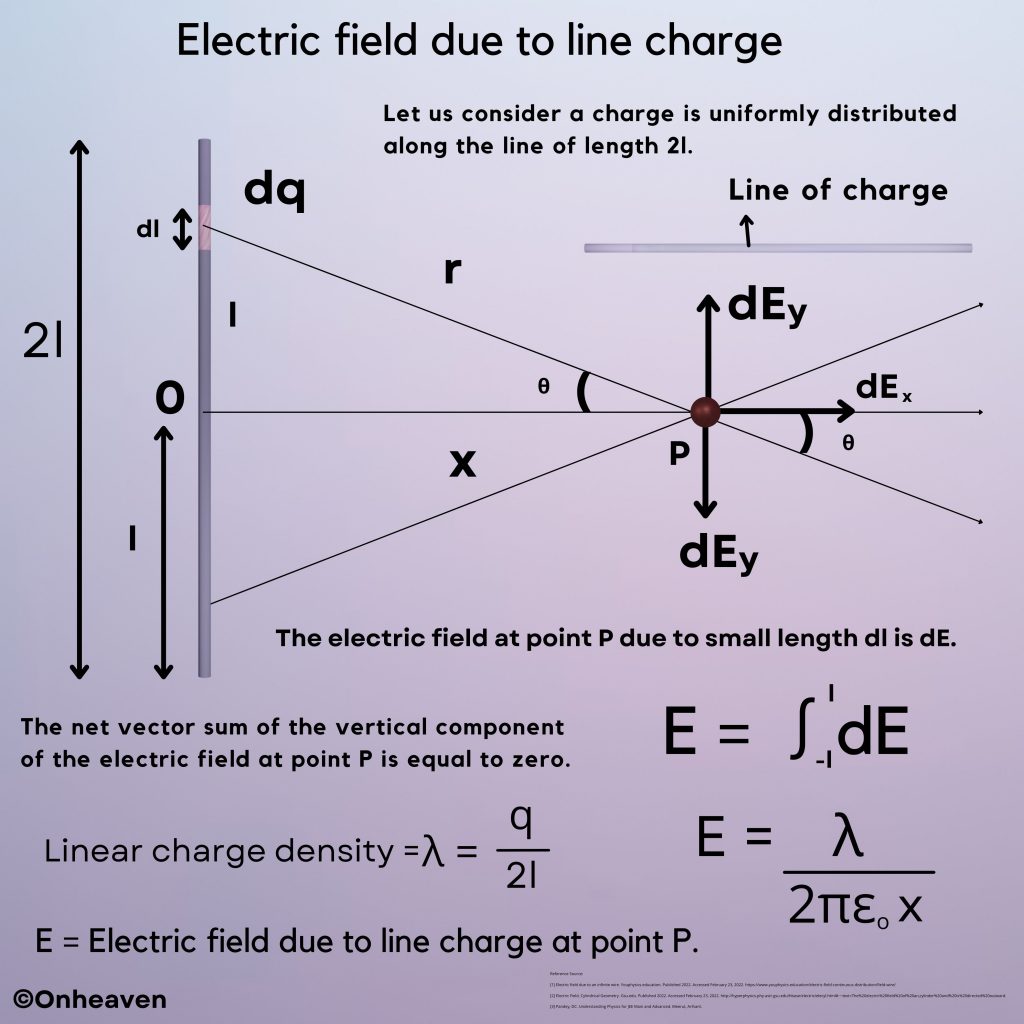
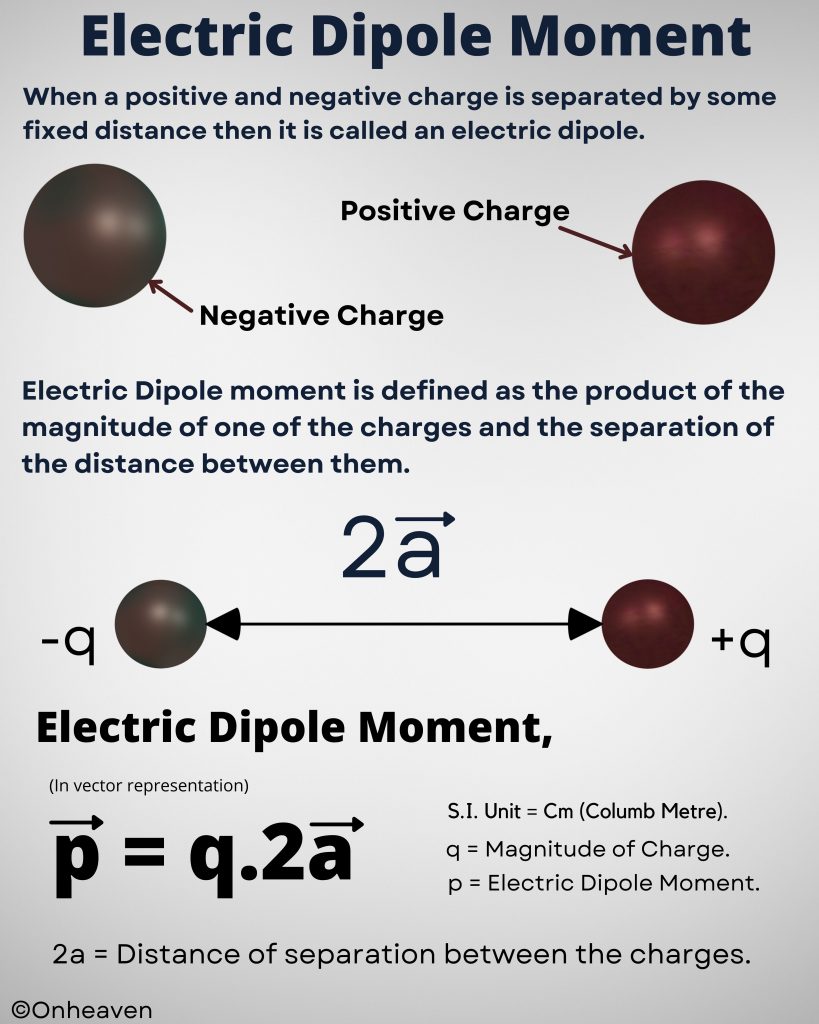
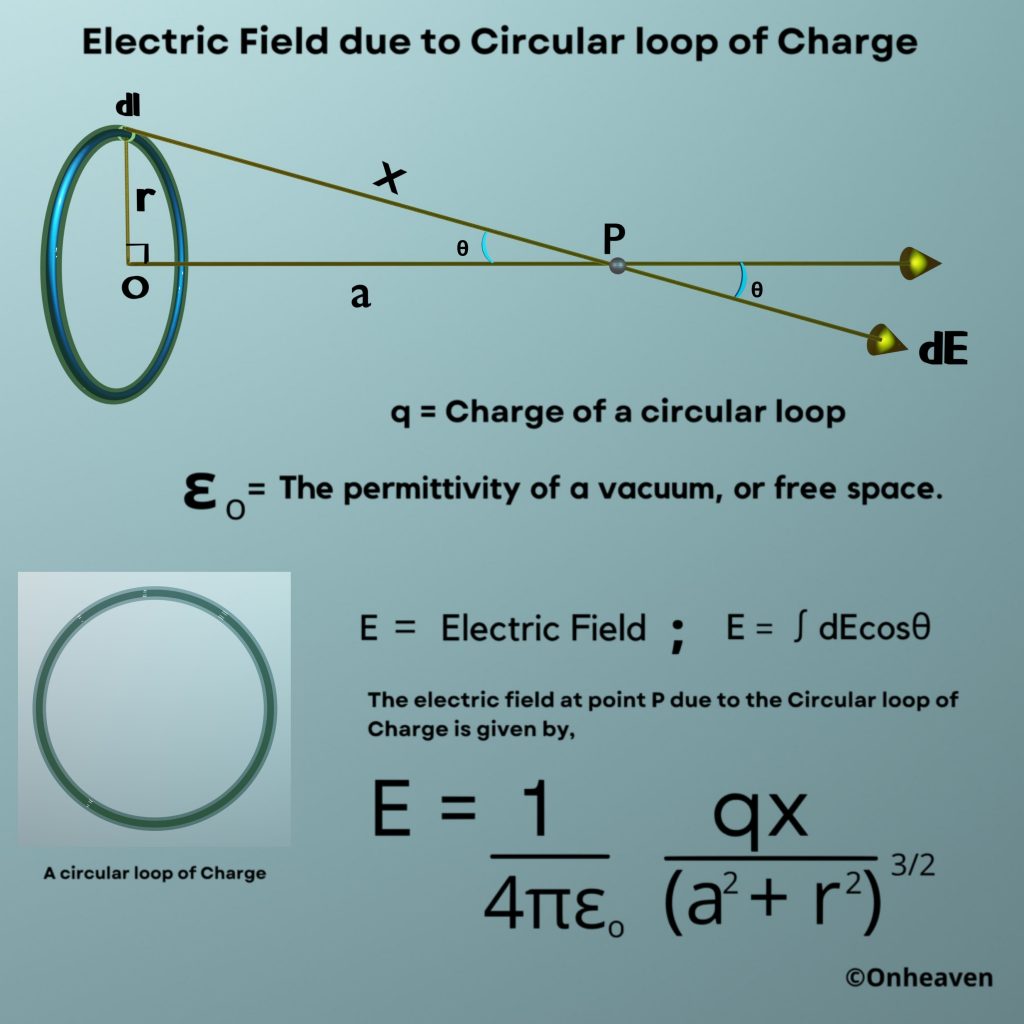
