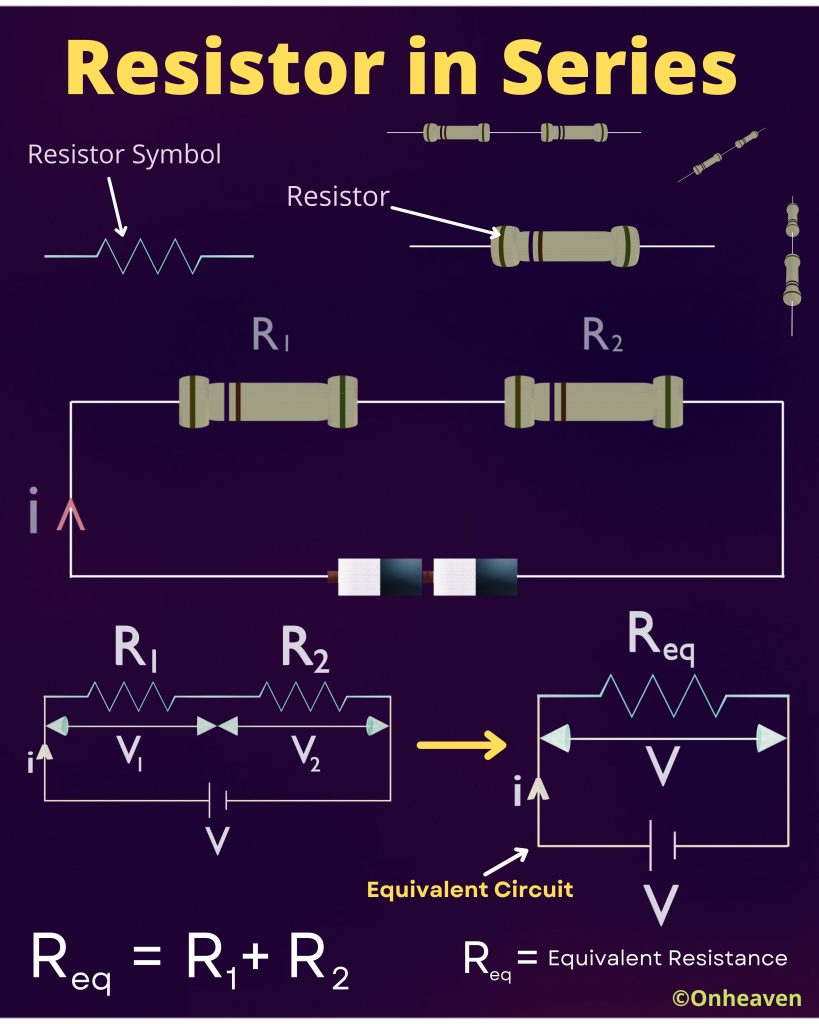
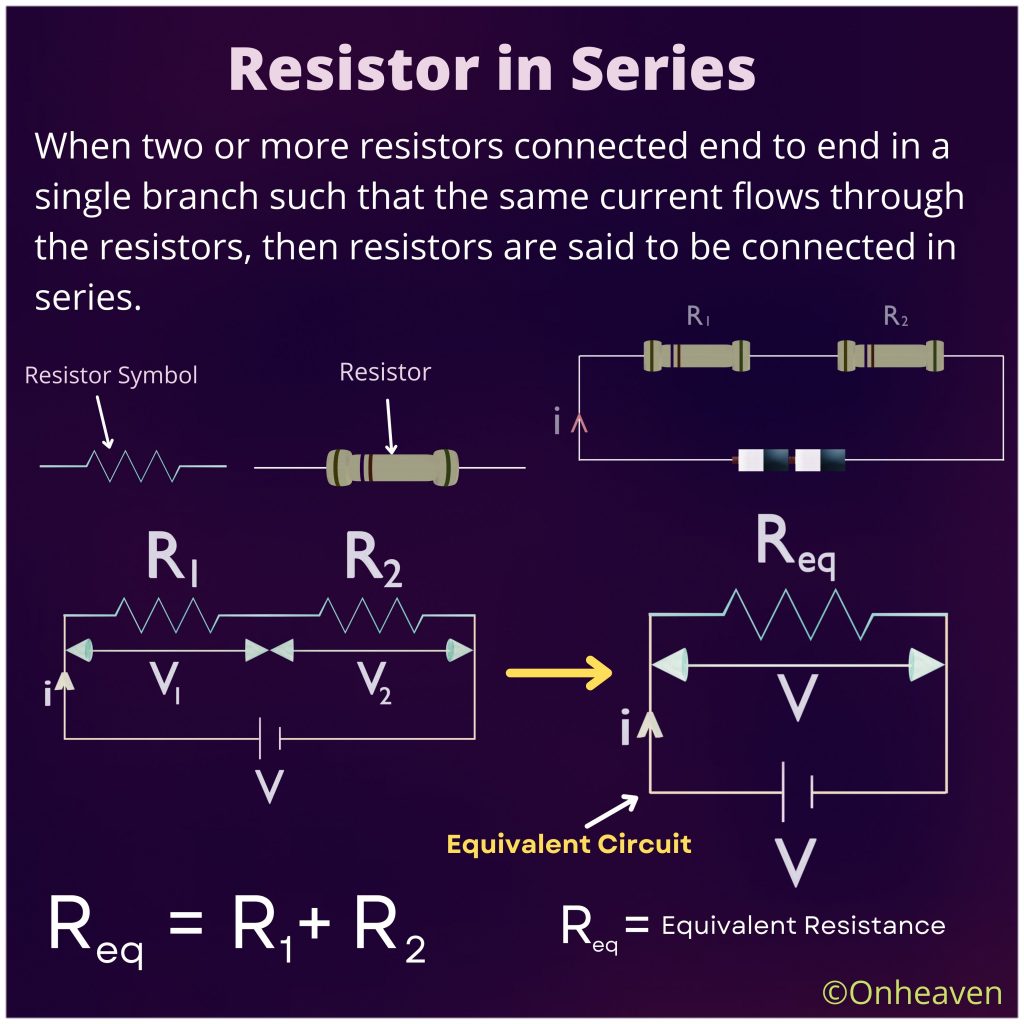
When two or more resistors connected end to end in a single branch such that the same current flows through the resistors, then resistors are said to be connected in series.
Voltage across each resistor is given by,
V = IR
V = Voltage across resistor.
I = Current across resistor.
R = Resistance of resistor.
From the illustration diagram given below,
V = V1 + V2 .
V = i( R1 + R2)
From the equivalent circuit
V = iReq
iReq = i(R1 + R2)
Req = R1 + R2.
Similarly equivalent resistance for ‘n’ number of resistors connected in series.
Req = R1 + R2 + R3 + …………… + Rn.
Reference Source:
[1] Electrical4u.com. Published February 24, 2012. Accessed March 28, 2022. https://www.electrical4u.com/resistances-in-series-and-resistances-in-parallel/
[2] Simple Series Circuits. Allaboutcircuits.com. Published February 9, 2015. Accessed March 28, 2022. https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/direct-current/chpt-5/simple-series-circuits/
[3] Resistors in Series – Series Connected Resistors. Basic Electronics Tutorials. Published August 27, 2013. Accessed March 28, 2022. https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/resistor/res_3.html
[4] Resistors In Series and Parallel – Circuit Components, Resistors in Parallel and Series, Videos, and FAQs. BYJUS. Published August 25, 2018. Accessed March 28, 2022. https://byjus.com/physics/resistors-in-series-parallel/
[5] Resistors in Series and Parallel | Boundless Physics. Lumenlearning.com. Published 2013. Accessed March 28, 2022. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-physics/chapter/resistors-in-series-and-parallel/