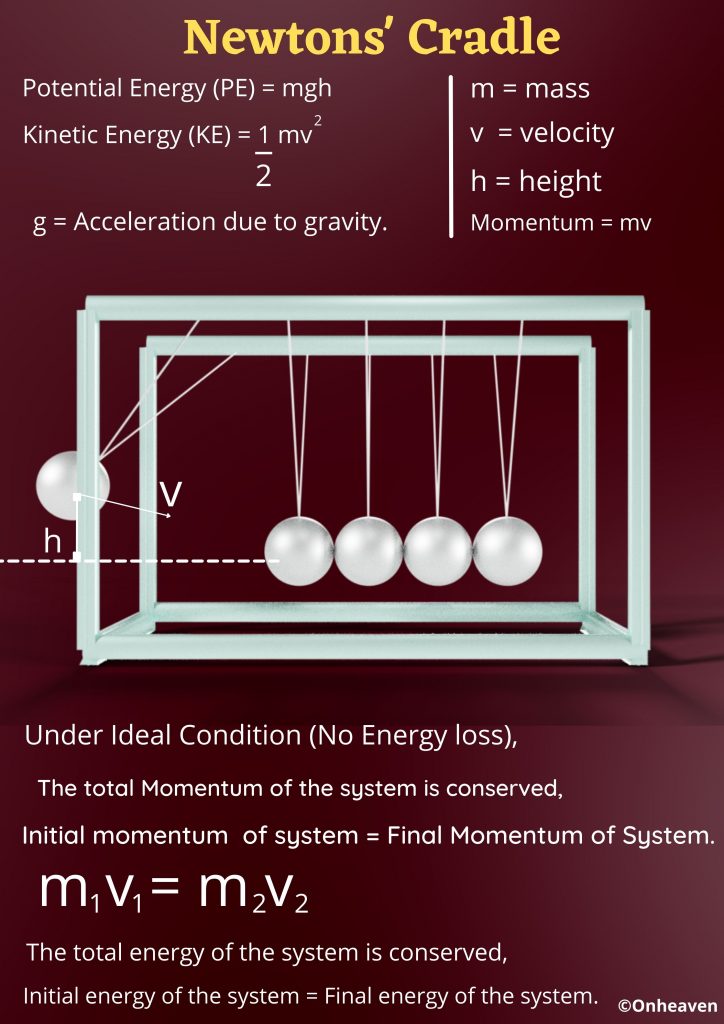
Newton’s cradle is based on the principle of conservation of energy and conservation of momentum.
When a ball from one end is lifted in the air and then released, it strikes the next ball in the cradle which remains motionless. But the ball on the opposite end side propelled towards the air, and then it get back and hit the ball which is next to it, and this process goes back and forth.
Newton’s cradle is named after Sir Isaac Newton.

Reference Source:
[1]Wikipedia Contributors. Newton’s cradle. Wikipedia. Published December 3, 2021. Accessed December 10, 2021. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton%27s_cradle.
[2] Palermo E. How Does Newton’s Cradle Work? livescience.com. Published August 28, 2013. Accessed December 10, 2021. https://www.livescience.com/39271-how-does-newtons-cradle-work.html.
[3] What Is Newton’s Cradle And How Does It Work? Science ABC. Published May 4, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2021. https://www.scienceabc.com/pure-sciences/what-is-newtons-cradle-and-how-does-it-work.html.
[4] The Action Lab. How Long Will Newton’s Cradle Move in a Vacuum? How Newton’s Cradle Really Works. YouTube. Published online November 24, 2018. Accessed December 10, 2021. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uWChuDS-CbQ.