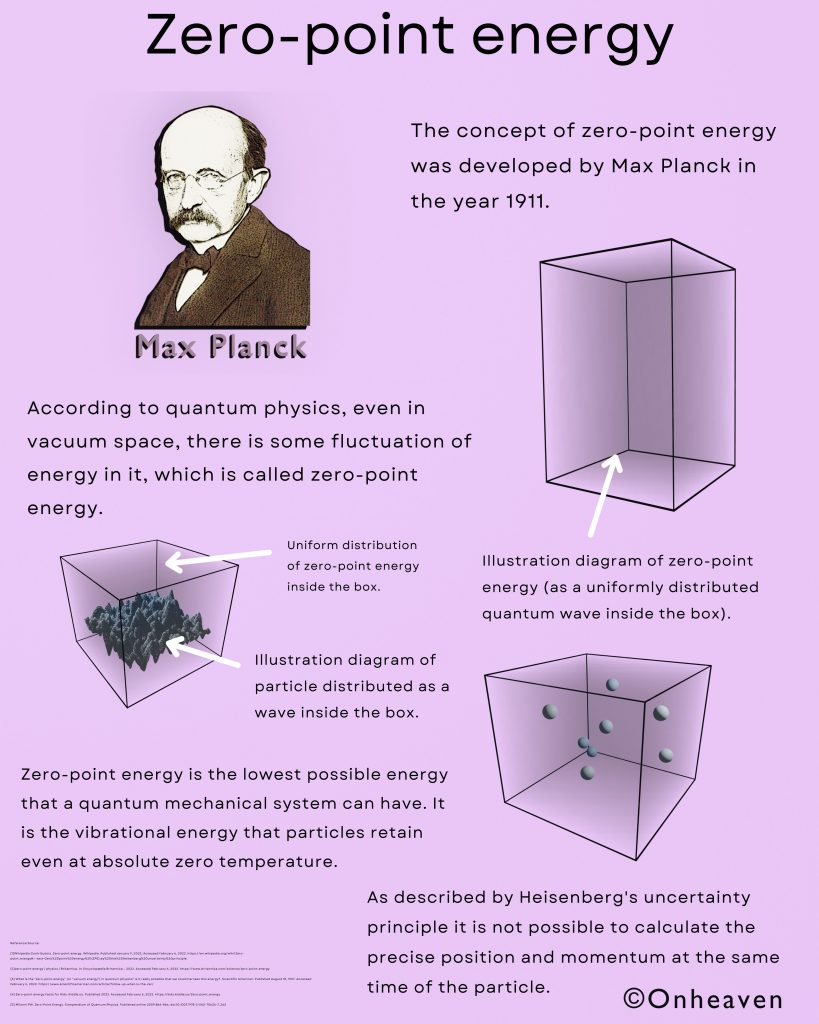
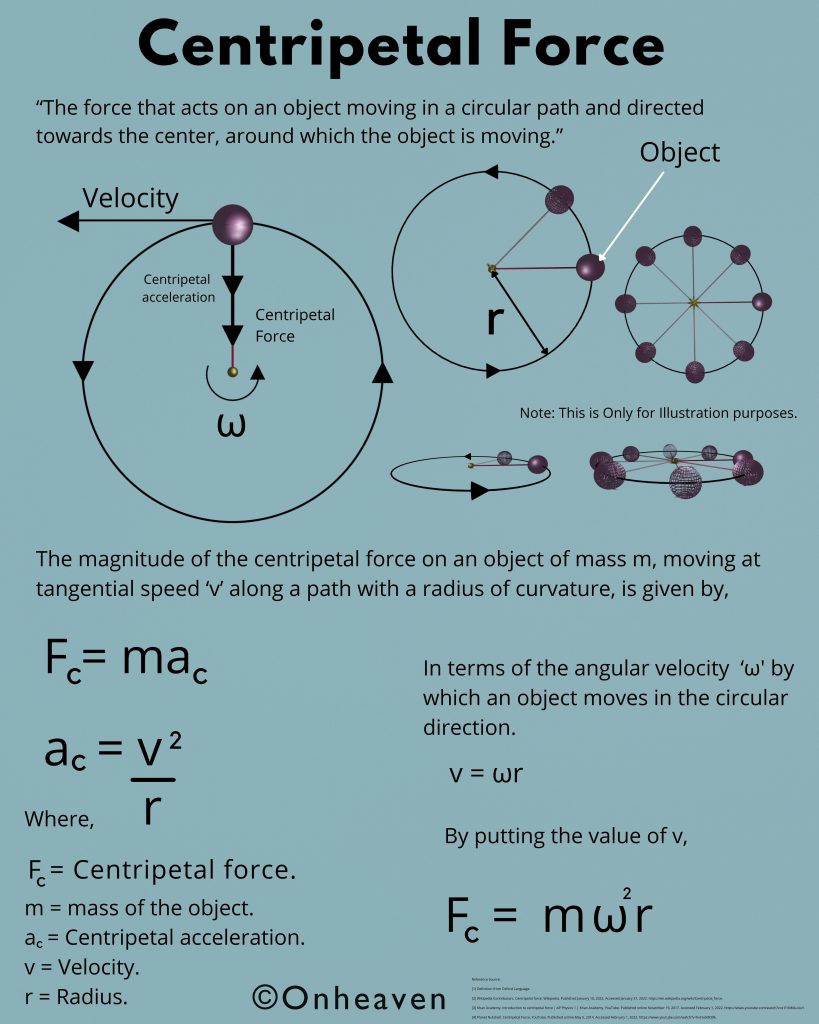
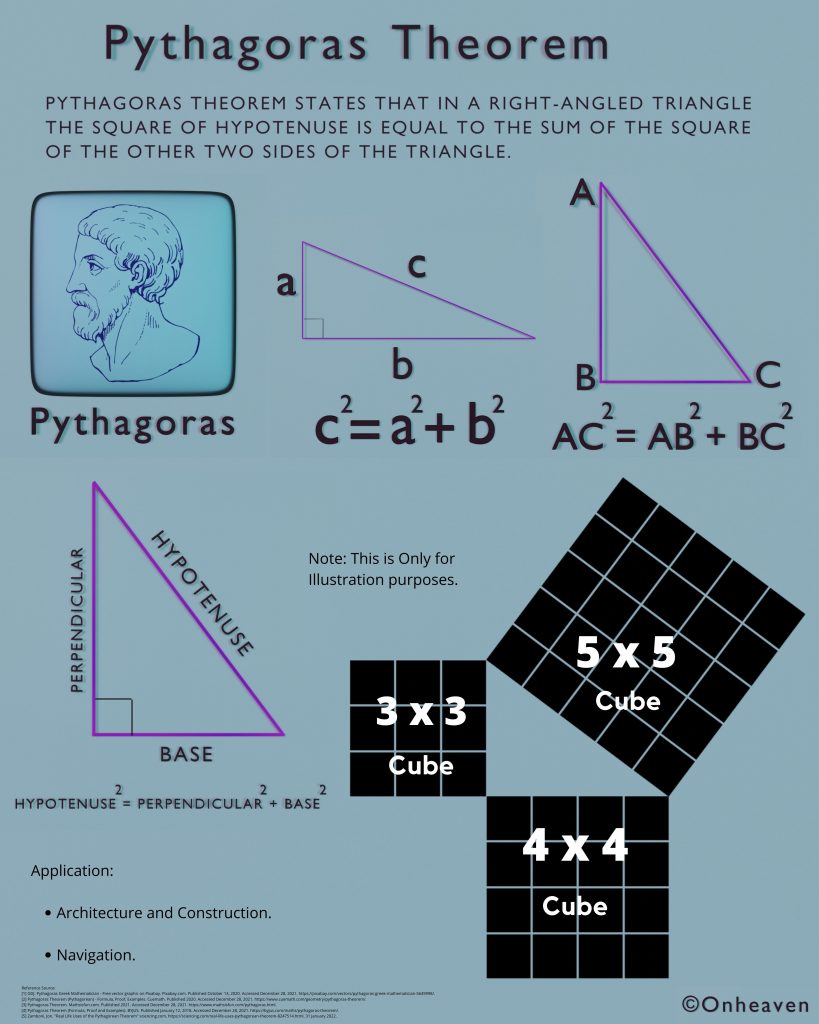
