😊The quantum field theory of the strong nuclear force is called quantum chromodynamics and describes the interactions of subnuclear particles such as quarks and gluons.
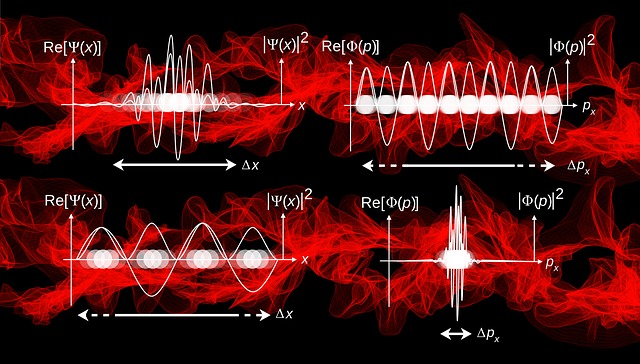
😊Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.
😊In the mid-1920s quantum mechanics was developed to become the standard formulation in support of atomic physics.
😊Largest theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large scale.
😊Quantum mechanics is essential in support of understanding the behavior of systems at atomic length scales and smaller.
😊Gravity is negligible in numerous areas of particle physics so unification between general relativity and quantum mechanics is not an urgent issue in those particular applications.
😊Relation to classical physics Predictions of quantum mechanics own been verified experimentally to an extremely high degree of accuracy.
😊Newer interpretations of quantum mechanics own been formulated do away with the idea of “wave function collapse”.
😊Quantum field theories in support of the strong nuclear force and the weak nuclear force own also been developed.
😊Max Planck corrected this model using Boltzmann’s statistical interpretation of thermodynamics and proposed what is now called Planck’s law which led to the development of quantum mechanics.
😊John Bell showed this EPR paradox led to experimentally testable differences between quantum mechanics and theories rely on local hidden variables.
😊In quantum mechanics it refers to a discrete unit assigned to certain physical quantities such as the energy of an atom at rest.
Source:
Wikipedia Contributors. “Quantum Mechanics.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 13 Oct. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_mechanics. Accessed 20 Oct. 2020.