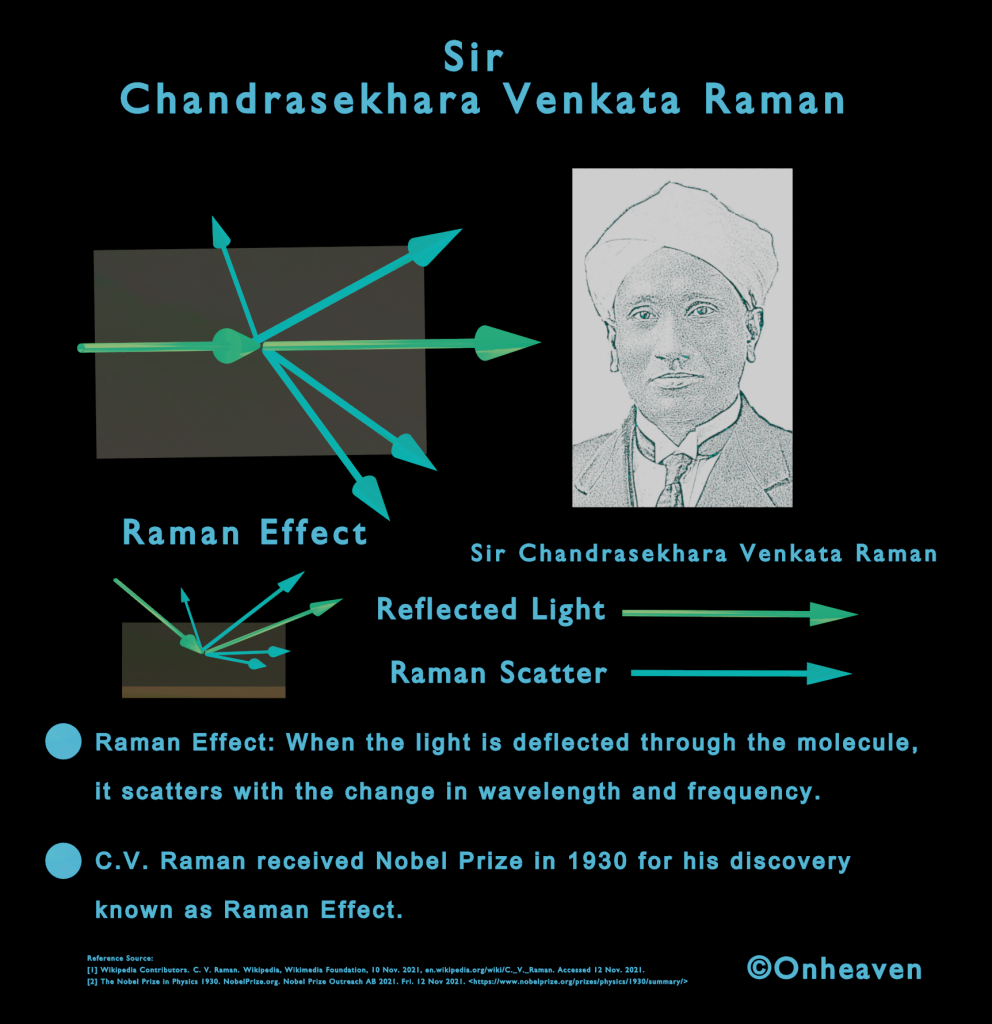
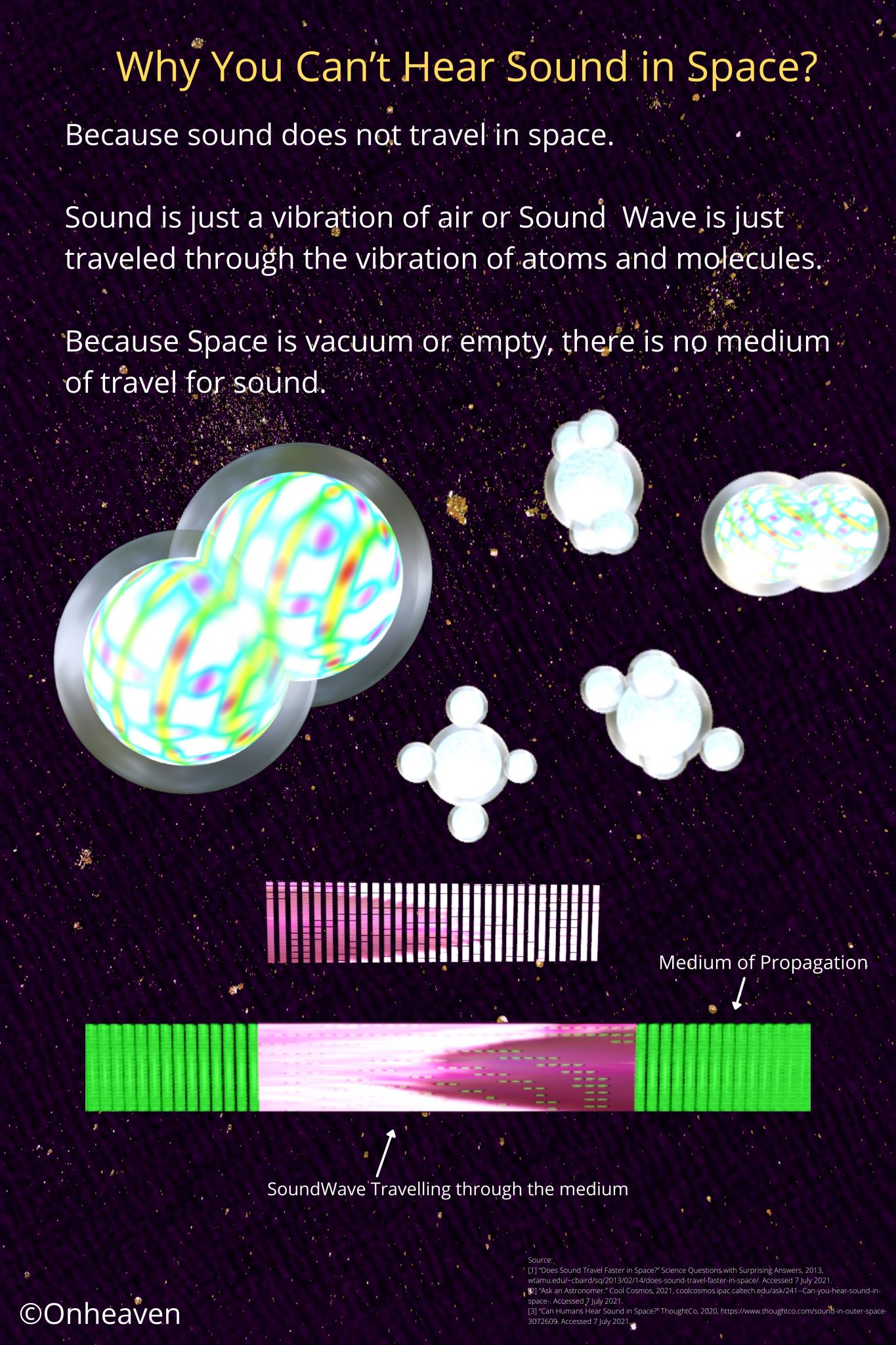
It is based on the electrostatic phenomenon.
It is also known as a high voltage generator.
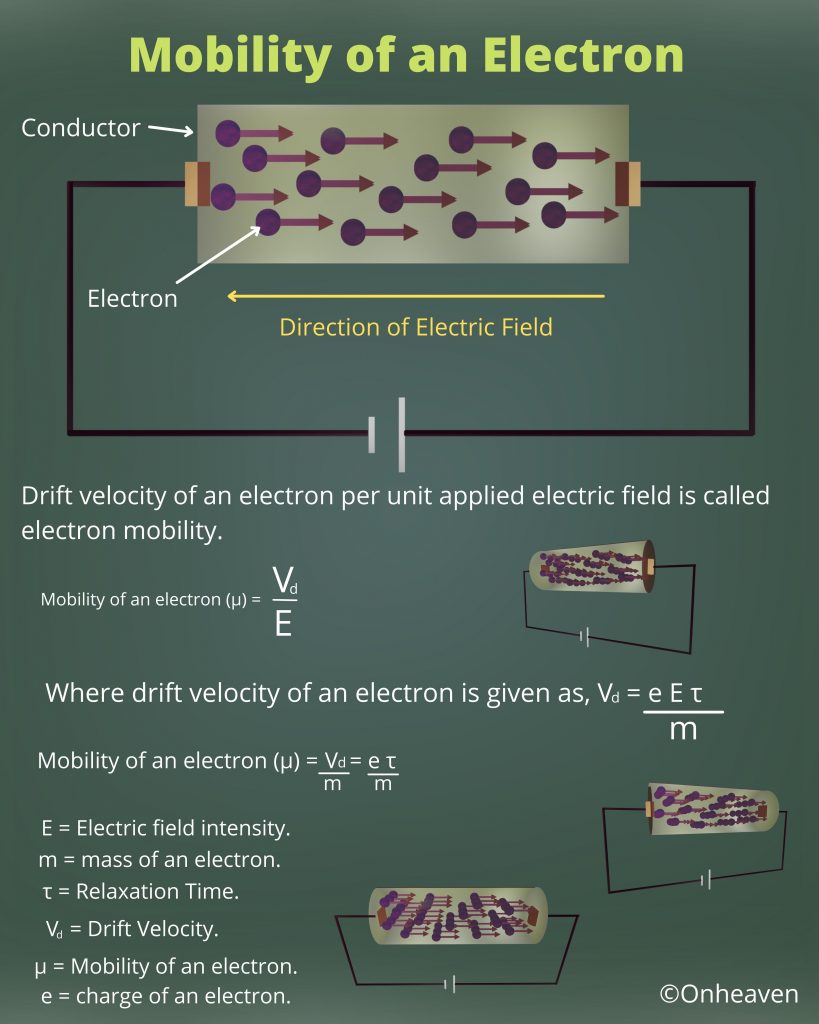
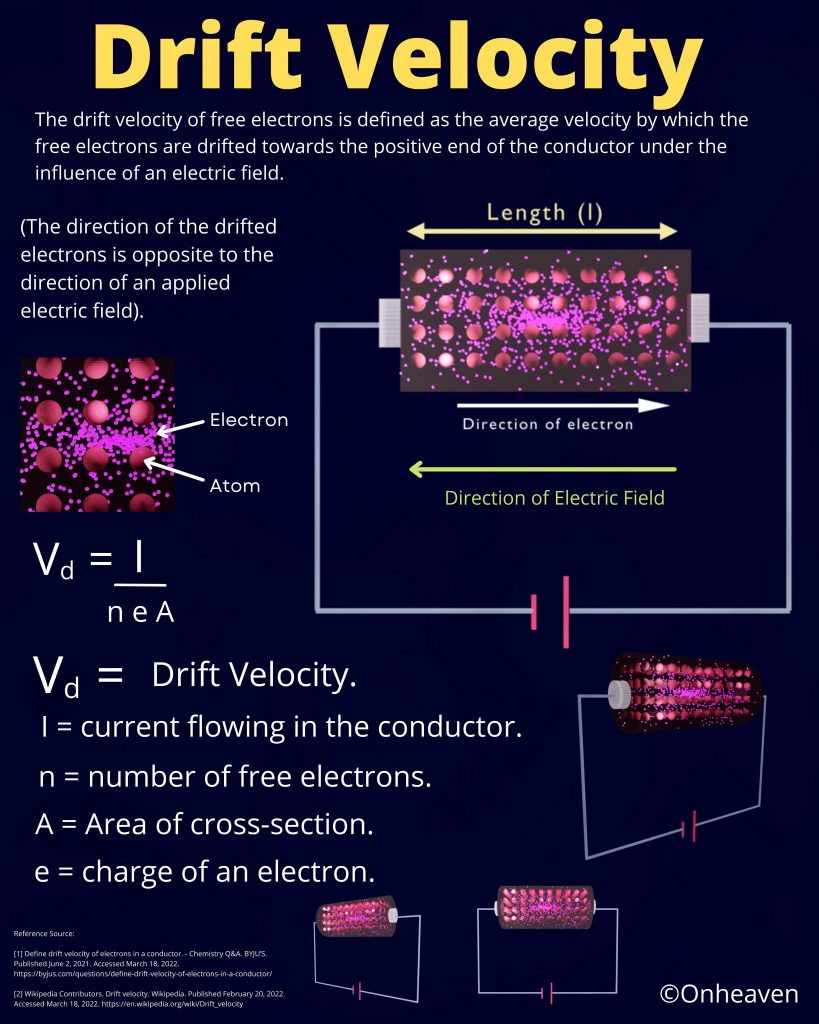
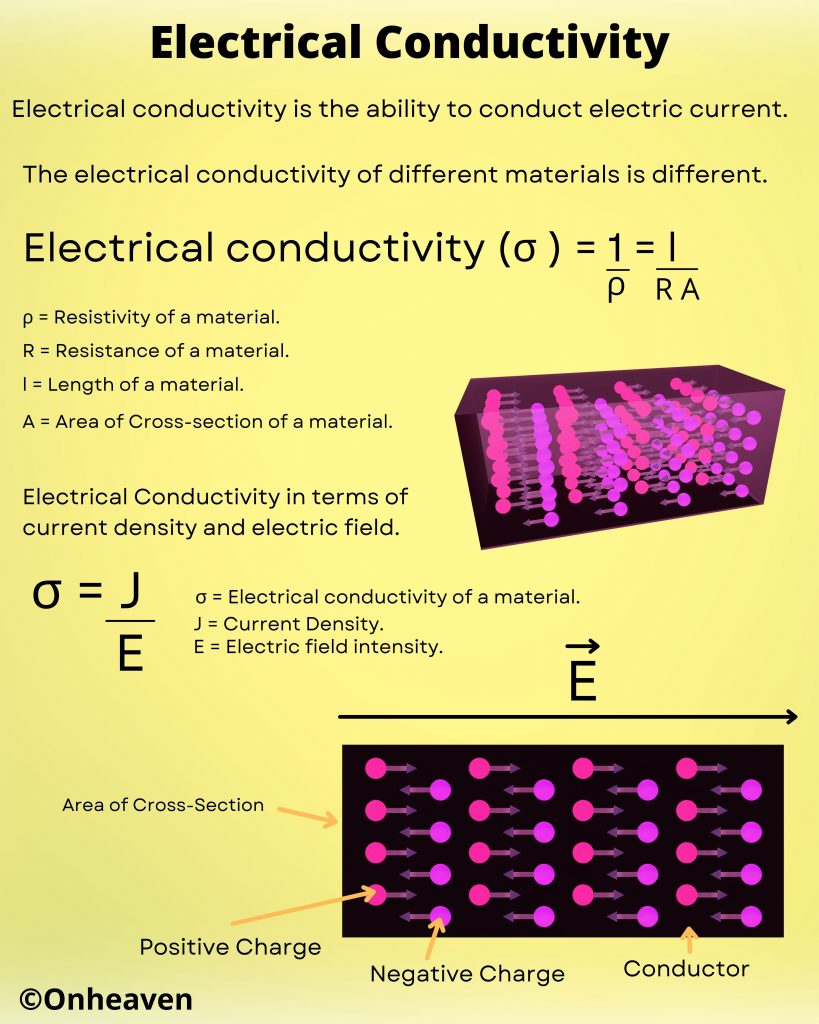
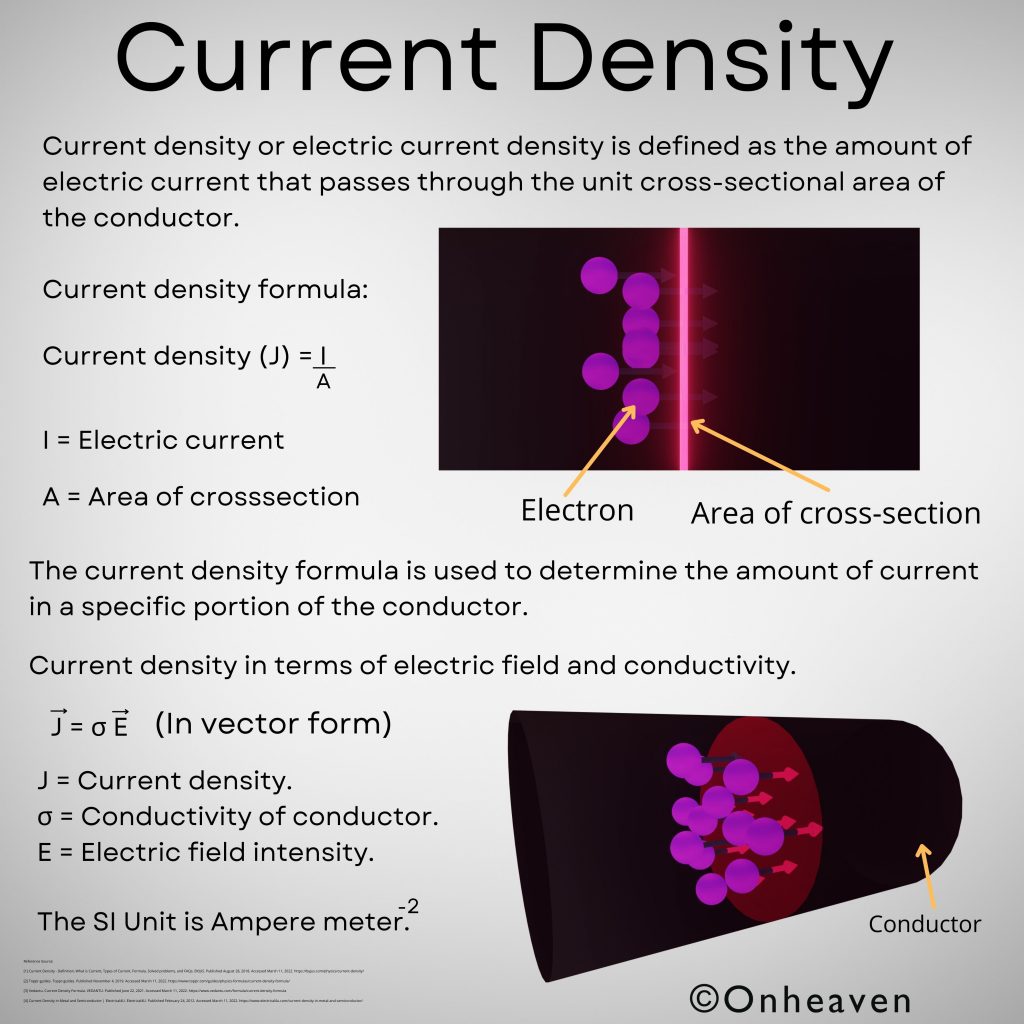
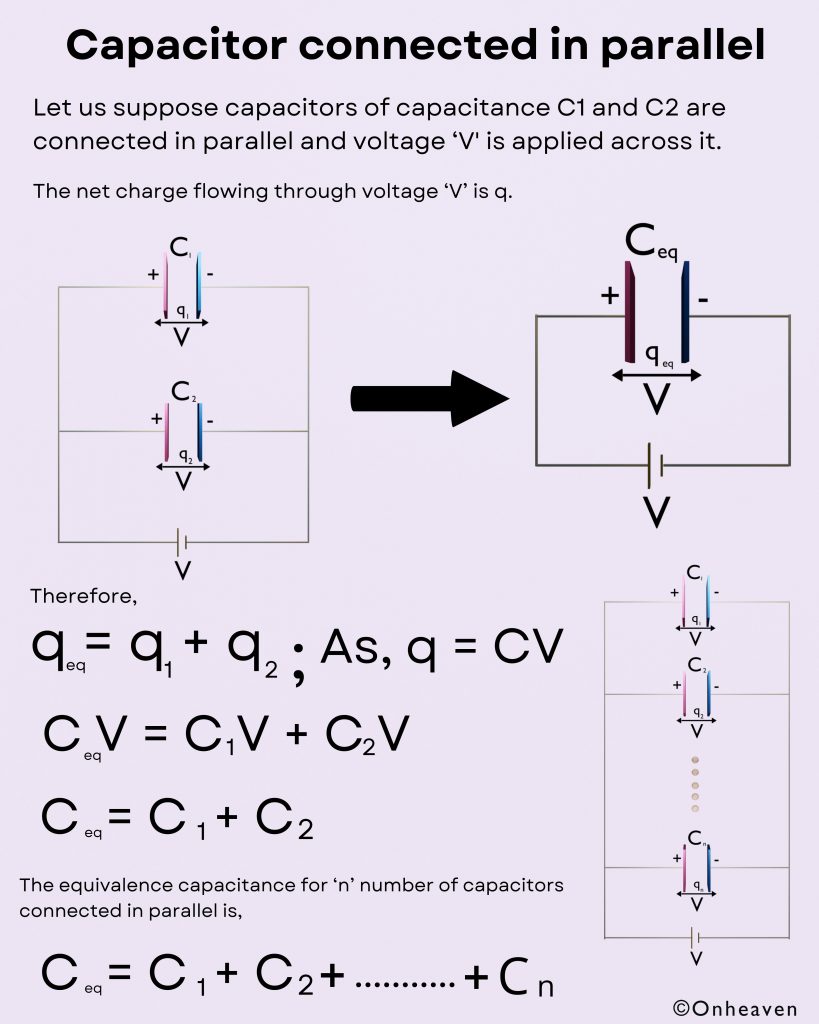
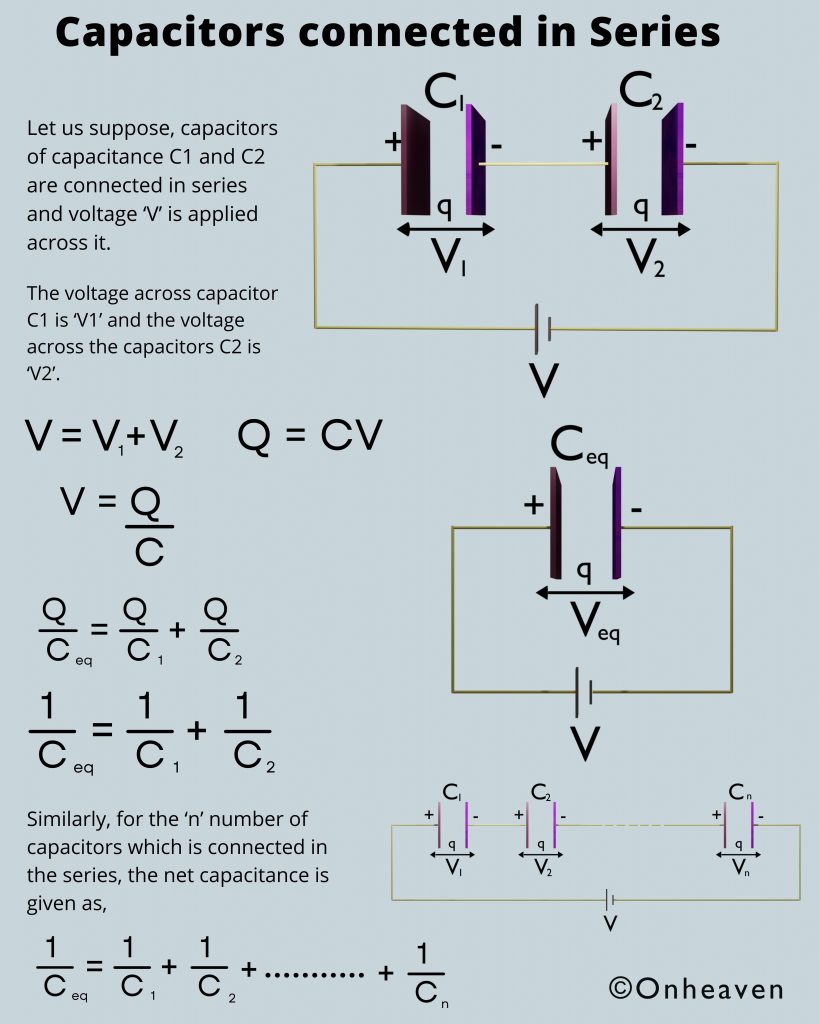
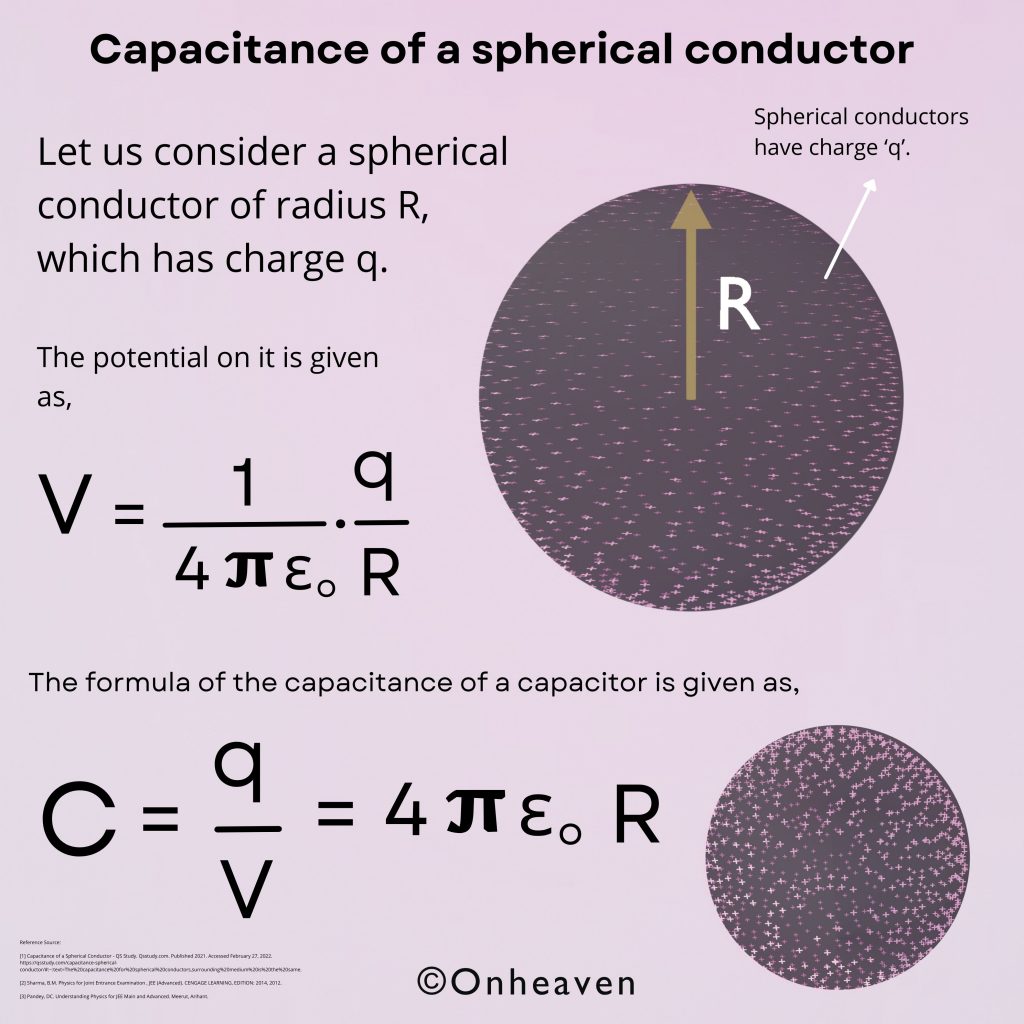
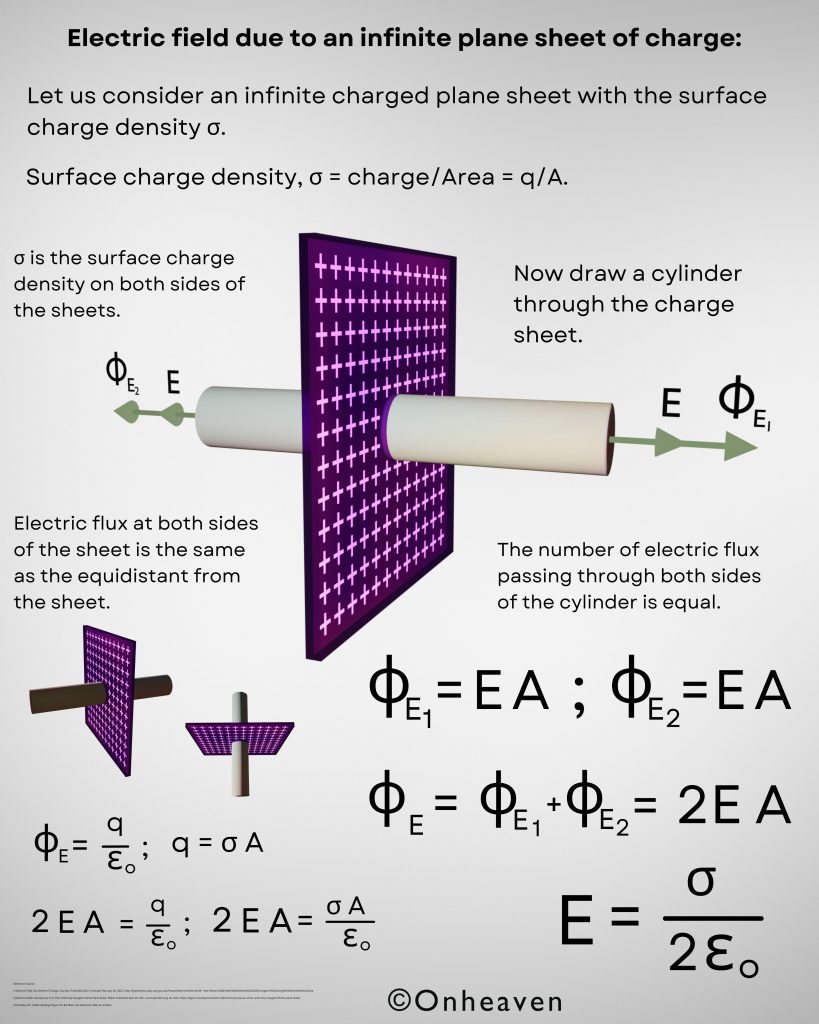
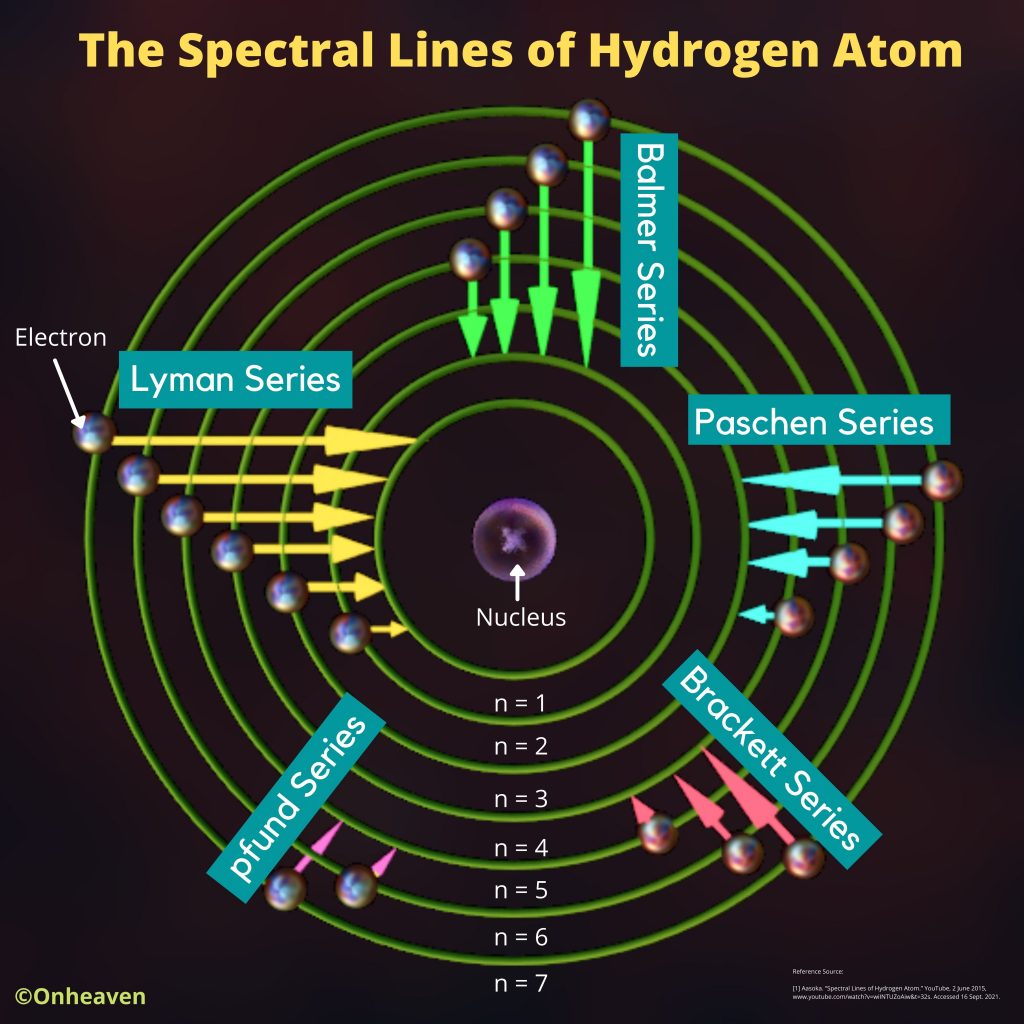
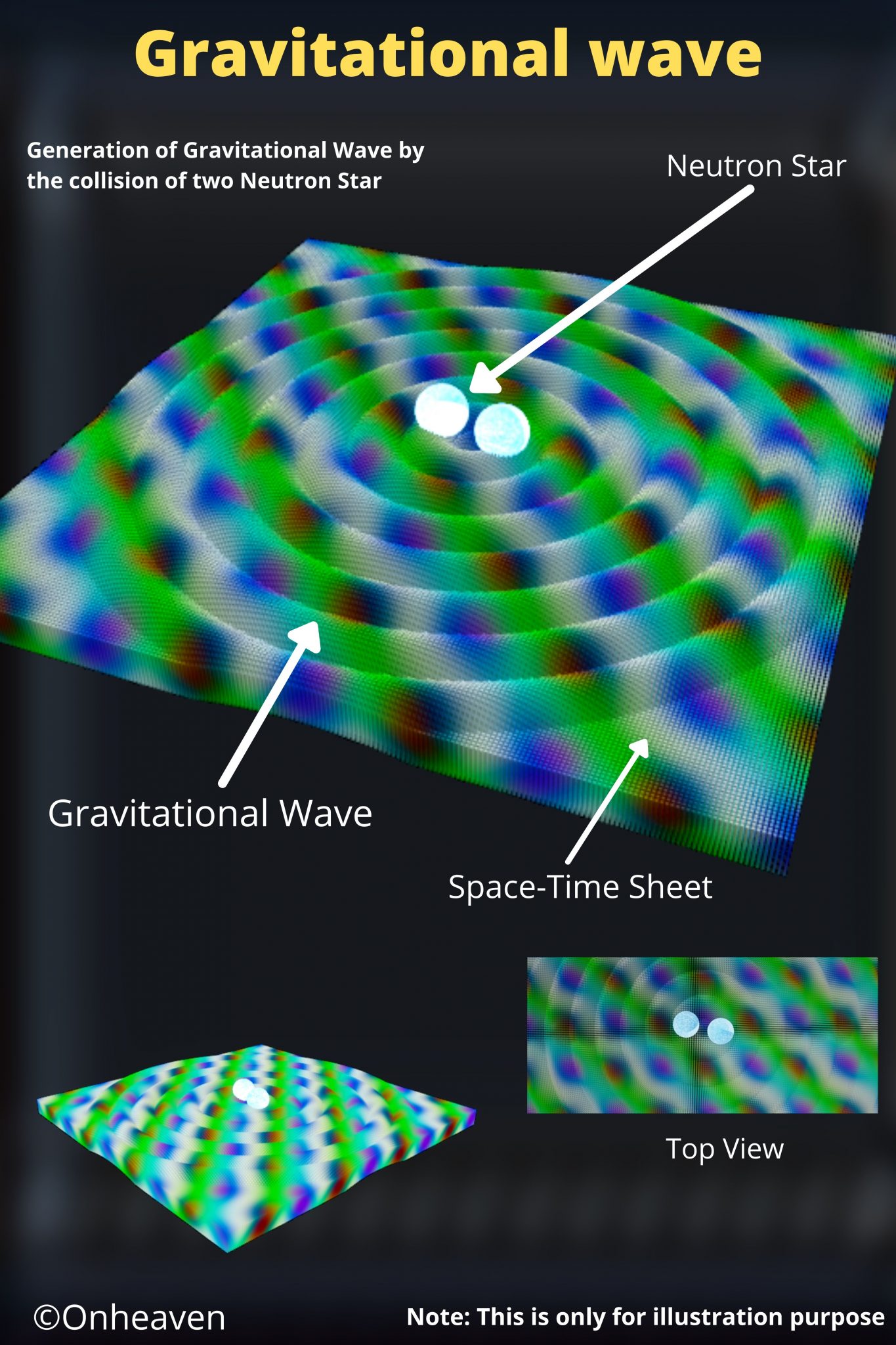
Van de Graaff generator is an electrostatic generator that is capable of generating high potential difference (in order of MV).
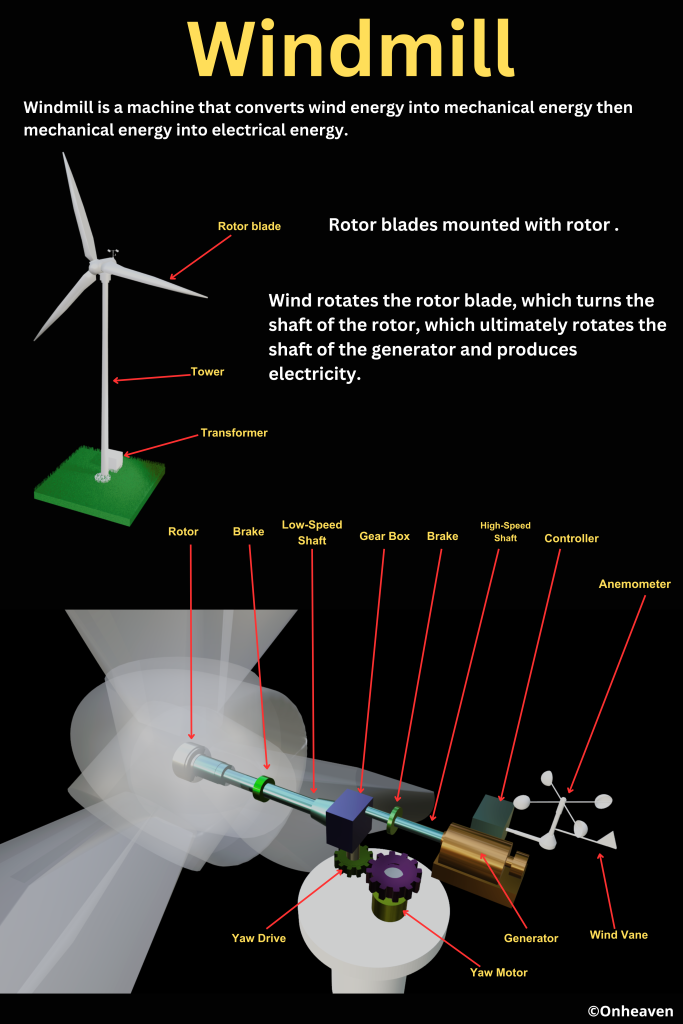
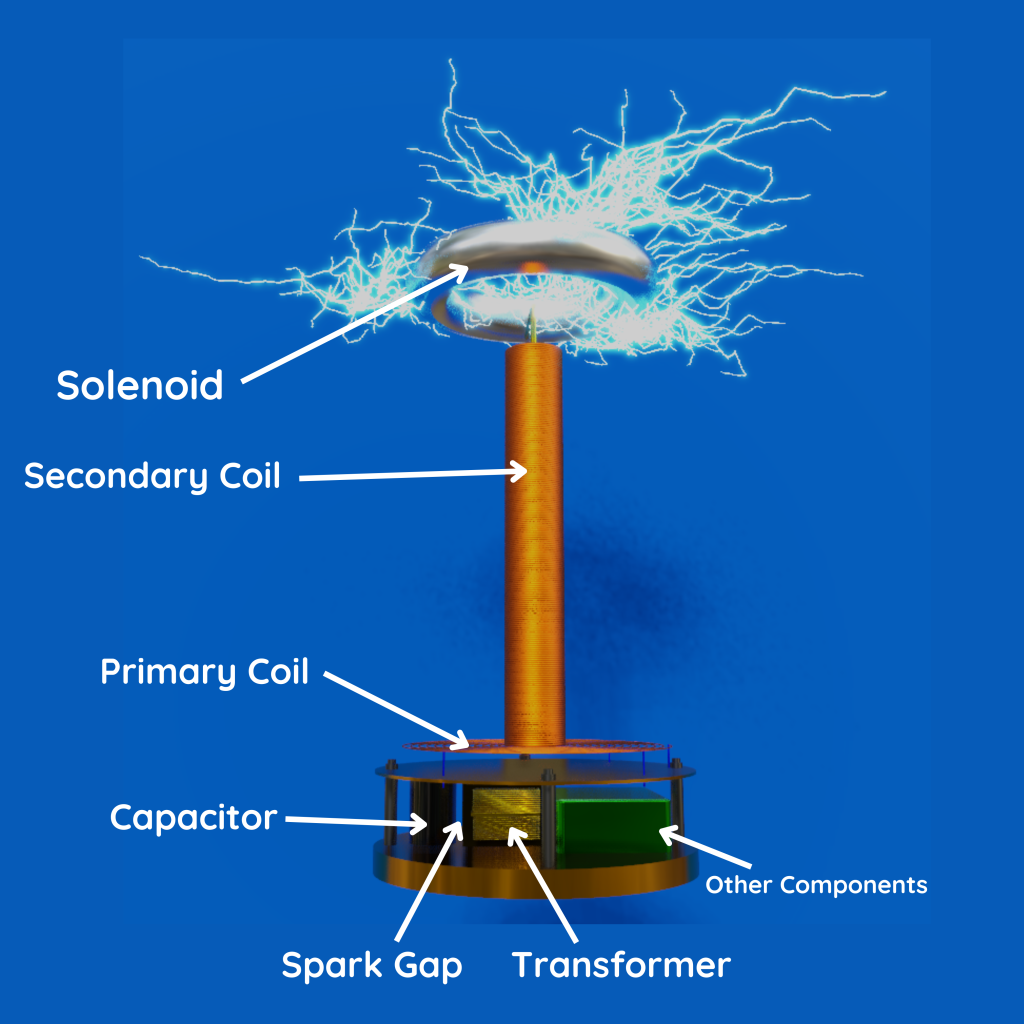
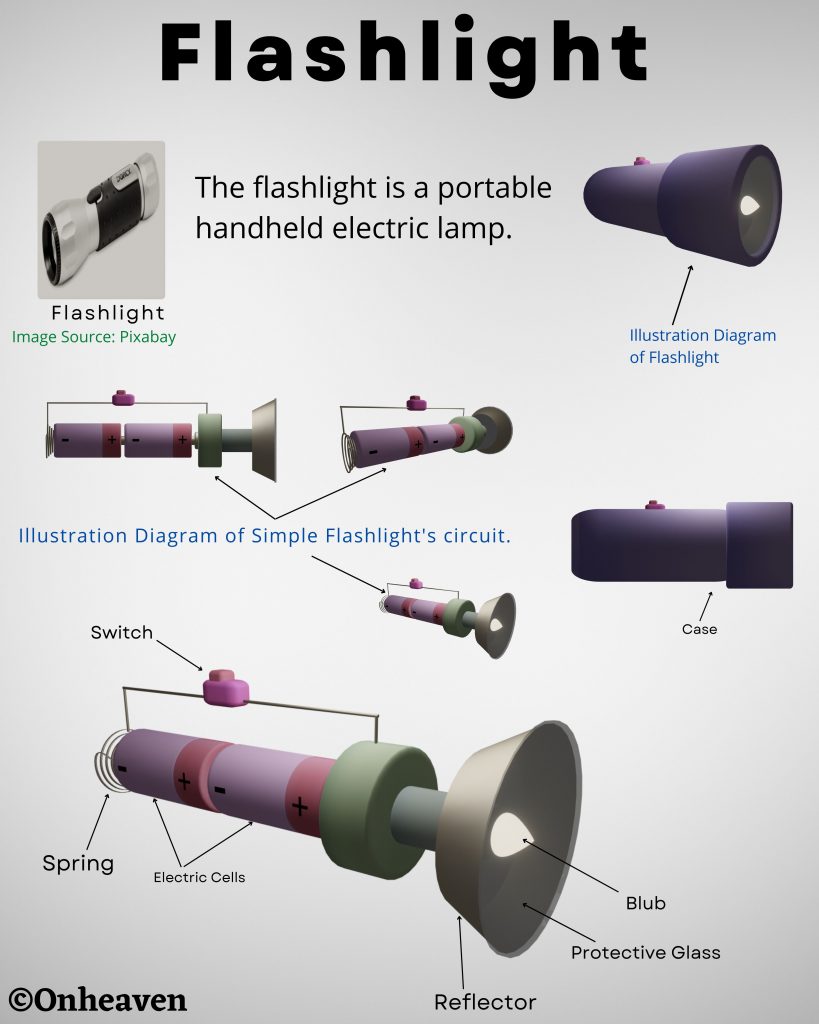
Spray comb spread the positive charge to the belt, which carries upwards, collected through the collector comb, and then transfer to the hollow sphere.
Charge immediately shifts to the outer surface of the hollow conductor.
The outer sphere carries an enormous amount of charge.
When the potential of the spherical shell exceeds the breakdown value of air, then the air around the sphere is ionized and leakage of charge takes place.

Reference Source:
[1] Wikipedia Contributors. Van de Graaff generator. Wikipedia. Published February 22, 2023. Accessed March 25, 2023. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Van_de_Graaff_generator
[2] Wikipedia Contributors. Robert J. Van de Graaff. Wikipedia. Published December 28, 2022. Accessed March 26, 2023. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robert_J._Van_de_Graaff
[3] National MagLab. How Van De Graaff Generators Work. YouTube. Published online February 28, 2017. Accessed March 26, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y20lKZB5BR0
[4] Scholarswing. Vande Graff Generator. YouTube. Published online November 7, 2016. Accessed March 26, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xqt2gAalV4Y
[5] File:Robert Van de Graaff.jpg. (2022, May 28). Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Retrieved 06:34, March 26, 2023 from https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Robert_Van_de_Graaff.jpg&oldid=659505985.